Capsules Vs Tablets
When you are not feeling well and go to the hospital, doctors will prescribe medicine for you. But in the process of taking medicine, have you ever hesitated about whether to take capsules or tablets?
In fact, most of the medicines in the world are in the form of capsules and tablets. Now, follow this article below you will know well about the differences between capsules and tablets. Let’s have a look together!

Capsules Vs Tablets- photo credits: medicaldarpan
1. What Are Capsules and Tablets?
Do you know what is a capsule or is a tablet? What are their roles? It’s okay if you don’t know because this article will tell you the answers.

Capsules- photo credits: healthfully
Capsules: Capsules are solid preparations made from raw materials or filled hollow hard capsule shells, supplemented with suitable auxiliary materials, or sealed in elastic soft capsule shells.
It can be divided into hard capsules (commonly known as capsules), soft capsules (capsules), sustained-release capsules, controlled-release capsules, and enteric-coated capsules.

Capsules Clip Art -photo credits: buzzrx
Capsules are basically medicines in gel or powder form, almost cylindrical containers.
This allows the drug to enter your system faster than most forms. In fact, fast-acting drugs come in the form of capsules.
Containers such as gels used for capsules are susceptible to moisture and therefore have a shorter shelf life.

What is a tablet -photo credits: laafon
Tablet is a round or special-shaped solid preparation, which is made by mixing drugs and appropriate auxiliary materials, and can be divided into ordinary tablets, dispersible tablets, chewable tablets, effervescent tablets, buccal tablets, sublingual tablets, sustained-release tablets, enteric-coated tablets, etc.
Tablets- photo credits: sfaf
Tablet is a preparation made by mixing a drug and excipients from compressing.
Tablet is a compressed medication in the form of a disc. It is usually coated with sugar or some other compound to delay the release of the drug into our system. They are less expensive to manufacture and are accepted by most people.
From the outside, capsules and tablets are actually easy for you to distinguish.
2. What Are the Main Types of Capsules and Tablets?
In your daily life, when you get any capsules or tablets, could you distinguish their types and functions?
Main Types of Capsules and Tablets -photo credits: singlecare
Main Types of Capsules:
Capsules can be divided into hard capsules, soft capsules, enteric-coated capsules, etc., and are generally used for oral use.
Capsules can mask the bad smell of drugs, avoid the destruction of drug components by gastric acid and pepsin, improve the stability of drugs, and improve the bioavailability of drugs.
- Hard Capsules: It refers to the preparation of a certain amount of medicinal powder or auxiliary materials into uniform powder or granules, which are filled into hollow capsules.

Hard Capsules -photo credits: capsugel
- Soft Capsules: It refers to a capsule made by processing liquid medicine or liquid-solid medicine into a soft capsule material.

Soft Capsules -photo credits: health
- Enteric-coated Capsules: These refer to hard capsules made of granules or pellets coated with enteric materials and filled in capsules.
When taking capsules, the temperature of the water should not be too high. If the temperature is too high, the capsule shell with gelatin as the main raw material will be softened or even destroyed, which will affect the bioavailability of the drug in the body.

Taking Capsules -photo credits: pbleiner
Therefore, capsules should be taken whole and not taken apart, especially slow-release and controlled-release capsules.
If the capsule shell is peeled off, the drug will be suddenly released, absorbed too quickly, or even cause adverse drug reactions.
Main Types of Tablets:
Tablets mainly include ordinary tablets, chewable tablets, coated tablets, effervescent tablets, dispersible tablets, soluble tablets, controlled-release tablets, multi-layer tablets, and oral tablets.
The dosage of the tablets is accurate, the quality is stable, the transportation and storage are convenient, and the patients are more convenient to use.

Regular Tablets -photo credits: vecteezy
- Regular Tablets: When taking regular tablets, you need to take them with plenty of water. If you don’t drink enough water, it may reduce the effectiveness of the drug or cause esophageal or kidney damage.
For example, when you are taking sulfonamides, you can cause kidney damage if you drink too little water.
- Chewable Tablets: Chewable tablets should be chewed well in the mouth and swallowed.

Chewable Tablets -photo credits: healthaid
Adequate chewing can accelerate the dissolution of the drug and improve its efficacy. After chewing, you can take it with a small amount of warm water.

Coated Tablets -photo credits: rheonics
- Coated Tablets: They usually can be divided into sugar-coated tablets, film-coated tablets, and enteric-coated tablets.
You should take the enteric-coated tablet whole, not torn apart. Because the enteric coating prevents the drug from being damaged by gastric acid and gastric enzymes.
Pills -photo credits: time
At the same time, the enteric coating can also prevent the drug from irritating the stomach and causing adverse reactions.
A typical drug representative is aspirin enteric-coated tablets. The role of the enteric coating is to reduce the damage of aspirin to the stomach.
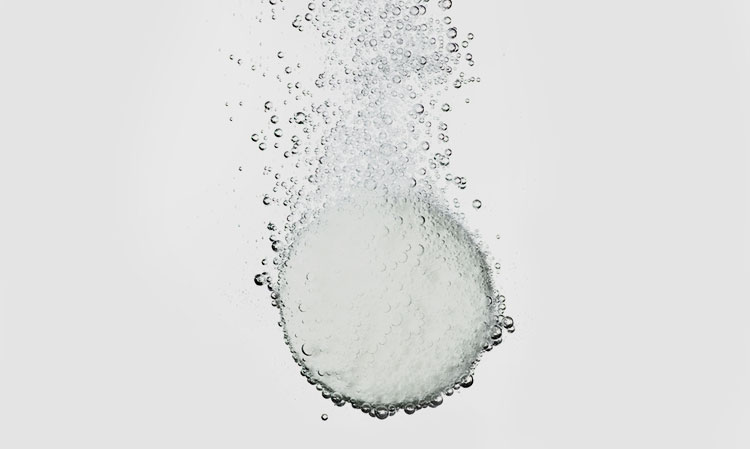

Effervescent Tablets -photo credits: making
- Effervescent Tablets: This is a tablet that contains an effervescent disintegrant. Effervescent disintegrant refers to a mixture of sodium bicarbonate and organic acids such as citric acid.
When the drug meets water, the two react to produce large amounts of carbon dioxide gas. So that the tablet disintegrates quickly and facilitates absorption.
Effervescent tablets should be dissolved in the appropriate amount of warm water before taking them.

Effervescent Tablets -photo credits: amerilabtech
This medication is suitable for children and people who have trouble swallowing pills. It is important to remember that effervescent tablets cannot be swallowed directly.
There have been incidents in which children over one-year-old swallowed effervescent tablets directly, causing carbon dioxide to be released into the body and causing suffocation.
Dispersible Tablets
- Dispersible Tablets: It is a tablet that disintegrates rapidly and uniformly disperses in contact with water.
You need to add the dispersible tablet to water to disperse and drink it. Can also be chewed or taken. The more common drugs are cefaclor dispersible tablets.
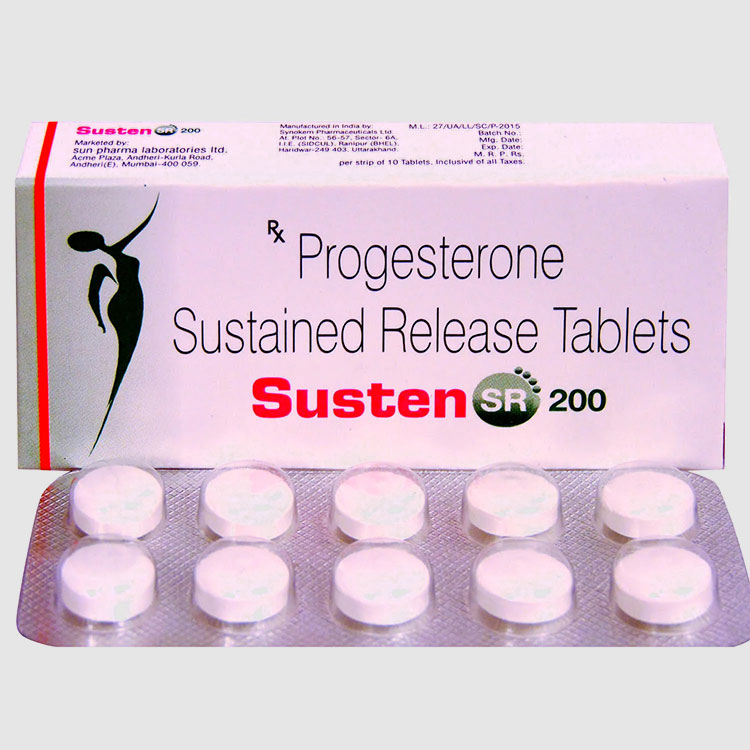
Sustained-Release or Controlled-Release Tablets
- Sustained-Release or Controlled-Release Tablets: This is a type of tablet that controls the rate at which the drug is released to prolong the action of the drug.
Sustained-release tablets or controlled-release tablets have the advantages of stable blood drug concentration, fewer doses (conducive to the elderly with poor memory), and long treatment times.
Unless otherwise specified in the instructions, controlled-release tablets cannot be taken apart.
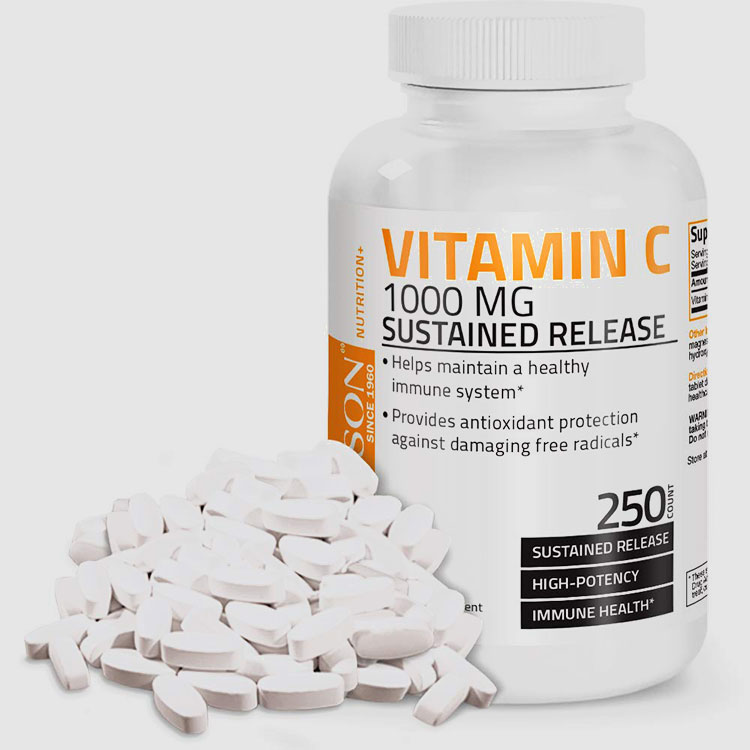
Sustained-Release or Controlled-Release Tablets
If the formulation is broken apart, the controlled release membrane or matrix will be destroyed. The drug will be released quickly, thus failing to achieve sustained release and long-acting purposes.
It is also possible that due to the release of the drug, your body absorbs a large amount of it in a short period of time, causing poisoning and adverse reactions.

Multilayer Tablets -photo credits: fette-compacting-parts
- Multilayer Tablets: This is a tablet that consists of two or more layers. It is generally made by pressing twice or more. Each layer contains a different drug or excipient.
This avoids chemical changes between the different drugs in the compound formulation or achieves the effect of slow-release and controlled-release. The tablet should be swallowed whole.

Sublingual Tablets -photo credits: anesthesiologynews
- Sublingual Tablets: Placing the tablet under the tongue. The drug is directly and rapidly absorbed through the mucosa for systemic action.
Common drugs are nitroglycerin. The sublingual tablet avoids the first-pass effect of the drug on the liver.
This drug is mainly used for the treatment of emergencies. Sublingual tablets should be administered promptly. You should put the tablet under the tongue when taking it.
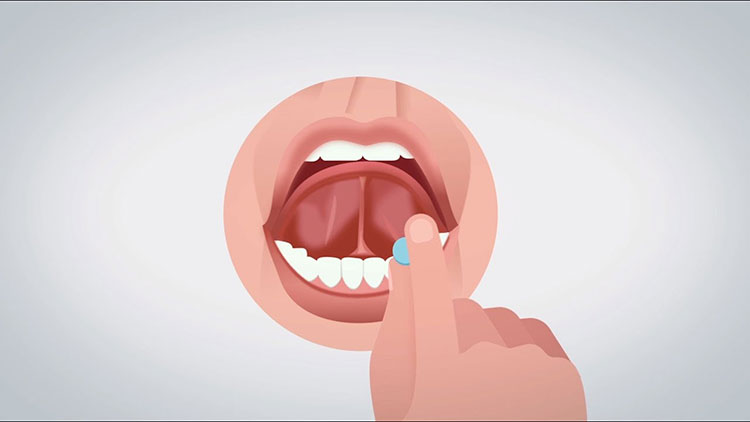
Sublingual Tablets -photo credits: ixsyrinx
The oral administration time is generally controlled at about 5 minutes to ensure full absorption of the drug.
You need to be careful not to chew or swallow the medicine and not eat or drink it within 30 minutes of ingestion.
Buccal Tablets -photo credits: pharmaceuticalmanufacturer
- Buccal Tablets: A tablet that dissolves slowly in the mouth for local or systemic therapeutic effects.
These tablets are commonly used in the treatment of oral and throat diseases. It is not advisable to drink water immediately after containing it.
The common oral lozenges include Watermelon Frost Throat Lozenges, Golden Throat Lozenges, and Cydiodine Buccal Tablets.
Capsules Vs Tablets Clip Art -photo credits: buzzrx
In your daily life, whether it is capsules or tablets, there are many types of them. However, no matter what kind of capsules and tablets it is, it will always be made in a way that is best for your body to digest and function.
3. What Are the Excipients for Capsules and Tablets?
Excipients are added to almost all capsules and tablets during the production process. The excipients used in different types of capsules or tablets may or may not be the same. Do you know some excipients in the capsules or tablets?
Excipients -photo credits: spipharma
- Excipients for Both Capsulesand Tablets:
Diluents and Absorbents: Mainly applied to increase tablet volume or volume. Reduce the main dose deviation, and also become a filler.
When the main drug in the tablet is only a few milligrams, it will not be possible to make a tablet without adding a suitable filler. Therefore, the diluent here acts to increase the volume to help it shape.
Commonly applied fillers are starch, sugar, cellulose, inorganic salts, and so on.
① Main Types of Diluents and Absorbents for Capsules and Tablets:

Starch -photo credits: starchinfood
Starch: Stable and compatible with most drugs with low hygroscopicity and low price. Cornstarch is often used.

Cornstarch -photo credits: suedzuckergroup
Lactose: It consists of equal molecules of glucose and galactose. It is a kind of white crystalline powder, and slightly sweet, which is easily soluble in water, and slightly soluble in ethanol.
It is generally used as a filler for tablets and capsules.

Pancreas Food Lactose -photo credits: columbiasurgery
Lactose is an excellent diluent. With the lactose, the finished tablet will be bright, clean, and beautiful.
It has no effect on the determination of the main drug content. Amorphous lactose is available for direct compression of powders.
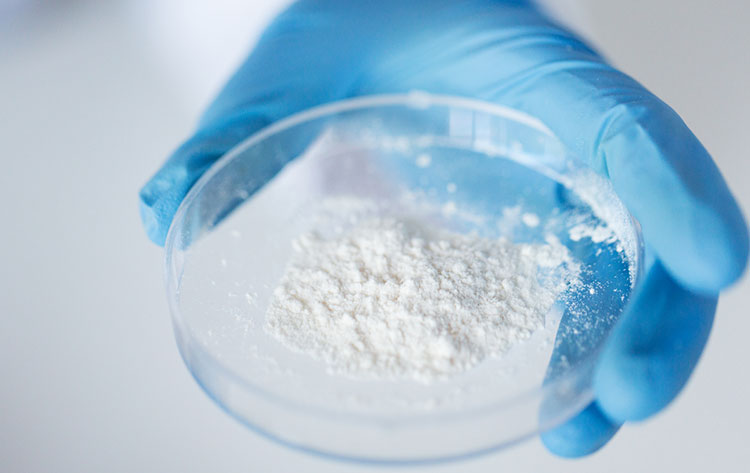

Microcrystalline Cellulose -photo credits: medium
Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC): Microcrystalline cellulose is a crystalline powder obtained by partial hydrolysis of cellulose, with a strong binding force and good compressibility.
It is also known as a “dry binder”, and it can be used for direct compression of powder. When the tablet contains more than 20% microcrystalline cellulose, the disintegration is better.

Sugar Alcohols -photo credits: kaynutrition
Sugar Alcohols: Mannitol and Sorbitol are in the form of granules or powders.
It is endothermic when dissolved in the mouth. Therefore, it has a cool feeling when you take it, and at the same time, it has a certain sweetness, and there is no gritty feeling in the mouth.
With good compressibility, it is more suitable for the preparation of chewable tablets.
But the price is slightly more expensive, and it is often used in conjunction with sucrose.
- Excipients for Capsules:
① Main Types of Excipients for Capsules:
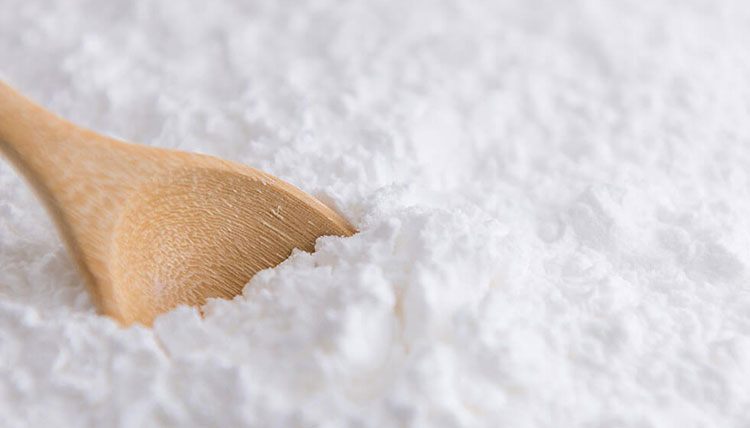

Pregelatinized Starch -photo credits: smscor
Pregelatinized Starch 1500: Pregelatinized starch is to break the starch granules partially or completely by chemical method or mechanical method so that the starch has fluidity and direct compressibility.
This material is specially used for capsule filling.
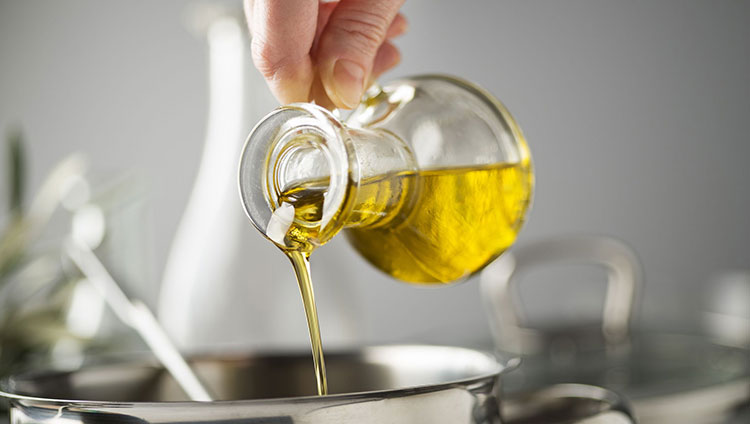

Oily Carrier -photo credits: goodhousekeeping
Oily Carrier: Including soybean oil, castor oil, medium chain fatty acid, etc.
- Excipients for Tablets:
Quality requirements for tablet excipients: Tablet excipients must have high chemical stability and not have any physicochemical reaction with the main drug.
It must be harmless to the human body, with no adverse reactions. The main efficacy and assays were not affected.
① Main Types of Excipients for Tablets:
Common Diluents and Absorbents For Tablets:
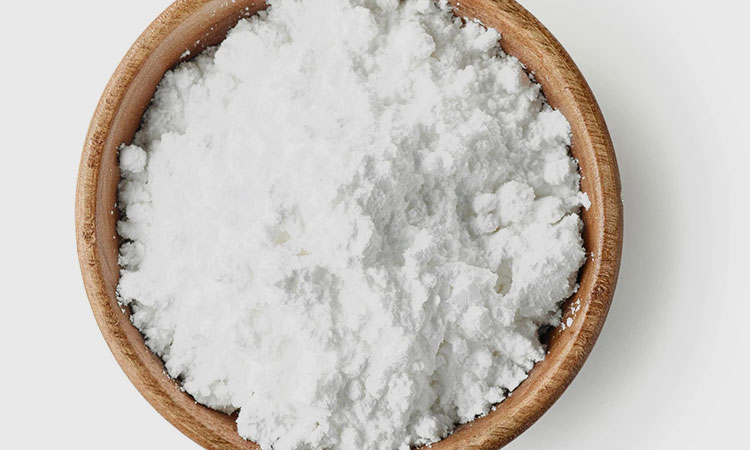

Powdered Sugar -photo credits: savoryexperiments
Powdered Sugar: It refers to the powder of crystalline sucrose dried and crushed at low temperatures.
Its advantage lies in its strong adhesion. It can be used to increase the hardness of the tablet and make the surface of the tablet smooth and beautiful.
It has strong hygroscopicity, so it is not suitable for acid-base drugs. It is often used in conjunction with dextrin and starch.
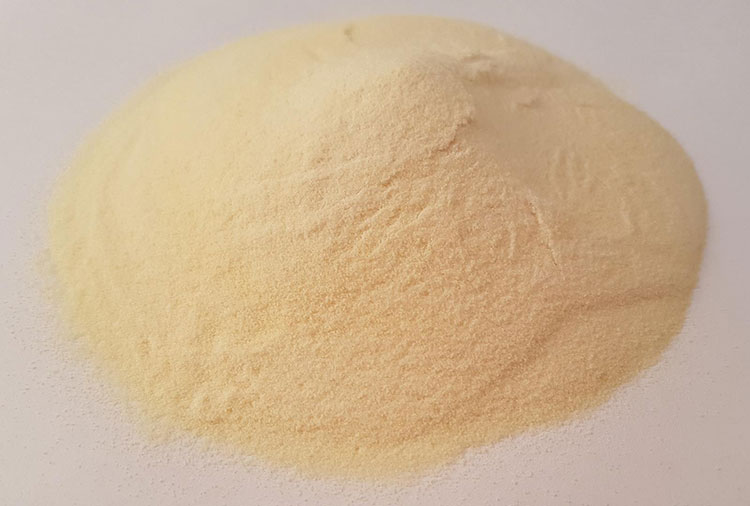

Dextrin -photo credits: inoxia
Dextrin: An intermediate product of starch hydrolysis. It is easily soluble in hot water, and dextrin is a weakly acidic viscous solution, but insoluble in ethanol.
Dextrin amount should be less, and it is advisable to combine it with powdered sugar. Dextrin will affect the disintegration and the content of the main drug.
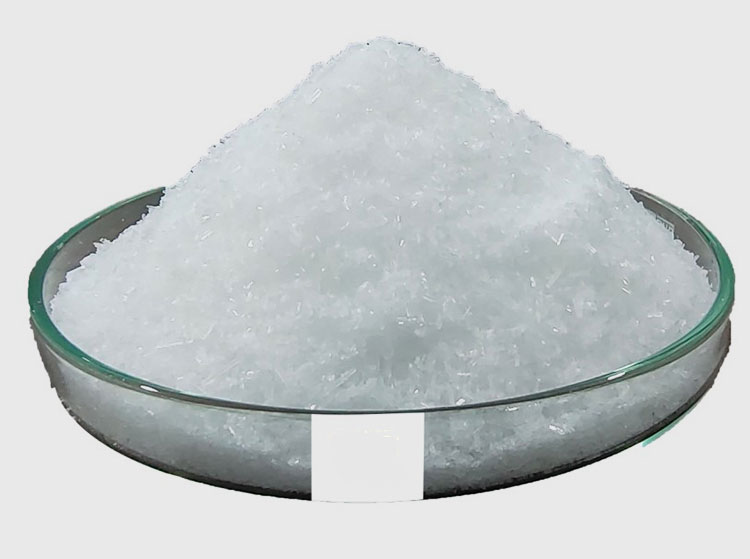

Inorganic Salts -photo credits: vragroindustries
Inorganic Salts: These mainly include some inorganic calcium salts, such as calcium sulfate, calcium hydrogen phosphate, medicinal calcium carbonate, as well as magnesium oxide, aluminum hydroxide gel powder, etc.
The general dosage is about 10%.

Wetting Agent -photo credits: corrosionpedia
Wetting Agent and Adhesive: The selection of wetting agent and adhesive must be appropriate, and the viscosity must be appropriate.
Not only the drug can be made into granules. When the drug is pressed into tablets, the appearance of the tablets should be smooth and the disintegration degree should be qualified.
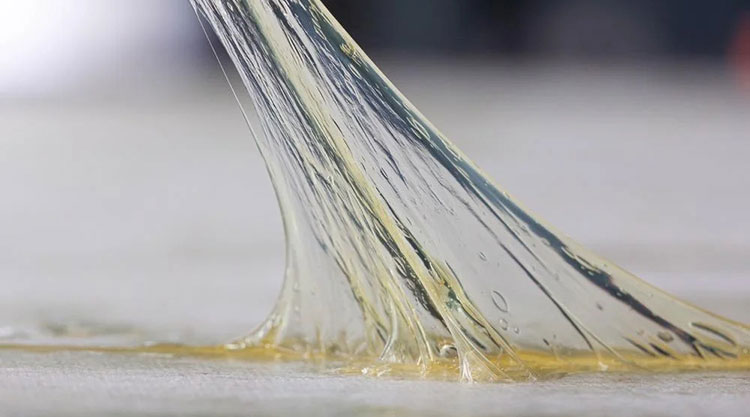

Adhesive -photo credits: azonano
Wetting Agent: It is non-viscous by itself but can induce the viscosity of the material to be granulated, so as to achieve the purpose of granulation and tableting.
Adhesive: It refers to non-sticky or insufficiently sticky materials to give stickiness. Thereby making the material agglomerate into granules of auxiliary materials.
Common Wetting Agent and Adhesive For Tablets:

Distilled Water
Distilled Water: It refers to pure water such as distilled water or deionized water. Water is the most commonly used humectant in tablet preparation. Colorless, odorless, tasteless liquid.

Ethanol -photo credits: ethanol
Ethanol: It can be used for drugs that are easily decomposed in contact with water. It can also be used for drugs that are too viscous in water.
The viscosity produced after wetting decreases with increasing ethanol concentration. Therefore, the concentration of alcohol depends on the nature of the raw and auxiliary materials, generally 30%-70%.

Starch Syrup -photo credits: cassavaindia
Starch Syrup: Starch syrup is the most commonly used adhesive in tablets. The concentration of 8%-15% is commonly used, and 10% starch slurry is the most commonly used.

Disintegrant -photo credits: pharmaexcipients
Disintegrant: Disintegrants are excipients that rapidly disintegrate tablets into fine particles in gastrointestinal fluids.
Except for sustained-release tablets and some special-purpose tablets (such as buccal tablets, chewable tablets, sublingual tablets, and implantable tablets), disintegrants should be added to general tablets.
Common Disintegrants For Tablets:
Sodium Hydroxymethyl Starch: It is a white amorphous powder with a degree of substitution of 0.3-0.4.

Effervescent Disintegrant -photo credits: pharmaexcipients
Effervescent Disintegrant: It is a special disintegrant specially used for effervescent tablets.
Surfactant: It is a kind of disintegration aid that can increase the wettability of hydrophobic or poorly soluble drugs.
Tablet Drug Pills -photo credits: pngitem
Lubricant: A substance that reduces the friction between the tablet and the walls of the die hole. To ensure the smooth progress of the tableting operation and the smooth surface of the tablet.
Common Lubricants For Tablets:

Micronized Silica Gel -photo credits: calpaclab
Micronized Silica Gel: Excellent tablet glidant.

Talc -photo credits: alpapowder
Talc: Mainly used as a glidant. It can fill up the depressions on the surface of the particles and reduce the roughness of the surface.

Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil -photo credits: rxlist
Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil: This product is prepared by spray drying method and is a lubricant with good lubricity.
The types of Excipients for capsules and tablets can be a little more complicated. But do not worry about this. All Excipients are safe and reliable.
4. What Are the Capsule Shells and Coating Materials Made of Capsules and Tablets?
- Capsule Shells
Capsule shells are mainly used in the medicine and pharmaceutical industries.
Medical hollow capsules are mainly used to hold solid medicines, such as self-made powders, health care products, pharmaceuticals, etc.

Capsules with Powders -photo credits: healingpharma
The capsule shell solves the insufficiency of difficult entrance and poor taste for users, and truly solves the problem that good medicines are no longer bitter.

Gelatin for Capsules -photo credits: outsourcing-pharma
The hollow capsule shell is made of gelatin. Gelatin is a water-soluble protein extracted from collagen. After the gelatin film is dried and hardened, the capsules can be synthesized. Then you can remove it from the mold.
The hollow capsule shell is made of starch. Hydroxypropyl starch capsules are made from hydroxypropyl starch.
It does not need to add additional additives and is a natural, healthy, and green material. Moreover, the source of starch is simple and cheap, and it is considered to be the most potential substitute for capsule raw materials.
Capsule shells can be made in different colors to distinguish functions and models. It is convenient for you to take.

Colored Capsules -photo credits: capsulcn
There are many types of edible gelatin. Capsule shells are made from pharmaceutical-grade gelatin that must meet stringent requirements for use in pharmaceutical products.
- Tablet Coatings
Coated tablets include sugarcoated tablets, film-coated tablets, and enteric-coated tablets.

Sugar Coated and Film Coated Tablets -photo credits: slideplayer
Sugar-coated tablets refer to tablets that are mainly coated with sugar as a coating material.
Film-coated tablets refer to tablets coated with films of polymer materials.
Enteric-coated tablets (enteric-coated tablets) refer to tablets with a coating layer that is insoluble in gastric juice but soluble in intestinal juice.

Enteric-coated tablets -photo credits: pharmapproach
The purpose is to prevent the drug from being destroyed in gastric juice and the irritation of the drug to the stomach.
5. Why Are Medicines Made into Capsules or Tablets?
In addition to capsules and tablets, medicines also include granules, solutions, and ointments. Next you will understand why some medicines are made into capsules and tablets.

Capsules Vs Tablets- photo credits: aor
Reasons for Capsules:
Some medicines are bitter, and taking them into capsules will save you from suffering.
Some medicines are mixed with a variety of powders or viscous liquids, and if you don’t need them much at one time, then it will be convenient for you to take them if medicines are filled into capsules.
Reducing the waste of medicine in the mouth and allowing the medicine to be fully absorbed in the stomach.

Capsules- photo credits: zaxisinc
Reasons for Tablets:
The measurement is accurate, and the difference in drug content in the tablet is small.
It’s easy for you to carry, transport, and take with stable quality.
With mechanized production, large output, and low cost, it’s easy for you to achieve hygiene standards.
Tablets- photo credits:pharmaceuticalmanufacturer
Some medicines can only be made in capsule form, such as oil-based medicines. Some medicines can only be made in tablet form.
6. What Are the Differences Between Capsules and Tablets?
The differences between capsules and tablets, in addition to appearance, content, production methods, and their respective advantages are different.

- Different Forms
Capsules are usually capsule shells containing some powder, granular, or oil medicines, while tablet medicines are ordinary medicines without special packaging.

Oil Capsules -photo credits: consumerlab
- Advantages of Capsules
One of the advantages of capsules is the solid dosage form of liquid medicines, that is, medicines with high oil content or liquid medicines that are difficult to be made into tablets are made into soft capsules, which have the characteristics of convenient use and clear dosage.

Empty Capsules -photo credits: medgadget
The hollow capsules used to encapsulate drug particles are a kind of special pharmaceutical excipients, which are equivalent to containers for medicines.
Although the hollow capsule itself has no curative effect, it is beneficial to improve the stability of pharmaceutical preparations and help the fixed-point release of the main drug components.

Oil Capsules -photo credits: speedrangespices
At the same time, it can cover up the unpleasant taste of the drug.
After oral administration, the capsule will wrap the medicine and enter the human digestive system together, and will eventually be absorbed by the human body, so the quality and safety of the capsule are also directly related to the quality of the medicine.
Oral Administration of Medication -photo credits: nursecepts
Capsules have the advantage of being easier to swallow and faster delivery time than tablets.
While tablets are less expensive than capsules, capsules are capable of mixing more sensitive medications because the container is an important oxygen barrier.
- Disadvantages of Capsules
If the contents of the capsule are bulky, the capsule will be larger. It also has a short shelf life.
- Advantages of Tablets
The dissolution rate and bioavailability of tablets are better than capsules.
The quality is stable.
Tablets are dry solids, and some drugs that are susceptible to oxidative deterioration and deliquescence can be protected by coatings. Therefore, light, air, moisture, etc. have less influence on it.

Sunlight to Medications -photo credits: everydayhealth
The body is easy to digest and absorb for you.
- Disadvantages of Tablets
Tablets have weaker dissolution and consumers have more concerns about those than capsules.
Tablets are cheaper and easier to dispense a dose, but they don’t release the drug into your system as quickly as capsules.
- Different Medicinal Properties
The particles in the capsule may irritate the esophagus and gastric mucosa and may also be inhaled into the trachea, so it needs to be loaded into the capsule to determine the stability of the medicinal properties and reduce damage to body organs.
Tablets are usually prepared as solid preparations that can be taken directly with water, which can reduce damage to gastrointestinal tissue.
Taking Tablets with Water -photo credits: medcline
- Different Efficacy
Capsules and tablets are both taken with warm water. Remember, they may be directly digested and absorbed in the mouth, which may lead to loss of efficacy.
Tablets Taking -photo credits: pharmaceuticalmanufacturer
However, capsule substances can usually reduce the damage to gastric mucosal stimulation, and need to enter the gastrointestinal tract before they can be dissolved and absorbed, and directly exert better efficacy.
- Preparation Technology
The capsule preparation process is relatively simple, mainly filling the drug in the capsule shell, which is mostly made of gelatin, so the capsule can be quickly dispersed, dissolved, and absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.
The tablet is compressed and formed under the impact of mechanical pressure, and there are many excipients in the tablet, which affect the dissolution and absorption of the main drug.

Drug Preparation -photo credits: healthline
Therefore, capsules of the same drug will work faster than tablets, not that tablets do not work.
After knowing so much about the differences between capsules and tablets, you will be better able to make better choices for your needs in the future.
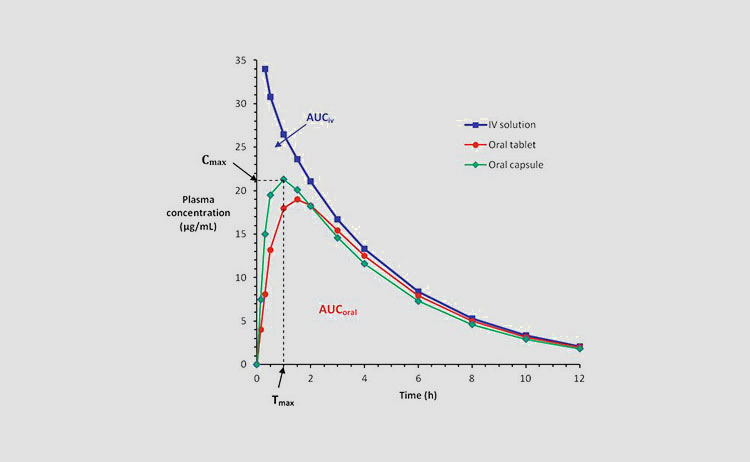
7. What Is the Absorption Rate of Capsules and Tablets?
When medicines are consumed by you, they are first dissolved and absorbed. Some capsules and tablets will dissolve in your stomach first. Some capsules and tablets will dissolve in your intestines. However, their absorption rates are different whether in your stomach or in your intestines.
From the point of view of absorption speed:
Drug-Absorption-and-Bioavailability -photo credits: basicmedicalkey
Solid preparations such as capsules and tablets are mainly taken orally.
After administration, the drug needs to be dissolved and then absorbed through the gastrointestinal epithelial cell membrane into the blood circulation to play its therapeutic role.
Oral Administration of Drugs -photo credits: pharmapproach
Oral preparations absorbed rates are generally in the order of capsules > tablets.
In addition, the drug in the capsule is filled in the capsule shell in the state of powder or granules, which is different from the tablet and does not need to undergo a process such as mechanical extrusion, so the capsule generally takes effect faster than the tablet.
From the point of view of disintegration time:
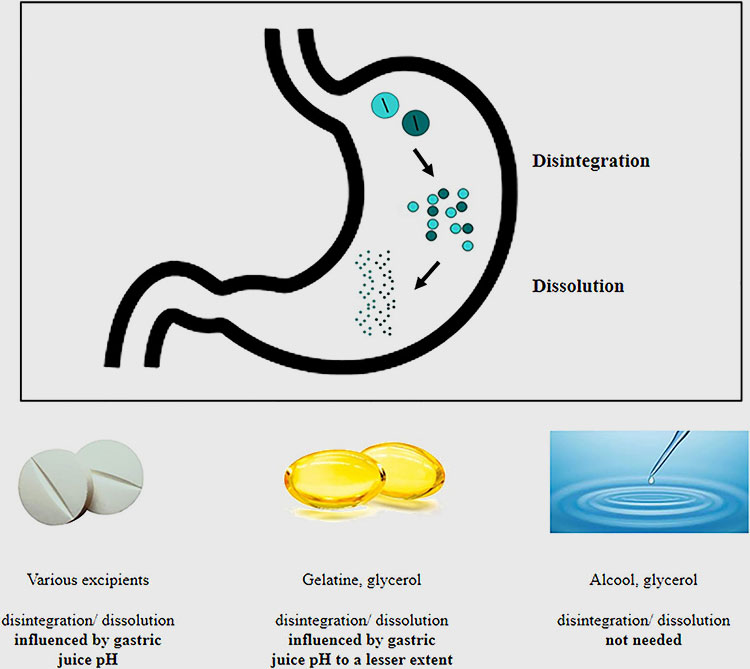
Disintegration and Dissolution -photo credits: frontiersin
Hard capsules can be completely disintegrated within 30min; soft capsules and enteric-coated capsules can be completely disintegrated within 1h.
The ordinary tablet disintegration time limit is 15min;
Dispersible tablet, the soluble tablet is 3min; the sublingual tablet, the effervescent tablet is 5min; the film-coated tablet is 30min;
Extract tablet, sugar-coated tablet, and enteric-coated tablet is 1h.
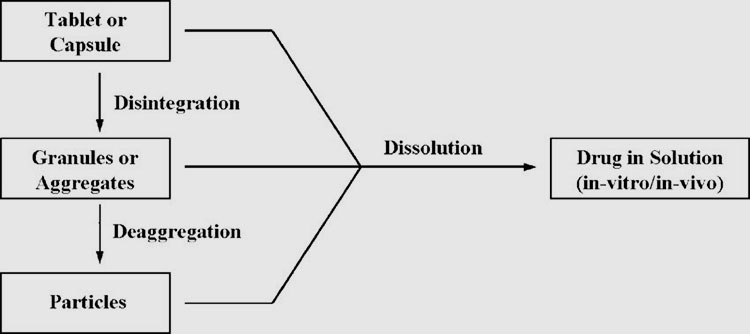
Dissolution and disintegration -photo credits: researchgate
All in all, capsules are prepared into powders, granules, small tablets or pellets, etc., and then filled in the capsule shell. Compared with tablets, the production cost is relatively high.
For budget considerations, the generic pharmaceutical company will prefer tablets over capsules.
In general, the absorption rate of capsules is much better than that of tablets. However, tablets are cheaper.
8. What Are the Characteristics of Capsules and Tablets?
There are significant differences between capsules and tablets in terms of odor, absorption, and drug release.
- Odor
Capsules: They can mask the bad smell of medicine and improve the stability of medicine.
Capsules -photo credits: pharmaceuticalmanufacturer
The medicine is packed in a capsule shell, which can be isolated from the outside to avoid the influence of light, air, and moisture, and has a certain masking protection and stabilization effect on the medicines with bad odor and instability.

Tablet Coating -photo credits: pharma knowledge
Tablets: During the tablet production process, there is also a coating added to the tablets. The coatings are divided into sugar coatings or film coatings.
The sugar coating of the tablet can mask the bitter taste of the tablet; the film coating can mask the bad smell of the tablet and make it easier for you to take.

Film Coating -photo credits: pharmapproach
- Absorption
Capsules: They can make the drug work quickly in the body.

Body Absorption -photo credits: youtube
Drugs are filled into capsules in powder or granular form. Compared with tablets and pills, there is no influence of mechanical pressure during preparation, and it can be rapidly dispersed, dissolved, and absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.
Tablets: Tablets are solid preparations in the form of flakes or special-shaped flakes, which are uniformly mixed with drugs and excipients and compressed.

Excipients -photo credits: innovationcompounding
Because a number of excipients are added to the tablets, and after compression molding, the dissolution rate of tablets is slower than that of powder and capsules, which sometimes affects their bioavailability.
- Drug Release
Capsules: It can delay or localize drug release.
The medicines are made into granules or pellets, and suitable coating materials are selected according to your needs, and then packed into capsules, so that the medicine has the effect of slow release and prolonged effect.

Drug Release -photo credits: freepik
Enteric-coated capsules allow the localized release of drugs in the small intestine. There are also controlled-release capsules that release the drug slowly and at a constant rate in a prescribed medium.
Tablets: They also can delay or localize drug release.
Because the outer layer of the tablet is sugar-coated, film-coated, or enteric-coated the medicine also has the effect of slow release and prolonged effect.
Tablets -photo credits: goodrx
If you cannot accept the strong taste of the medicine, then we strongly recommend the capsule form for you. If you find capsules difficult to swallow, tablets are a better choice.
9. Why Are Capsules and Tablets Made into Different Colors and Shapes?
If you have enough life experience, you will find that different capsules and tablets come in different shapes, colors, and sizes. And there are reasons for these differences.
- Distinguish
The color and shape of capsules and tablets facilitate differentiation between drug varieties or doses to ensure that drugs are not mixed up during manufacture and use.

Capsule Options -photo credits: ionlabs
Especially for those patients who need to take more than one medication a day, it can reduce their medication errors. Especially elderly patients, often remember the appearance of the drug (color, shape), not the name.
- Patents
Some drug manufacturers register the appearance of their products (including size, shape, color, texture, and aroma) as patents as property rights under trademark law, known as “trade dress”.

Tablets with Marks -photo credits: pharmaexcipients
You can even identify specific drug names based on their appearance. Generic drug manufacturers are not allowed to copy the shape, color, and size of these branded drugs.
Especially for new drugs, manufacturers try different drug names, colors, and shapes to avoid repeating other drugs.
Medication-pills in Different Shapes -photo credits: audiocardio
Many capsule shells or the sugar coating of the tablets are marked with the relevant numbers and numbers.
- Stability
Different drugs have different physical and chemical properties, such as different sensitivity to light. Drugs that are unstable to light can be protected from light by using dark coatings or capsule shells.
Dark-coated Capsules -photo credits: hindustantimes
- Flavoring Effects
The sugar coating on the outer layer of the tablet can play a role in correcting the taste, and different colors are set for the sugar coating in order to distinguish.
But capsule shells are generally tasteless. The capsule shell component is refined from medicinal gelatin or starch and auxiliary materials.
- Moisture Proof
Different drugs have different physical and chemical properties, such as different sensitivity to light. Drugs that are unstable to light can be protected from light by using dark coatings or capsule shells.

Water Proof -photo credits: flamingtext
The moisture-proof effect of the capsule shell is much better than that of the sugar coating.
So in your daily life, what shape and color of capsules and tablets do you prefer?
10. How Are Capsules and Tablets Made?
Due to the large demand for drugs, most of the capsules and tablets in the world are produced by fully automatic machinery. This can not only ensure the demand for large production volumes but also improve production efficiency and production safety.
- Capsule Filling Machine
A Capsule Filling Machine is a kind of equipment used to fill empty capsules with pharmaceutical ingredients.
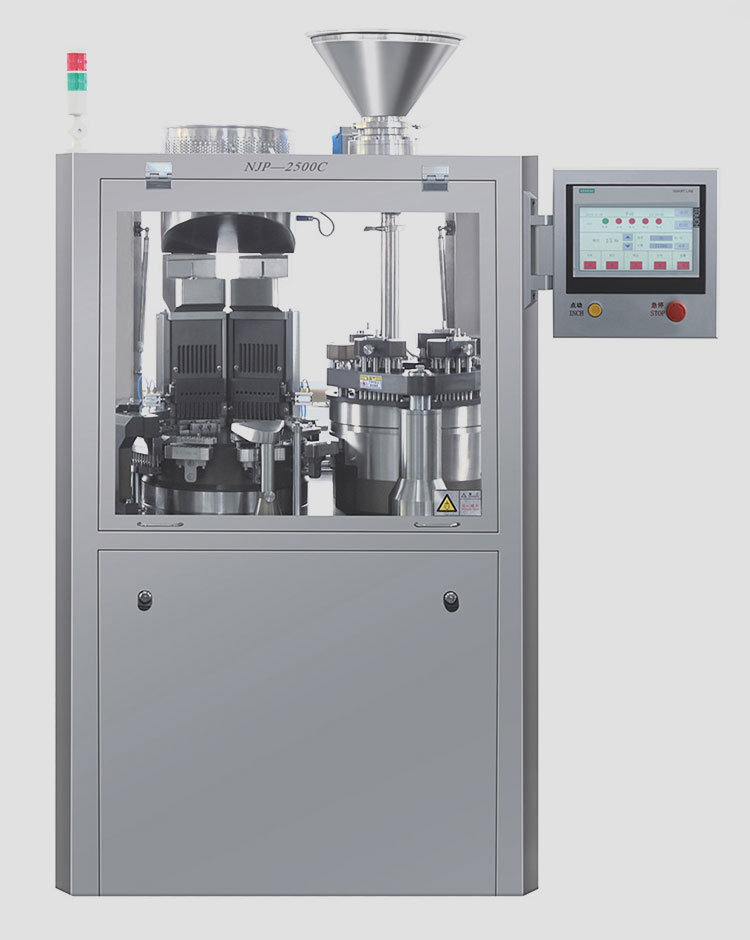

Capsule Filling Machine
Almost all capsules are done by capsule filling machines. Filling machines can be divided into automatic and semi-automatic styles with high efficiency and good accuracy. The whole process is clean and hygienic.
- Tablet Press Machine
The tablet press machine is an automatic continuous production equipment that can press granules into round, special-shaped tablets with characters, symbols and, graphics with a diameter of not more than 13mm.

Table Press Machine
The models can be divided into single punch tablet press, flower basket tablet press, rotary tablet press, sub-high-speed rotary tablet press, automatic high-speed tablet press and, rotary core-spun tablet press.
The tablet press machine has the characteristics of simple operation, convconvenience quick cleaning, especially when changing varieties, it is quick and convenient for you to clear the field.
If you have any interests and needs on the machine, you are welcome to consult us.
Conclusion
Through the introduction of this article, you can learn that different medicines are optimally selected into capsules or tablets by professionals. Therefore, you don’t need to be too concerned about choosing capsules or tablets. You only need to choose different doses and different types of drugs to take according to your actual situation and your doctor’s advice. Hope this article can answer your questions and make the most correct choice for you.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide

Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
