What Is The Difference Between Shrink Tunnel And Heat Tunnel?
When it comes to packaging products, there are a few different types of machines that can be used: shrink tunnels and heat tunnels. So, if you are in the shrink wrapping business, you may wonder what the difference is between a shrink tunnel and a heat tunnel. Both of these machines serve a similar purpose, but there are some key distinctions that you should be aware of before making a purchase.
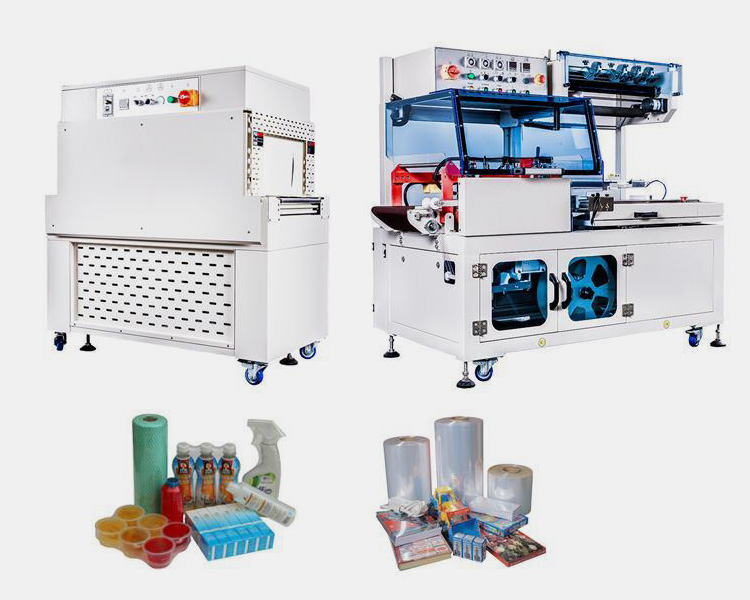

In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between shrink tunnels and heat tunnels and their advantages and disadvantages. By the end of this post, you will be able to make an informed decision about which machine is suitable for your business. Let’s get started!
1.What Is A Shrink Tunnel Machine?

A shrink tunnel machine is an industrial equipment used for shrink wrapping products. They are typically used in packing and packaging operations and consist of an adjustable heat source, fan, conveyor belt, and shrink wrap film.
The shrink wrap film is fed through the tunnel, where it is heated by the heat source to shrink tightly around the product. This shrink wrap film creates an air-tight seal that protects the product during transport and storage. The fan then cools the shrink wrap, thus completing the shrink wrapping process.
Shrink tunnel machines are designed to shrink various products, making them ideal for many industrial applications. Also, these machines provide a cost-effective and efficient way to package products for shipping and storage. Shrink tunnel machines are easy to use and maintain, making them a popular choice for many businesses.
2.What Is A Heat Tunnel Machine?
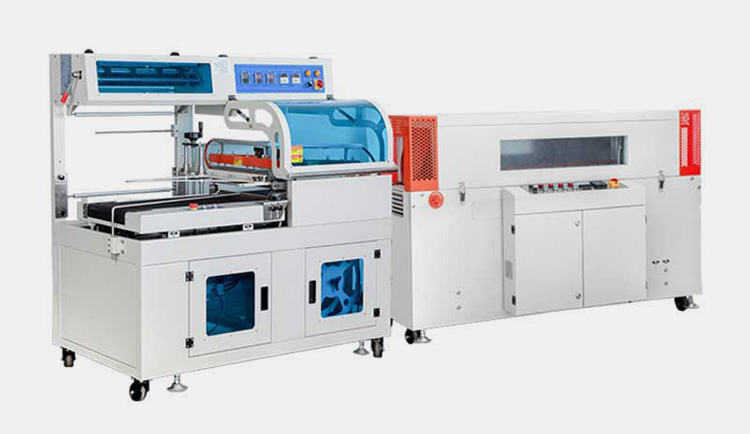

A heat tunnel machine is a device used for heat shrink wrapping products. Heat tunnels are typically used to reduce packaging size and improve product presentation. The heat generated by the heat tunnel shrinks the film around the item, creating a neat and secure package.
Heat tunnels provide consistent heat across all sides of the package, ensuring an even seal. This process is quick, efficient, and cost-effective. Heat tunnel machines are ideal for a range of products, including food items, beverages, cosmetics, and other small to medium-sized items.
Also, heat tunnels offer superior heat control and precise shrink wrapping capabilities, making them an essential tool in the packaging industry. Besides, this machine increases productivity by minimizing time and labor costs.
3.What Is the Difference Between Shrink Tunnel And Heat Tunnel Machine?
Composition
a) Shrink Tunnel

A shrink tunnel machine comprises several components that work together to ensure an efficient and successful shrink wrapping process. They include;
Conveyor Belt
The shrink tunnel conveyor belt moves the shrink-wrapped product through the tunnel, allowing it to be shrunk uniformly by heat.
Control Panel
The control panel houses all the electrical and mechanical components of the shrink tunnel, allowing for easy access and operation
Conveyor Motor
This is the motorized conveyor that moves shrink-wrapped products through the shrink tunnel.
Conveyor Adjustment
The shrink tunnel’s conveyor adjustment system allows the speed and width of shrink film rolls to be adjusted so that they fit perfectly with the type of product being shrink-wrapped.
b) Heat Tunnel
In comparison to a shrink tunnel, a heat tunnel consists of the following components:
Blower Motor
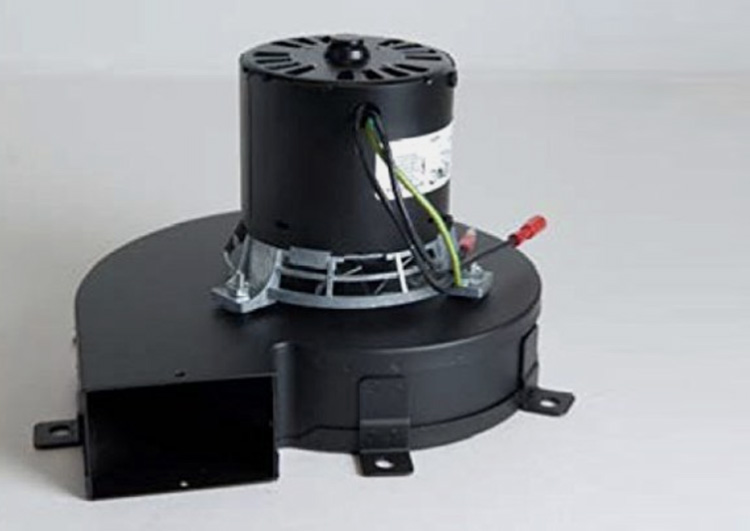

The blower motor forces air through the heat tunnel and is used to evenly heat the product.
Control Panel

The control panel allows for temperature adjustments, the conveyor system’s speed, and the heat source.
Fan
The heat tunnel also has a fan that helps evenly distribute heat within the shrink tunnel and circulates the shrink-wrapped product.
Exhaust System

An exhaust system relieves built-up heat and vapors from the heat tunnel.
Operation
a) Shrink Tunnel

The shrink tunnel works by heating the shrink film with hot air as it passes through an enclosed conveyor system. As the shrink film passes through the shrink tunnel, the hot air causes it to shrink tightly around the product. Once the product reaches the end of the shrink tunnel conveyor, it has been securely shrink-wrapped and is ready for packaging or storage.
b) Heat Tunnel
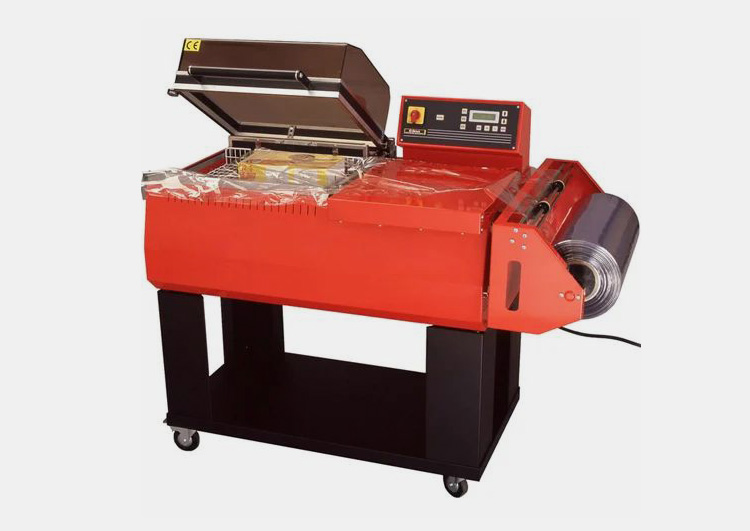

Unlike the shrink tunnel, this machine uses a heat source, such as hot air or infrared heaters, which is circulated through an enclosed chamber. The heat from the heat source causes the plastic to shrink, securely sealing its contents.
This process allows for more efficient packaging of goods and protects against potential damage during shipping.
Output Quality
As explained below, the output quality of shrink and heat tunnels can differ.
Shrink Tunnel

The output quality of a shrink tunnel is typically better because these machines often have built-in fans that help circulate the hot air, ensuring even distribution. Uniform heat circulation ensures that shrink wrap packages are correctly sealed and look identical. It also prevents shrinkage or shrink’s marks that often occur when using a heat gun.
Additionally, shrink tunnels use less energy than heat tunnels, which helps to reduce operational costs. The control systems of shrink tunnels allow users to adjust the temperature, speed, and conveyor belt settings for different shrink requirements.
In general, shrink tunnels produce better results with fewer wrinkles and more even shrinkage compared to their counterparts. By providing greater consistency in the shrinking process, shrink tunnels ensure better overall output quality for any shrink wrapped item.
b) Heat Tunnel

In a heat tunnel, the heat source is usually located at one end, so the product closest to the heat source will be cooked more than the product further away. This can cause uneven shrinkage and poor output quality.
However, to ensure consistent heat distribution and better output quality, heat tunnels have adjustable airflow, temperature control with digital controls, variable speed conveyor systems, and other features. With proper adjustment of these components, heat tunnels can generate an even shrinkage pattern for product packaging and a higher level of output quality.
Additionally, heat tunnels can use multiple heat sources to improve heat distribution and output quality further. Companies can achieve excellent output quality from their heat tunnel by using the right combination of heat source locations and settings for heat tunnel components.
Advantages
a) Shrink Tunnel
Increased Efficiency

One of the most significant benefits of shrink tunnel machines is their ability to increase efficiency in production lines. By allowing for faster shrink wrapping processes, shrink tunnel machines reduce labor and material costs, making them cost-effective solutions for many businesses.
Improved Quality Control
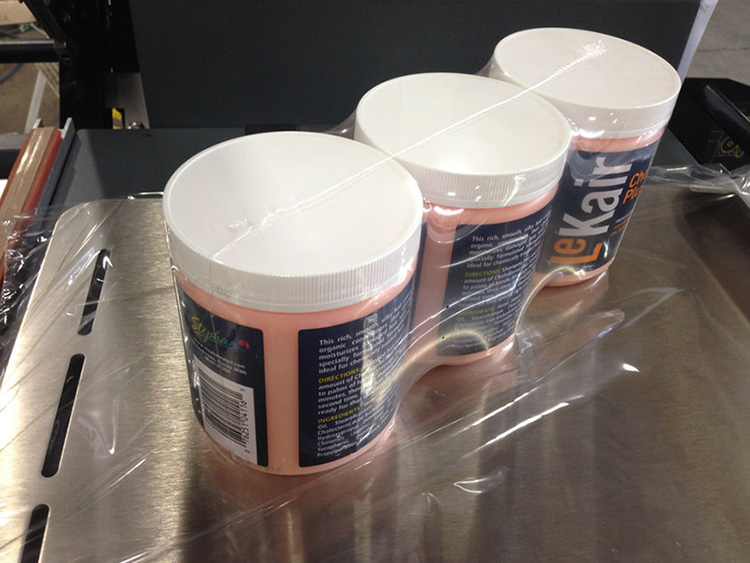

Shrink tunnel machines also help improve quality control on production lines by ensuring that each product is shrink wrapped properly, without any loose ends or gaps. This helps ensure that products stay secure during transport and storage, resulting in improved customer satisfaction with the final product.
Easy to Operate

Shrink tunnel machines are designed to be easy to operate and maintain. They have simple control panels that make it easy to adjust shrink tunnel parameters, such as shrink time and temperature, ensuring a secure shrink wrap every time.
Versatile Performance
Lastly, shrink tunnel machines can offer versatile performance in different settings. In addition, the devices can easily accommodate multiple materials, from PVC and shrink film to Polyolefin and more.
b) Heat Tunnel
Cost Savings

Heat tunnels are more cost-effective than shrink tunnels because they require less energy and fewer materials, resulting in lower operating costs over time.
Durability
Heat tunnels are designed to be durable and reliable so that they can withstand harsh environments and last longer than manual heat sealers.
Disadvantages
a) Shrink Tunnel
Environmental Concerns

shrink tunnel machines can emit hazardous chemicals into the air, leading to environmental concerns. Choosing an eco-friendly shrink wrap machine that complies with all local regulations to minimize potential safety and environmental risks is essential.
Inefficient
shrink tunnel machines can be slow and weak, resulting in slower production times. This means that it may take longer to get packages out the door, which can lead to customer dissatisfaction
Expensive
shrink tunnel machines are typically costly to purchase and maintain, making them cost-prohibitive for businesses on a budget. Additionally, shrink wraps require unique shrink films, which adds to the overall cost.
Labor Intensive

shrink tunnel machines usually require an operator to monitor and adjust production parameters to ensure quality shrink-wrap packaging results. This labor-intensive process can be time-consuming and expensive if not properly managed.
b) Heat Tunnel
High Maintenance Costs

Heat tunnel machines require frequent maintenance and repairs due to the heat and steam associated with their operation. The constant heat can cause parts of the device to corrode over time, which leads to expensive repair costs for businesses.
Increased Risk of Injury
Heat tunnel machines can be dangerous if not correctly operated or maintained. Due to the heat generated by these machines, employees who drive them are at risk of burns from contact with hot surfaces or scalding from steam condensation within the heat tunnel itself.
Possibility of Overheating
Heat tunnel machines can overheat if not properly monitored and adjusted for temperature levels, leading to costly breakdowns and product damage. Additionally, heat tunnel machines generate a large amount of heat that must be dissipated to prevent overheating from occurring.
4.Which Machine Is More Cost Effective -Shrink Tunnel Or Heat Tunnel?

Shrink tunnel is becoming the preferred method for shrink-wrapping items. This is because shrink tunnels are more cost-effective than heat tunnels and have a minor environmental impact due to their energy efficiency. Also, shrink tunnels use less electricity and generate less waste, helping businesses save money in the long run.
Additionally, shrink tunnels are better equipped to shrink-wrap irregularly shaped items as they can be adjusted accordingly without extra effort or resources. Furthermore, shrink tunnels offer faster packaging speeds with minimal shrinkage issues, unlike heat tunnel machines.
Heat tunnel machines also require more labor during operation due to their manual nature, which adds to their overall cost of production. All these factors make shrink tunnels far superior to heat tunnel machines regarding cost effectiveness and eco-friendly shrink-wrapping.
Overall, when it comes to cost-effectiveness and eco-friendliness, shrink tunnels are the superior machine choice over heat tunnels. With their lower operational costs and minimal environmental impact, shrink tunnels offer far greater value. Therefore, shrink tunnel machines are the ideal choice for businesses looking to shrink-wrap their products in a cost effective and eco-friendly manner.
5.What Is The Difference Between The Products Packaged Using A Shrink Tunnel And Heat Tunnel?
a) Shrink Tunnel
Food and Beverage Items

These can include pre-packaged foods, such as candy and snacks, canned goods, and other heat-sensitive items.
Household Items

This includes toiletries, cleaning products, and other housewares that require heat-sealed packaging.
Cosmetics

Many cosmetic products come in heat-sealed packaging, and shrink tunnels are an efficient way to package these items quickly and efficiently.
Retail Items

Smaller items, such as toys and games, can be heat-sealed with a shrink tunnel to protect them during shipping and handling.
b) Heat Tunnel
Gift Boxes
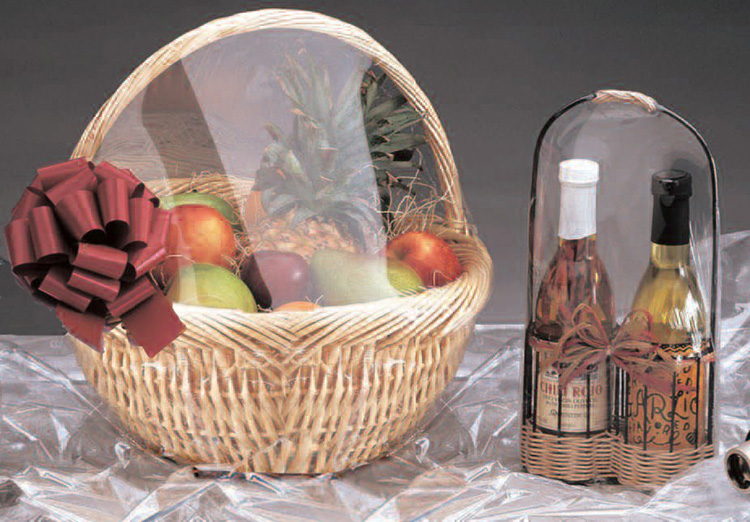

Heat tunnels can heat shrink gift baskets and boxes, making them easier to store and ship without worrying about the contents being damaged during shipping.
Electronics
Heat tunnels can heat shrink electronics into a secure package, making them easier to transport and protect from damage.
Clothing
Heat tunnels can heat shrink clothing into a secure package, allowing easy shipment and protection from dirt, dust, and moisture.
Bottles and Cans
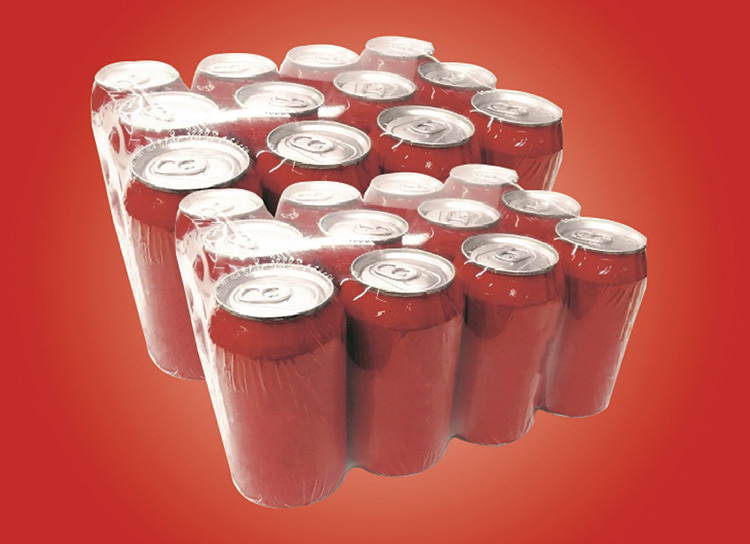

Heat tunnels can heat shrink plastic wrap around bottles and cans, making them easier to transport and store.
6.What Materials Can Be Used In Shrink Tunnel And Heat Tunnel?
Several types of material can be used for shrink wrapping with shrink tunnels and heat tunnels, as discussed below.
a) Shrink Tunnel
Polyolefin

This is the most commonly used shrink-wrap material and provides superior clarity, puncture resistance, and strength. It shrinks evenly at low temperatures, making it ideal for shrink tunnel machines.
PVC
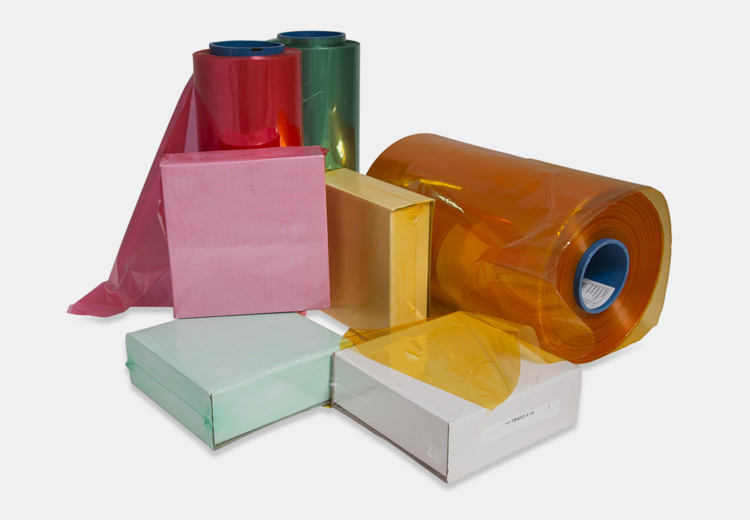

PVC shrink wraps offer sound clarity, low porosity, and an excellent range of shrinkage options. However, it requires higher temperature settings compared to Polyolefin for shrinking.
Polyethylene
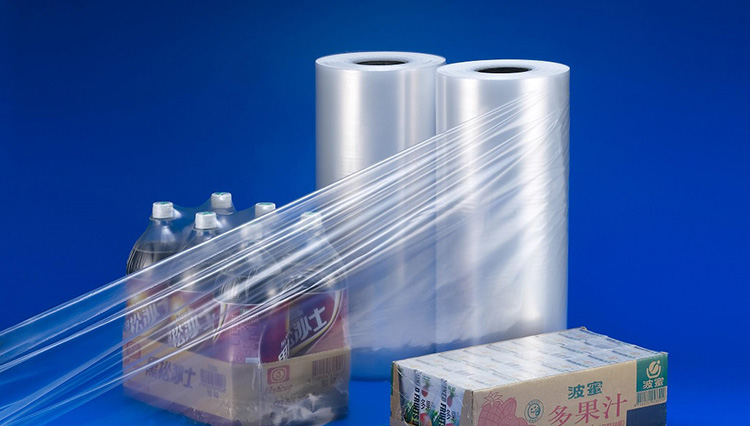

This is a budget-friendly shrink wrap option that offers good strength and shrinkage. It comes in both light gauge and heavy gauge types, with the latter offering better shrinkage results.
b)Heat Tunnel
In contrast with shrink tunnels, the most common types of heat tunnel materials include:
Metal

Metal is a great heat conductor and is often used for the outer frame and parts of heat tunnels to ensure robust and durable construction.
Glass

Heat-resistant glass makes windows on heat tunnels so operators can monitor performance outside the machine. This type of glass also provides an effective barrier between hot and cool air, reducing energy loss and maximizing efficiency.
Ceramics

Heat-resistant ceramics are usually used as insulation materials on heat tunnels because they can withstand high temperatures without breaking down or cracking easily.
7.What Are The Differences In Shrink Tunnel And Heat Tunnel Production Speeds?
As discussed below, there are some critical differences in shrink tunnel and heat tunnel production speed.
Shrink Tunnel

The speed of shrink tunnels is slower than that of heat tunnels. This is because shrink tunnels involve shrinking wrap, which needs to be heated and tightly shrunk onto a product to create a secure wrap. The shrink wrap must also be cut precisely to fit the shape of the package.
In addition, the type of shrink film also plays a vital role in setting shrink tunnel speed. Thicker films require higher temperatures, which can cause slower production speeds for shrink-wrapping machines.
Heat Tunnel

Heat tunnels are typically faster than shrink tunnels as they do not require lengthy heating periods like shrink tunnels. Heat tunnel production rates depend on several factors, such as the size and power of the tunnel, the type of product being sealed, and its size, shape, material, weight, and thickness.
More oversized products may also need longer passes through a heat shrink tunnel to securely shrink wrap the product. Heat tunnels can typically attain speeds of up to 200 feet per minute for shrink-wrapping purposes.
8.Which Tunnel Machine Is Popularly Used Between Shrink Tunnel And Heat Tunnel?
Shrink tunnel
The following large scale industries normally use the shrink tunnel to wrap their products:
Food Industry

Shrink tunnel machines are commonly used to shrink wrap food products like boxes of chocolates, pizzas, and other food items. This helps to protect the product from spoilage, damage, or contamination.
Beverage Industry

Shrink tunnels are also great for shrink wrapping beverage bottles or cans. This helps to keep beverages safe during transport and storage.
Pharmaceutical Industry
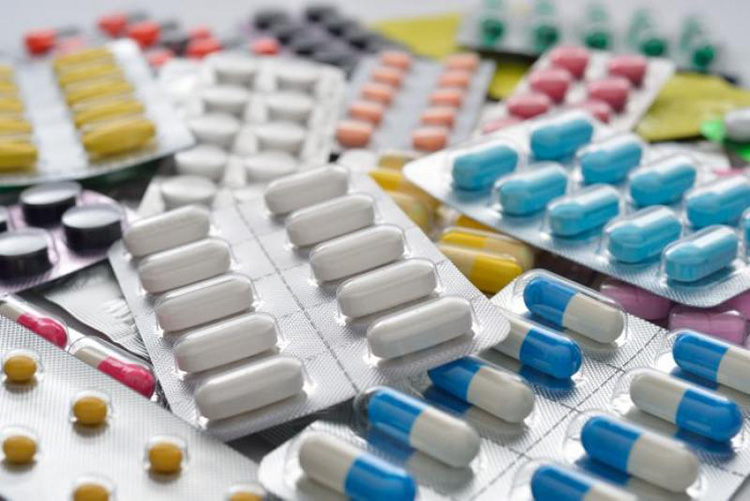
Shrink tunnels can be used to shrink-wrap pharmaceuticals, including tablets, pills, and syrups, to ensure their safety during transport and storage.
Cosmetics Industry
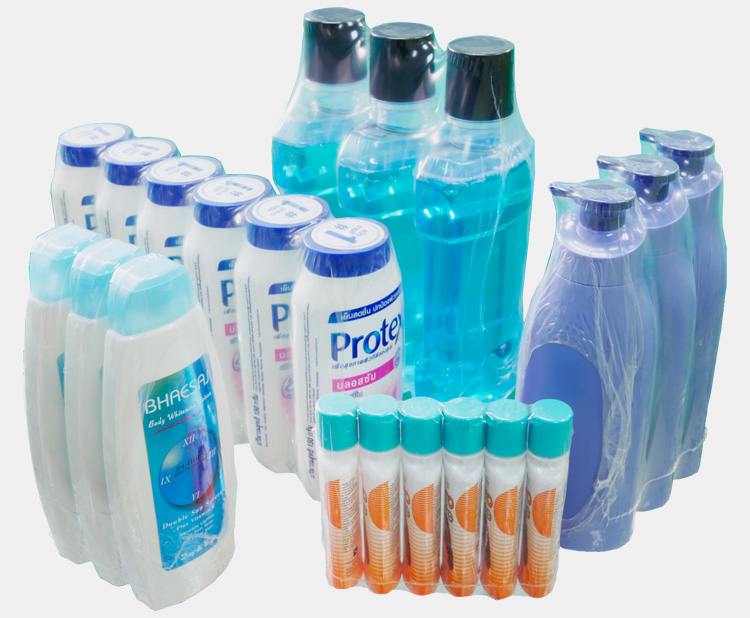

shrink tunnels can be used to shrink wrap cosmetics such as lotions and creams as it provides a safe way to store these products away from contaminants.
Hardware Industry
Shrink tunnels can be used to shrink-wrap hardware items, such as nuts and bolts, screws, and other parts which need to be kept safe from moisture or contamination.
Retail Industry
shrink tunnels can also be used for shrink-wrapping retail products like books, CDs, DVDs, stationery, etc., ensuring a safe packaging solution when shipping out orders.
Heat Tunnel
In comparison to the shrink tunnel, heat tunnel is also applying in the following industries:
Plastic Industry

Heat tunnel machines heat shrinking plastic products and components and heat seal them together to create a stronger bond that can withstand heat, moisture, and other environmental conditions.
Aerospace industry
Heat tunnel machines heat shrink insulation on aircraft parts and equipment, helping reduce the risk of corrosion or wear over time.
Automotive industry
Heat tunnel machines are used for heat-shrinking plastic auto body parts, fusing upholstery materials, and creating air-tight seals on electrical components of cars and other vehicles.
Textile industry

Heat tunnel machines are used to fuse fabric or other materials together to create a seamless and uniform look on clothing and accessories.
9.What Are The Different Types Of Shrink Tunnels And Heat Tunnels Available On The Market?
Many shrink tunnel and heat tunnel machines are available for shrink wrapping applications. Here is a breakdown of the most common for each:
a) Shrink Tunnels
Hot Air Shrink Tunnel
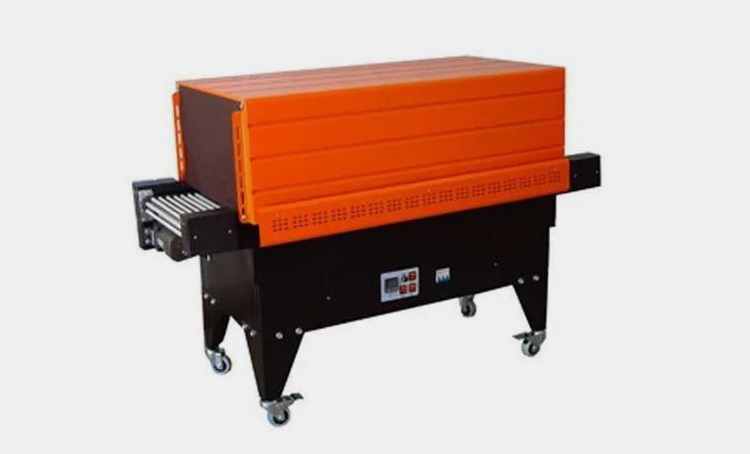

These shrink tunnels use hot air to shrink film around packages, typically using a fan-driven system to provide even heat distribution across the entire package. They can be used with PVC, POF, and Polyolefin shrink films.
Steam Shrink Tunnel

Steam shrink tunnels use steam heat to shrink film around packages. The steam is generated by an internal boiler or external steam generator and delivered through heated pipes that evenly distribute the heat over the product’s surface area. This type of shrink tunnel is ideal for shrink wrapping shrink film with shrink ratios higher than 40%.
Infrared Shrink Tunnel

Infrared shrink tunnels use infrared energy to shrink film around packages. These shrink tunnels are well suited for lightweight or thin products, as the heat is easily absorbed and maximizes the shrink ratio of the shrink film. They are also ideal for shrink wrapping PVC, POF, and Polyolefin shrink films.
High-Temperature Shrink Tunnel

High temperature shrink tunnels use very high temperatures to shrink heavy gauge shrink films around products quickly. These machines can be combined with various shrink films, including PVC, POF, and Polyolefin. They are often used when a high degree of product protection is required.
b) Heat Tunnels
Continuous Heat Tunnel Machine
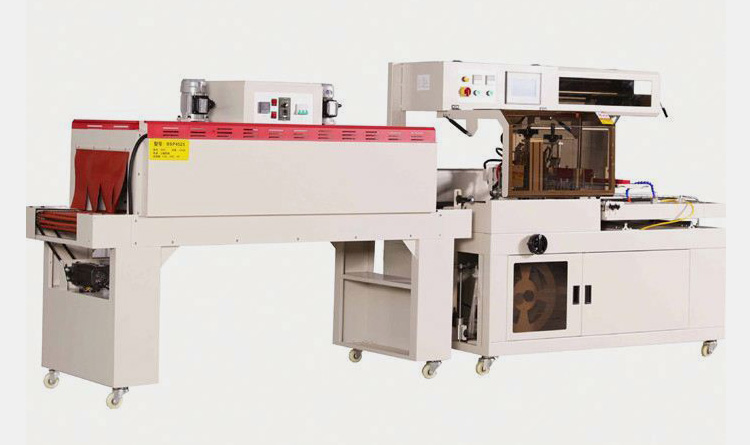

This heat tunnel machine is designed to continuously heat product batches by passing them through an enclosed chamber. It is usually equipped with adjustable temperature settings and product speed controls.
Batch Heat Tunnel Machine

A batch heat tunnel machine is a static unit that heats a single batch at once in a stationary heating chamber. It can be adjusted for variable temperatures but only allows for variable speeds or continuous product processing like the constant heat tunnel.
Impulse Heat Sealer
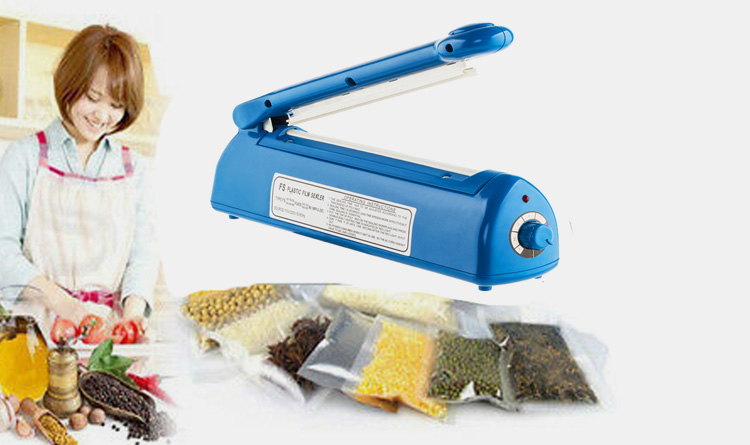

An impulse heat sealer is a heat tunnel machine that only applies heat to packaging material at specific intervals. It is a faster and more efficient heat sealing method than other heat tunnel machines, requiring less energy and time.
Hot Melt Heat Tunnel

A hot melt heat tunnel utilizes hot glue to seal products into their packages and maintain the box’s integrity until its contents are ready to be used. This heat tunnel can also be used for labeling, providing a tamper-proof solution for consumers.
10.Which Type Of Machine Is Right For You-Shrink Tunnel Or Heat Tunnel?
The following key factors should be considered before deciding on which machine you should purchase depending with your needs.
Cost

Shrink tunnels tend to be more expensive than heat tunnels. So, it is important to factor in both the initial purchase price and long term running costs before buying either type of machine. cost
Shrink
Speed
Heat tunnels typically move faster than shrink tunnels as heat is more efficient and quicker at shrinking the film of a product.
Versatility
Heat tunnels are more versatile as they can shrink different types of shrink films, whereas shrink tunnels are designed for one type of film.
Power
Shrink tunnels use much more power than heat tunnels, so energy costs should be taken into consideration when making a purchase decision.
Size of Product

Heat tunnels may not be suitable for large products, while shrink tunnels are better suited for packaging large items.
Size of Machine
Heat tunnels are typically smaller than shrink tunnels, so they take up less space in production lines and do not require as much room for installation. Shrink tunnels, however, are more extensive and need more space for operation.
Conclusion
Investing in the right shrink-wrapping equipment is key to ensuring your products look great, stay secure, and remain shelf-ready. As you can see, heat tunnels and shrink tunnels both have unique purposes. Which one you need will depend on your product, desired outcome, and budget. If you are still unsure which type of machine is right for your needs, Don’t hesitate to reach out to Allpack. We will be happy to help you select the perfect equipment for your business and provide any additional information you may need.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide

Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
