Yogurt Manufacturing Process: The Complete FAQ Guide in 2025
Do you know yogurt is constant breakfast essential which is a go to option for every age group? Do you wonder how these nutritional packets of yogurt make to your breakfast table? Yogurts are consumed ever day by millions of people around the world. Yogurt packed with probiotic and essential nutrients are produced by the fermentation of milk transforming it into delicious dairy product.
This FAQ guide give you in depth knowledge about yogurt manufacturing process, equipment used in this process, different types of yogurt and their uses in different industry. What is the innovation and science behind this process? Let’s begin this topic with commonly asked questions and their expert answers.
1.What is the yogurt manufacturing process?
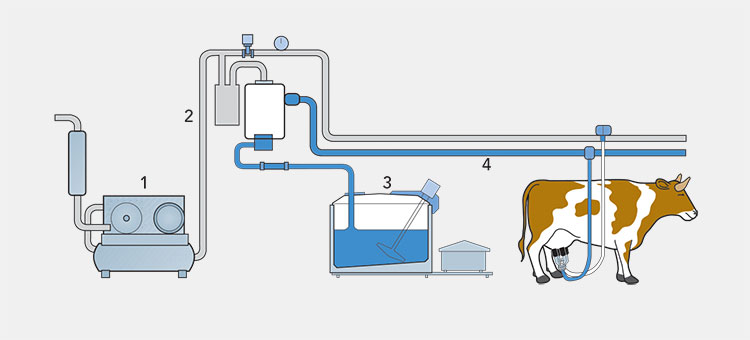
Yogurt Manufacturing Process- Picture Courtesy: Dairy Processing
The yogurt manufacturing process is a series of step that involve changing of milk component at turning it into commercial yogurt which you consume daily. This involves high temperature around 90⁰C for specific culturing period and may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer.
Milk and other dairy products are consumed from ancient time but need of fermentation arises from Middle Eastern times. Through this process, they extend the shelf life of milk and reduce spoilage of milk.
During milk processing and further yogurt manufacturing causes physiochemical changes that effect flavor and texture of yogurt while standardize process developed which provides desirable textural and flavor characteristics.
2.What are the raw ingredients used in the yogurt manufacturing process?
Raw Ingredients in Yogurt Manufacturing Process- Picture Courtesy: Little Green Dot
Yogurt is dairy product which is produced through culturing process of one or more microorganism culture which contain bacteria like streptococcus thermophilus and lactobacillus bulgaricus which are key factor for converting milk lactose into lactic acid and help in curdling of milk. Few other ingredients are also added to support whole process. Let’s unfold each ingredient for you in detail.
Selection of good quality milk
Good Quality of Milk- Picture Courtesy: UCLA Health
Most of the commercial yogurt which you consumed are manufactured from cow and buffalo milk. The fat content of cow milk, depending on breed and diet ranges from 3-3.5 gm per 100 ml of milk and this content may be change by separation or addition of cream depending on the required texture of yogurt, taste and consumer demand.
The usual desirable range of fat in yogurt is lies in between 1.0-4-.5 gm per 100ml. However, most important factor in cow milk is solid-non-fat (SNF) which varies from 8.5-9.0 gm. /ml containing around 4.5 g lactose and 3.3g protein.
All raw dairy ingredient material should be selected for high bacteriological quality. Mastitis milk, rancid milk and milk containing antibiotic and sanitizing chemical residue cannot be used for yogurt manufacturing process.
Starter culture
Bacterial Culture for Yogurt Manufacturing Process- Picture Courtesy: Cultured Food Life
The starter culture is critical ingredient in yogurt manufacturing process. The starter culture comprises of one microorganism or may be a mixed culture comprises of two or more microorganisms. The culture is responsible to convert milk sugar (lactose) into lactic acid so that milk become sour (fermented).
This time taken process required 5hours at a maintained temperature of 45⁰C or more time required at lower temperature for the production of lactic acid, if frozen yogurt concentrate culture is used. There is different starter culture available but most commonly used starter culture in commercial yogurt manufacturing are streptococcus thermophilus (ST) and lactobacillus bulgaricus (LB). These bacteria are ultimately responsible for flavor and aroma of final product.
The milk protein coagulates or curdles due to drop in pH which is carried out by starter culture. The streptococci are responsible for lowering pH to 5-5.5 and lactobacillus further reduced pH to 3.8-4.4. These two bacteria are considered safe to use in food and an absence of pathogenicity.
Stabilizer
Stabilizer – Picture Courtesy: Virasmart.co
Stabilizers are the excipients which are used to give smooth texture, firmness and consistency to yogurt. Stabilizer is also helpful in reducing wheying of yogurt during storage. You need to keep in mind few things while choosing a good stabilizer, it is will not affect taste or flavor of yogurt and also work at standardize low pH. Most of the commercial yogurt manufacturer used gelatin as stabilizer. Some plant source stabilizers are also used like carrageenans and guar.
Gelatin is the first choice of stabilizer in yogurt manufacturing process because it gives shiny gel appearance to yogurt which melts in mouth. But, it is preferred in frozen yogurt because its activity is temperature dependent and can be denatured at high temperature loosing texture and firmness. There are few other options of stabilizer which are used in yogurt like starch and caboxymethylcellulose.
Sweetener
Sweetener - Picture Courtesy: Ragus sugar
Sweeteners are added to give pleasant taste and mask acidic flavor in yogurt. It is noticed that high amount of sweetener greatly influences flavor or taste of yogurt. In almost every commercial yogurt, sucrose is used as sweetener. Sucrose may be added in dry, granulated and in form of crystal containing not more than 67% sucrose. Liquid sweeteners are used in large scale yogurt production settings for less problematic in handling.
Most commonly used sweeteners in yogurt production are sucrose, corn syrup or honey are added to overcome the acidic taste and produce firmer texture. Since sugar increase osmotic pressure of milk base, addition of excessive sweetener (>10gm/100ml) before fermentation inhibit the starter culture activity. Due to this reason sugar are added with fruit to stirred yogurt just before filling.
Most of the commercial yogurt you find in markets are comprises of lactose around 4.06%, galactose 1.85% and glucose estimated around 0.05% with pH of 4.40. Some manufacturer used artificial sweeteners as well on customer demand who are concerned about lower calorie content.
Flavoring agent
Flavoring agent- Picture Courtesy: Thrillist
The flavoring agent are specifically selected on the basis of market demand depending on consumer need. Flavoring agent used in yogurt are commonly added in the form fruit blend. The amount of flavoring blend you find in yogurt is mostly around 10-20 % and is approved by regulating food authority for safe use. They are added in yogurt to give eye appealing appearance and flavor closet to actual fruit. But there are few things which you need to look while choosing fruit blend.
- Fruit blend does not alter the flavor and color of yogurt, when added.
- The pH of yogurt is not altered due to fruit blend or their pH is balancing with each other.
- Fruit blend must be carefully checked for microbial content, otherwise it leads to spoilage of yogurt.
- The fruit blend is easily mixed in yogurt and dose not separate in storage.
Fruit flavor vary depending on the season of the year like different fruit are available in different time of the year. Mostly flavor of yogurt which are liked all over world are strawberry, raspberry, cherry, mango, apricot, peach, plum and pineapple etc.
Frozen fruit, canned and dried fruit are added as fruit blend in yogurt production. Fruit base pH is also important in balancing fruit flavor and color. Yogurt is refrigerated or stored at optimum temperature for flavor and color retention, and for extended shelf life.
3.What steps are involved in yogurt manufacturing process?
It will give you idea about steps involved in yogurt manufacturing process. It involves steps from milking animal to treating and processing till packaging. Come along and you will learn step by step process.
Initial treatment of milk
Initial Treatment and Milking- picture Courtesy: Tetra pack
When milk arrived at plant it undergoes clarification process to remove bacteria and other solid impurities because bacterial growth can be occurring during milking and transportation, as it takes time long as days. The level of bacterial growth depends upon the hygiene during milking, temperature and storage period. Spoilage of milk with bacteria causes lactic acid fermentation.
Afterward, mild heating process is performed known as thermalization at temperature of 60-69⁰C for 20-30 seconds to kill most of vegetative microorganism or partial inactivation of some enzyme. After thermalization, milk is cooled 4-5⁰C or incorporated with micro floras to control growth of bacteria.
Standardization of milk components
Centrifugal Separator and Milk Standardization- Picture Courtesy: Tetra pack
The second step in yogurt manufacturing process is standardization of milk. Standardization is performed to remove almost all the fat and solid-non-fat content. The fat content for yogurt is adjusted to range from 0.1-10% depending on consumer demand.
Standardization is performed in continuous manner and accomplished by separator. You need a separator to remove cream and sediment from milk at the same time. To achieve desired fat level, standardization of milk done by removing fat in form of cream leaving skim milk, then mixing both in desired ratio to obtain desired consistency and texture. Because fat content greatly influences characteristics of yogurt, increasing fat content can increase consistency and viscosity of yogurt.
The term standardization is also referred to SNF (solid-non-fat) content. SNF content in yogurt manufacturing is ranges from 9-16%. It is noticed that fat and SNF content in milk impact fermentation, an increase in fat and SNF content in milk increases the fermentation process duration.
Pasteurization
Pasteurization- Picture Courtesy: Wikipedia
It is a process of heating at very high temperature around 71⁰C and holding it for shorter period before cooling. This step is crucial in yogurt manufacturing. During this process, it destroys most of the pathogen, vegetative bacteria, yeast and mold. Additionally, it denatured several enzymes without altering flavor of yogurt. It also aids in denaturing wheying protein which results in yogurt of good consistency and firmness. This process is also known as High temperature short term pasteurization (HTST).
Pathogens that grow during bad hygiene practice can be killed with heat treatment ensuring processed milk is safe for consumption. Most commonly high temperature pasteurization is used in yogurt manufacturing process.
Homogenization
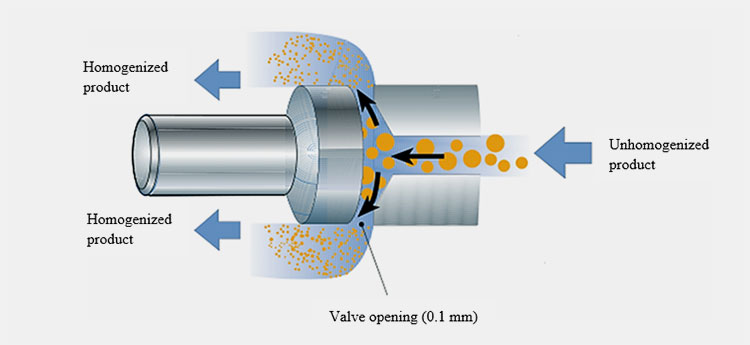
Homogenization of milk –Picture Courtesy: Milk-ed
After pasteurization, milk is passed through fourth step of homogenization. In this process, at high pressure molecule size is reduced to prevent wheying off (separation of fat layer and aqueous phase). You have to apply high pressure or high frequency. In this shear stress and due to temperature gradient cavitation occur that contributes to homogenization process.
Homogenization best occur at temperature more than 37⁰C. This process is conducted at two stages. At first stage pressure of 2000psi is to subjected to reduce fat globule diameter from 2-10µm to 0.1-1 µm and in second step, 500 psi pressure applied to break cluster of globule inhibiting creaming of milk.
Homogenizing prevents creaming and wheying off, give whiter appearance and enhance textural development of yogurt.
Fermentation and cooling:
Fermentation in Yogurt Manufacturing Process-Picture Courtesy: The simple little life
Fermentation is carried out after homogenization at the maintained temperature of 40-45⁰C and combination of lactobacillus bulgaricus and streptococcus thermophilus is added as starter culture in the same amount.
When the desired pH is reached, microorganism starts its activity leading fermentation till required pH and acidity is reached. Addition of high level starter culture will lead to loss in texture and aroma of finished yogurt. The optimum amount of starter culture added should be 1-2% or may be increased to 4-5% if the sugar content is high (10-11%).
After fermentation is completed yogurt is immediately cooled to stop further bacterial activity. It is done in two phases. In first phase Yogurt temperature is decreased to 10⁰C resulting low consistency coagulum. In second cooling phase, the coagulum temperature decreases rapidly to 5⁰C (storage temperature) with increased viscosity.
Packaging
Yogurt Packaging Machine-Picture Courtesy: Waldner
After inoculation, milk is filled in carton for incubation. Once the cartons are filled, you need to heat sealed with aluminum foil and transfer to incubation room to at 42⁰C. The optimum growth temperature for starter culture is 35-50⁰C. If you incubated for long time so there are higher chances of post process acidifying. You must be cautious to avoid yogurt from turning sour and bitter.
After incubation yogurt is set at 15-20⁰C and chilled at >5⁰C. Ready for final distribution.
4.What equipment is used in the process of yogurt manufacturing process?
Do you know how equipment work and lined in yogurt manufacturing process? Here you find all details about yogurt production equipment. Let’s get into it.
Centrifugal separator
Centrifugal Separator-Picture Courtesy: Synelco
Centrifugal separator is used to separate cream and skimmed milk from whole milk. Cream and skim milk have different densities so under the influence of gravity, they are separated. This process is done to get desired level fat on consumer demand.
Working principle
It worked on principle of centrifugal force. It creates rotating force which throw away heavy particle to the side from there they are collected in the bottom of separator chamber and solid free liquid is collected from the top inlet of separator.
Mixers
There are different types of mixer used in yogurt manufacturing process. The mixer is used at different steps to mix homogenously thick and viscous liquid like for adding milk powder in yogurt, adding fruit purees and other additive.
a-Gentle In-line mixer
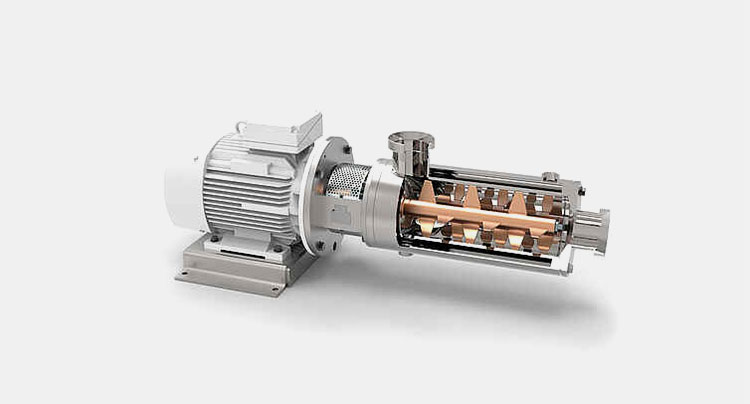

In-line Mixer – Picture Courtesy: Indag
Gentle in-line mixer is used to mixed product with high shear sensitive. In-line mixer is used to add fruit puree, fruit pieces, fruit syrup in yogurt. It is crucial for product which are sensitive to high shear. It is gently mixed with paddle mixing.
Working principle
In in-line mixer rotor used suction rotation which create mixing of ingredient with the help of centrifugal force. Due to force they are pushed to the wall and again sucked to the center which create milling action and give homogenous evenly distributed mixture.
b-Solid-liquid in-line mixer
Solid-Liquid In-Line Mixer -Picture Courtesy: Indag
Solid-liquid in-line mixer is used to mix dry ingredient like dry milk powder or dry fruit mixes where fruits are added in chunks. It will provide continuous homogenous mixing.
Working principle
It works on same principle like in-line mixer to use centrifugal force but it works on high shear and without disturbing texture and consistency of liquid ingredient. Its rotor suck ingredient to center and producing milling action and reducing particles size as well resulting in uniform mixture.
Pasteurizer
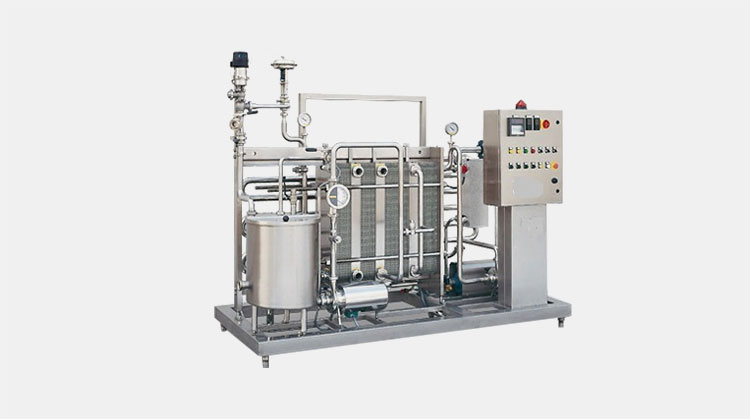

Milk Pasteurizer –Picture Courtesy: Agico
Pasteurizer is device used to heat milk to destroy harmful bacteria and maintain the quality of milk and cool milk at desired temperature. It is stainless steel container which maintained temperature.
Working principle
Pasteurizer work by heating raw milk in large container with the help of steam or heat. After that milk is hold in pasteurizer for few time to kill all microorganism. After heating is complete, milk is immediately cooled to desired temperature to inhibit spoilage and bacterial growth.
Homogenizer
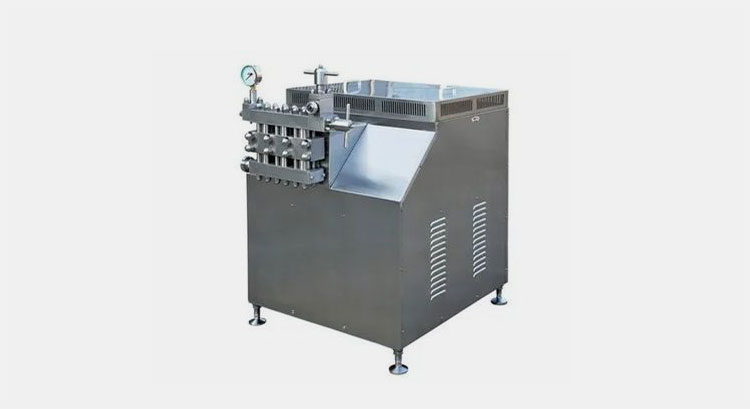

Homogenizer –Picture Courtesy: Ajjo
Homogenizer used in yogurt manufacturing process to maintain consistency and quality of milk. This equipment reduces the size of fat globule resulting in uniform texture. This process will increase viscosity of milk and help in stable yogurt production.
Working Principle
Homogenizer are operated high pressure in piston create pressure and pressurized milk is pass through very small orifice. Exerted pressure causes fat globule to shrink and dispersed in small sizes. This help in more uniform structure resulted in stable and consistent texture in yogurt.
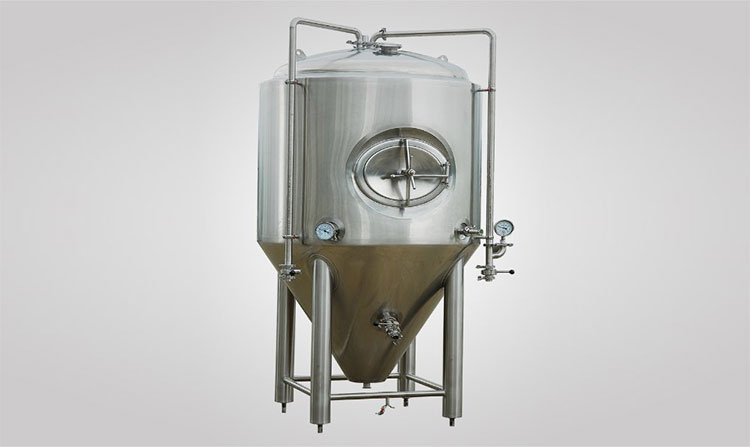
Fermenter
Fermenter Tank- Picture courtesy: Tiantai Brewtech
Fermenter is sterilized and enclosed large tank which is used for control growth of microorganism. They provide consistent temperature across mixture and ensure even distribution.
Working principle
In a fermenter, nutrition rich medium is provided at controlled temperature and pH for introduction of cell culture. Fermenter is equipped with sensor and control system to monitor pH, mixing and temperature. Product is fermented till desired result. Agitator are installed for proper mixing and even temperature across culture.
Filling and packaging machine
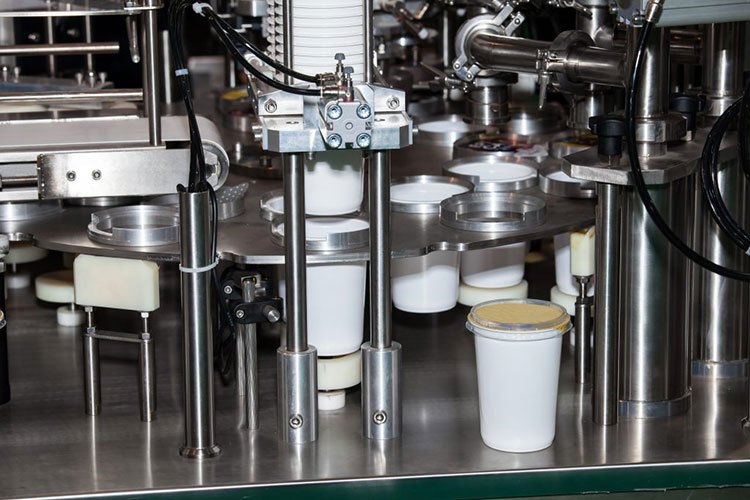

Yogurt Filling and Packaging Machine-Picture Courtesy: Lom Tech
Yogurt filling and packaging machine fill yogurt in cups and seal them. This machine help in accurate cup filling with maintain product hygiene. Filling machine are designed in this manner so they can handle different shapes and sizes of cups
Working Principle
The machine consists of conveyer belt which hold cup and nozzles which are connected to storage tank of yogurt through pipelines. The nozzles filled cup with pre-set capacity standard for each cup. When yogurt filling is completed, it enters sealing section, where plastic caps or heated sealing is done depending on packaging types.
5.How different industries use the yogurt manufacturing process?
There are many industries which use the same process and machinery which are used in yogurt manufacturing process. Here you will learn application of yogurt manufacturing process in other industries.
Cosmetic industry
Cosmetic Industry-Picture Courtesy: Earth.org
Some cosmetic industry uses the by-product of yogurt (whey). It is used in different skincare product like cream, face mask, body yogurt and moisturizer. Lactic acid which is produced in yogurt manufacturing is used for gentle exfoliation and hydration. Some hair care industry also incorporated yogurt in hair product like hair mask, shampoo and conditioners. They also use same equipment high shear mixer and homogenizer which is used in yogurt production.
Pharmaceutical industry
Pharmaceutical Industry-Picture Courtesy: Dezan shira & associate
Yogurt culture is used in pharmaceutical industry to improve gut health because it contains live bacteria. These cultures are used in producing probiotics in capsule, powder and liquid form to improve digestion and immunity booster. Due to innovation these culture is also used as supplements for immunity and digestion. Here you see another application of yogurt manufacturing process.
Textile industry
Textile Industry- Picture courtesy: Camachem
Due increase in demand of sustainable and environment friendly product, lactic acid which is produced in yogurt manufacturing is used for dyeing of natural fiber like cotton and silk. This gives more sustainable and bio-based dyeing instead using harsh chemical. This way helps some consumer which are allergic to some chemical which are used in dying process.
Veterinary industry
Veterinary Industry
In veterinary industry, yogurt manufacturing is helpful because by-product of it used as feed for livestock because they contain micro flora so it enhances food digestibility and gut health. Whey protein concentrate is also incorporated in feed to increase protein content in livestock especially in cattle and poultry. So it enhances livestock growth and health.
6.What are the factors that affect the quality of yogurt manufacturing process?
Yogurt is fermented milk product in yogurt manufacturing process. During manufacturing many factors influence yogurt consistency and texture. Let’s get into this topic so you get idea about what you have to consider during yogurt manufacturing process.
Content of protein in yogurt
Protein Content in Yogurt Manufacturing Process-Picture Courtesy: BBC
Protein content is really important in maintaining rheological and physical properties of final product in yogurt manufacturing process. If you increase protein content, it enhances gel firmness and decreases syneresis in yogurt. It is advisable to limit protein content ratio as it will effect flavor of yogurt.
Fat percentage in yogurt
Fat Percentage in Yogurt- Picture courtesy: Baladna
Fat percentage in yogurt greatly impact mouthfeel and creamier texture of yogurt. The desirable percentage of fat in yogurt is 0.5%-3.5%, value greater and lower can impact texture. Nowadays manufacturer done great work on acquiring good texture with low fat content due to health concern.
Impact of starter culture
Impact of Starter Culture
The use of contamination free starter culture with a required activity is crucial in yogurt manufacturing process. Starter culture is capable of fermenting lactose in lactic acid. This optimum state of activity in starter culture is obtained by providing optimum temperature and incubation time. The activity and type of starter culture has great impact on the flavor and quality of yogurt. So the activity of starter culture must be maintained for consistent texture of final product in yogurt manufacturing process.
Stabilizer effect yogurt texture
Stabilizer Effect Texture in Yogurt Manufacturing Process-Picture Courtesy: Dairy Foods Magazine
Stabilizer are hydrophilic colloid that will bind water and prevent wheying off. It gives yogurt smooth texture. Quantity of stabilizer added must closely monitored because if you add excess it will give yogurt rubbery texture leading to hard solid mass. So optimum quantity is need for smooth and creamy texture yogurt.
Effect of heat treatment
Effect of Temperature on Yogurt Manufacturing Process-Picture Courtesy: Ecency
Temperature is crucial in yogurt manufacturing process. Milk is heated to reduce microbial load, Increasing yogurt texture, stability and consistency. If you over heated milk it will denature all enzyme and bacteria resulting thick consistency, pale color and unstability.
It is noticed that heating process increase medium value for starter culture and other lactic acid bacteria. But excessive heating will lead to denatured all organism leading to decolored and off flavor yogurt.
7.What are the challenges commonly encountered during yogurt manufacturing process?
There are few problems which you face during yogurt manufacturing process. But here you will get solution for these commonly encountered challenges.
Yogurt become granular during fermentation
Granular Yogurt-Picture Courtesy: Brod & Tylor
At times manufacturer set high temperature during fermentation to speed up the process. It is applicable to some extent but we have seen by increasing temperature culture ferment lactose in lactic acid faster which can shock dairy protein resulted in granular texture.
Solution
If problem is created due to high fermentation temperature. Then you have to lower incubation temperature. By decreasing fermentation temperature culture produce lactic acid at slower rate resulting in less chances of disturbing dairy protein. If you are facing granular texture in yogurt, try lower temperature setting with same culture you will be amazed by result.
Yogurt is too sour
Yogurt is too Sour – Picture Courtesy: How to eat this
This problem mostly you faced when pH got too low and make your yogurt sour. Why this problem happens? You need consider breaking pH of yogurt (at pH where yogurt is fermented). It usually happens when you break pH at 4.3 and pH goes down during cooling and packaging process turning yogurt sour.
Solution
The solution is simply to raise break pH to 4.6-4.7 so pH does not get lower down from desired pH during cooling and packaging. You can also control this problem by cooling yogurt immediately or using mild culture which does not produce acid, when yogurt is break.
Texture of yogurt is too thin
Texture of Yogurt is Runny-Picture Courtesy: The Paupered Chef
It happens when yogurt is over stirred after fermentation leading to thin and less viscous texture of yogurt before entering final packaging. Consider that when desired pH reached, avoid over-stirring at every step of processing.
Solution
Minimize agitation of yogurt during filling process. This can be done by stirring at interval and decreasing shear of mixing tank. When product is waiting to be filled in container avoid too much stirring.
Conclusion
Yogurt is semi-solid fermented product produced by culturing dairy product with one or more microorganism. Yogurt also flavored and ingredient specific depending market trend and consumer demand. Here you understand complete science behind yogurt manufacturing process, equipment and factors you need to keep in mind while yogurt production. However, to meet consumer demand of desirable flavor and texture in yogurt required quality practice to ensure you get same texture and maximum quality product with safety. For further information about yogurt manufacturing process, you are encouraged to contact our service team.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply to you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply to you ASAP within 24 hours