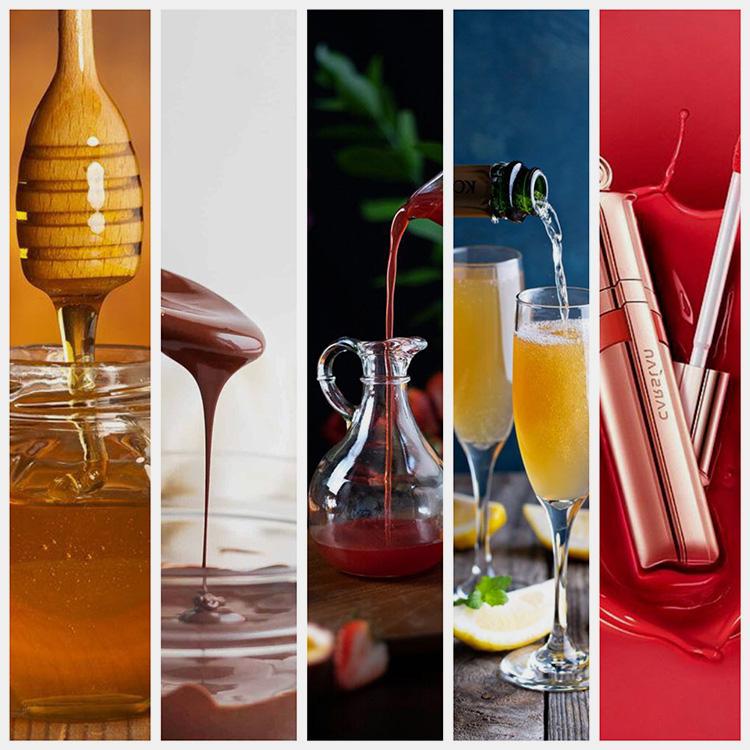
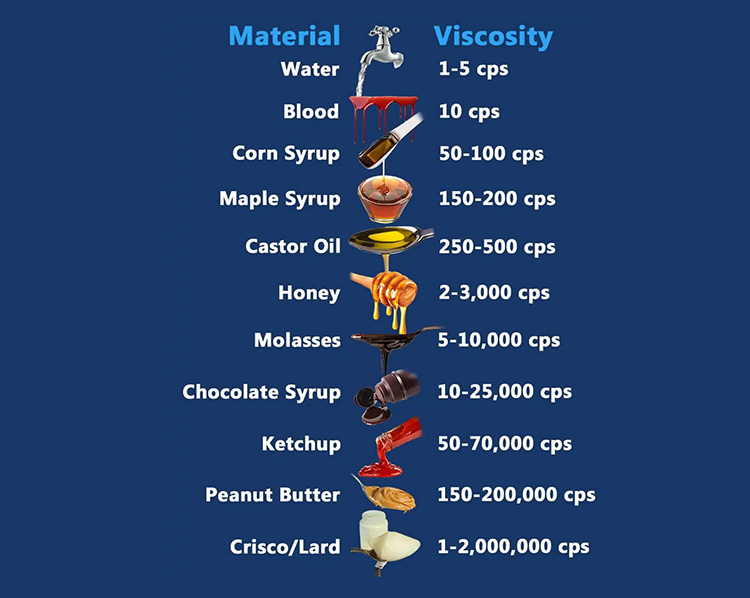
Viscosity Chart
Have you ever noticed the non-stop contact with liquids? From morning toothbrush to evening coffee we are utilizing immeasurable liquids. Do you know how these liquids are different from one another? Of course, on the basis of their viscosity! It is essential to have knowledge of the nature of material we use.
However, in most cases it becomes obligatory to know especially when it comes to industrial processing where different formulations depends upon the viscosity of material used, such as pharmaceutical industry, chemical industry, food industry and similar other areas. Viscosity chart can greatly help in this way. Here, we have provided you with a precise essay that will clearly display the purpose of viscosity chart and its significance in different sectors. Stay tuned and make sure to read it thoroughly!
1.What Is Meant By Viscosity?
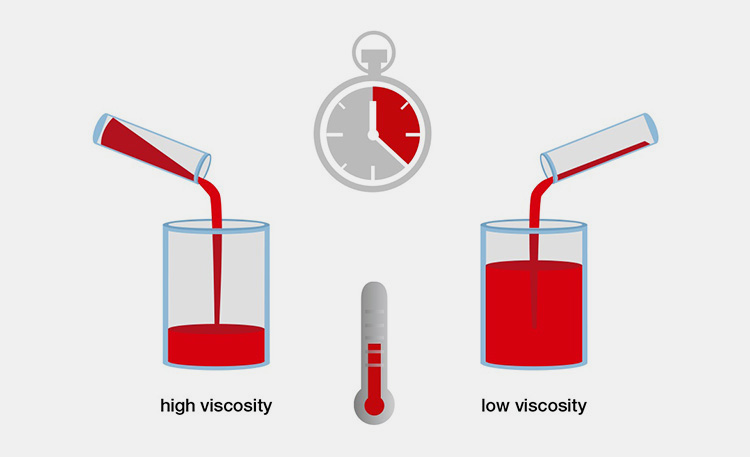
The term "viscosity" refers to the property of any fluid that how much it is thick and sticky. Such materials show resistance in their flow which is caused by the internal friction. This resistance in flow of material is the result of molecular makeup of the substance taken, and at the same time, it will indicate the degree of viscosity a material possess. For instance, the quicker the flow of liquid the lower will be viscosity, in opposition, the low speed of material flow means it is highly viscous.
Viscosity is the key indicator for determining the rate on which material will flow. It is also considered as an important quantity while checking the quality control of different substances. Therefore, it has broad spectrum of application for various formulations in diverse sectors among which pharmacy is the prominent one.
2.How Would You Define Viscosity Chart?
| Type of Liquid | Centipoise (cp) | Centistokes (cSt) | Saybolt Second Universal (SSU) |
| Water | 1 | 1 | 31 |
| Milk | 3 | 4 | 40 |
| Blood or Kerosene | 10 | ||
| No.4 Fuel Oil | 12.6 | 15.7 | 80 |
| Anti-Freeze or Ethylene Glycol | 15 | ||
| Cream | 20 | 20.6 | 100 |
| Vegetable Oil | 40 | 43.2 | 200 |
| SAE10 Oil | 88 | 110 | 500 |
| Tomato Juice | 180 | 220 | 1000 |
| SAE 30 | 352 | 440 | 2000 |
| Glycerin | 800 | 1100 | 5000 |
| Honey | 1500 | 2200 | 10000 |
| Glue | 3000 | 4500 | 20000 |
| Mayonnaise | 5000 | 6250 | 28000 |
| Molasses | 8640 | 10800 | 50 ,000 |
| Sour Cream | 15000 | 19000 | 86 ,000 |
| SAE 70 Oil | 17640 | 19600 | 90000 |
| Window Putty | 100,000 |
Viscosity chart can be defined as data sheet or table that display the viscosity of materials with respect to various measuring factors such as temperature, specific gravity and viscosity etc. It is beneficial for knowing the viscosities of various fluids under different temperatures.
The types of viscosity chart may vary on the basis of certain elements as line some charts contain information only about viscosity, while as, others may show the gravity, type of viscosity and conversion factors etc.
3.What Is The Importance Of Viscosity Chart?
Viscosity chart has an important role in determining the successful formulations in small to large scale industries. With the help of this chart, it is possible for researchers to make new prescriptions and avoid repetition of measuring same fluids.
Viscosity chart has gained special importance in the field of pharmacy where the testing of viscosity is considered as a part of quality control. In addition, the viscosity of syrups, syringes, vaccines and other drugs proved beneficial in determining their dissolution and essence time in body.
4.Where Do We Need Viscosity Chart?
Viscosity chart is needed where there is any sort of liquid formulation or emulsion. The following details will further reveal about the areas where it is required:
Pharmaceutical Processing
It must be noted that all the drugs including tablets, capsules, syrups and injections are made either from emulsion or mixture of different ingredients. Here, viscosity is the prime concern of pharmacies to look for, to reach the standard quality requirements essential for drug manufacturing.
Food Processing
Food processing is another field where you would find the essence of viscosity in making baking products, confectioneries, oil and dairy products. Keeping in mind the viscosity of products in reference to temperature, they can be well utilized for various purposes.
Industrial Processing
Large industries including metal processing industry, paint manufacturing company, chemical industry and lubrication oil industry can also take advantage of the viscosity chart in their respective spheres.
Cosmetic Processing
In the formulation of cosmetics such as shampoo, lotion, cleansing products and makeup items, it is a matter of fact that help of viscosity chart is taken to gain the desired level of viscosity.
5.Which Details Does A Viscosity Chart Display?
A viscosity chart shows number of details about material and their viscosities. Following points are well explained to enable you in understanding the information:
Reference Material: In the beginning of viscosity chart, a reference material is mentioned. For example, in viscosity chart water is taken as a reference material with respect of whom all other fluids are measured.
Product name: Now comes the fluids name, which are mentioned in a sequential column, for example, syrup, juice and batter etc.
Fixed Gravity: It is also known as relative density which shows the density of a material with that of reference item. In addition, the reference material for all fluids is water and for all gases is air.
Absolute Viscosity: Absolute viscosity is the liquid's internal opposition caused by shearing pressure. It may vary due to change in temperature and rate of deformation.
Temperature: Temperature is another element mentioned in the viscosity chart. Absolute viscosity of each fluid is recorded under particular temperature which is written with them.
Type of Fluid: There are two types of fluids; newtonian fluids and non-newtonian fluids. The former cannot be affected by shearing, while as later can change the viscosity due to applied force. Hence, these fluids are symbolized with relevant types for easy recognition.
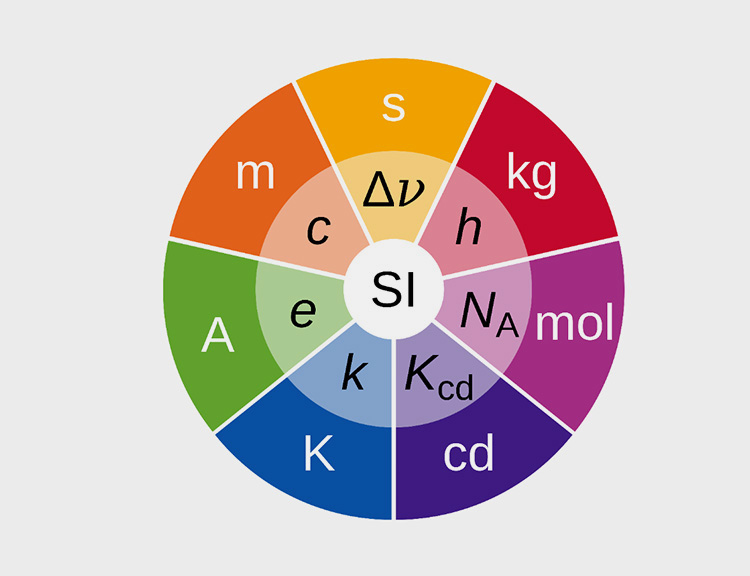
6.What Are The Units Of Viscosity?
Following are the major units of viscosity based on SI unit and SCG units:
Poise and Centipoise
Poise is the SCG unit of dynamic viscosity. In most cases it is also known as centipoise, however, there is difference between both on part of the degree of fluid's viscosity. For instance, 1 poise (P) is equal to 100 centipoise (cP).
Pascal Second
Pascal second is another SI unit of viscosity for measuring smaller viscosity. It is abbreviated as Pa.s and based on the Newtown's second per meter square. It is also known as poiseuille PI which is qual to 10 poise.
Stokes and Centistokes
Stokes is the standard SCG unit for kinematic viscosity. It is often reported as centistokes which is equal to 0.01 stokes.
Saybolt Seconds Universal
Another unit of viscosity is saybolt seconds universal which is used for measuring 60 milliliters of fluid by passing it through the orifice of Saybolt universal viscometer at the fixed temperature of 100°F. In case, the viscosity of fluid is high, then Saybolt Seconds Furol test is done at the temperature of 120°F.
Degree Engler
Degree Engler is the viscosity measurement ratio where 200mL of viscous fluid is compared with water by passing both from same orifice.
7.Which Tools Are Used For Measuring Viscosity?
Modern technology has introduced new and standard quality tools for measuring viscosity. They are as follows:
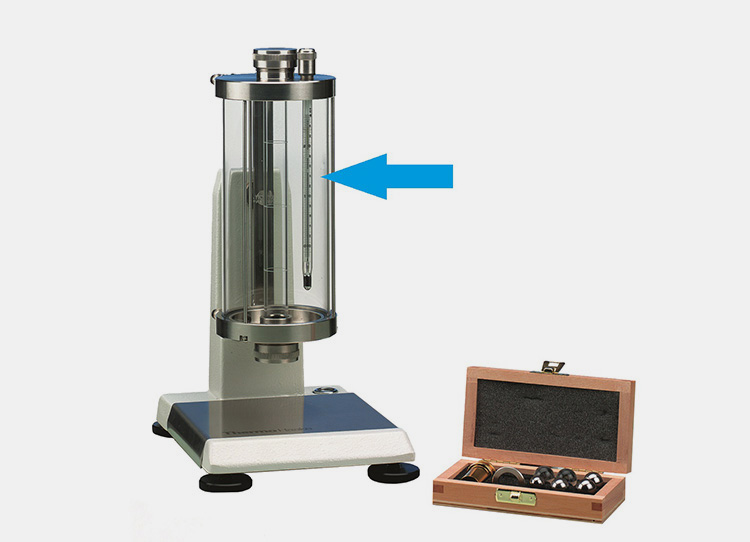
Falling Ball Viscometer
Falling ball viscometer is an excellent instrument used for measuring newtonian fluids by putting ball in the tube filled with fluid whose viscosity has to be determined. The speed of ball falling will show the level of viscosity possessed by the fluid.
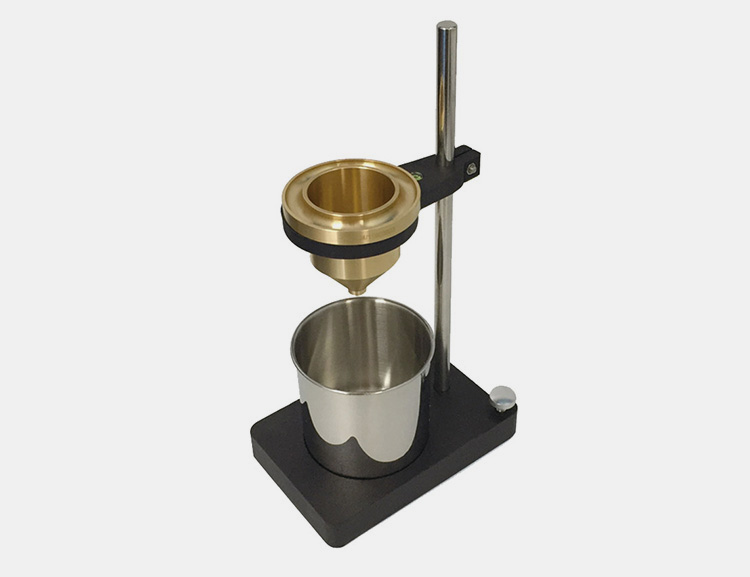
Viscosity Cup
Viscosity cup is an instrument utilized for measuring the viscosity of non-newtonian fluids such as paints, inks and garnishes etc. It is composed of a precise structure in form of a stand holding a cup on the top and an empty container fixed right under the cup. The measurement is done by recording time when fluid laying inside the viscosity cup start draining into the container.
Consistometers
Consistometers are small metal gadgets with numericals imprinted over their bases. They are highly suitable for exploring the viscosity of diverse fluids such as sauces, jam garnishes, paints and cosmetics etc. Due to the low maintenance, convenient usability and flexibility, most of the industries prefer using consistometers for knowing viscosity of fluids.
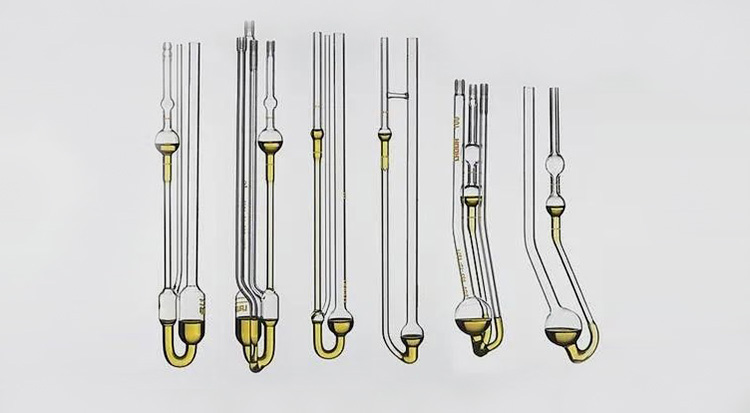
Glass Capillary Viscometers
As the name indicates, glass capillary viscometers are small tubes made up of transparent glass. They are highly effective for ascertaining kinematic viscosity. There are broad range of glass capillary viscometers available in market among which prominent are Ubbelhode, Zeitfuchs and Cannon-Fenske viscometers.
Tuning fork Vibration Viscometers
This instrument is very effective for attaining high level of measurement accuracy with the help of immersing two sensing rods in a container filled with fluid. The constant electric supply produce vibration in rods who eventually detect the viscosity ratio of fluids.
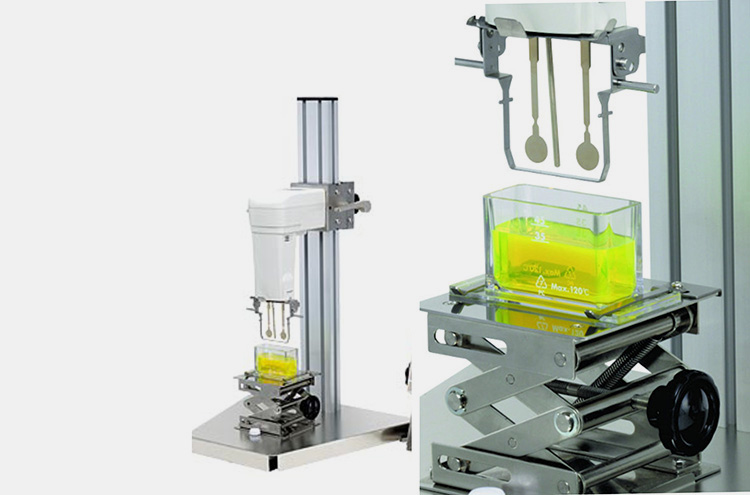
Rotational Viscometers
Rotational viscometer is highly versatile apparatus utilized for measuring highly viscous fluids having millions of centipoises. It carries out the function of measuring viscosity by moving spindle attached to the viscometer. This spindle is submerged into the liquid substance whose rotary motion calculate the viscosity with the help of torque.
8.Highlight The Factors Which Can Influence The Viscosity?
While discussing viscosity chart we cannot ignore the factors which influence the viscosity of fluids. Here, you will know them one by one:
Nature of Fluid
One of the prominent factor which can affect the viscosity of any substance is its own nature. For instance, the viscosity of newtonian fluids such as water and honey will remain same than those belong to non-newtonian category including ketchup, milk and custard etc.
Temperature
Temperature is another cause for influencing viscosity, as we know, that high temperature can increase the speed of molecules resulting in reducing the thickness of fluids like honey and cream. This consequently enhance the flow of material.
Pressure
Pressure is not so effective element for impacting viscosity, however, in some cases it may increase the viscosity because excessive compression lessen the movement of molecules as a result the increase in friction reduce material flow.
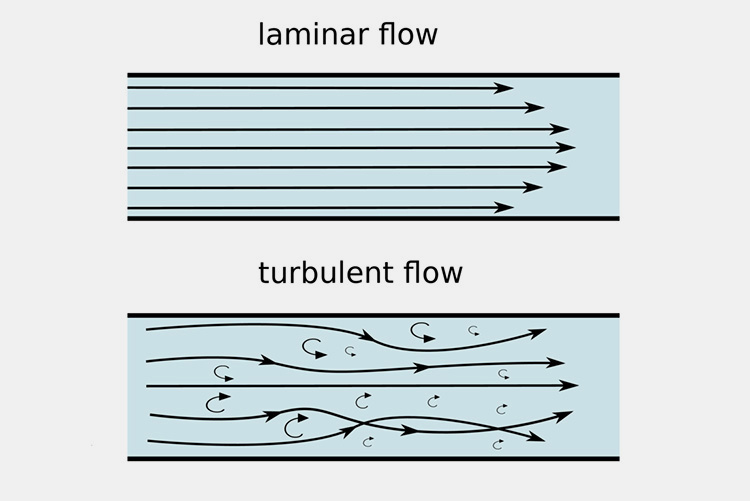
Flow Conditions
Flow condition is among other factors that dominate viscosity. In addition, the irregular turbulent flow cause change in viscosity. Contrary to that, material in state of laminar flow remains constant.
9.What Are The Different Categories Of Viscosity?
There are two main categories of viscosity which are expressed under the following headings:
Dynamic Viscosity
Dynamic viscosity is also known as absolute viscosity or coefficient of viscosity which is derived from Newton's law of viscosity. It refers to the measurement of a liquid's flow when external shearing or force is applied.
Kinematic Viscosity
Kinematic viscosity is a quantity which shows the substance internal opposition to move or flow under gravitational force. The kinematic viscosity of any liquid can be found by dividing the absolute viscosity over density under controlled temperature.
10.Differentiate Between Viscosity And Density?
Both viscosity and density are the features of fluids, however, they are different in several ways which can be understood by reading the points explained below:
| No | Factors | Viscosity | Density |
| 1 | Definition | Viscosity is a tool for measuring the thickness of any liquid substance | Density is the quality of ascertaining the space present between particles inside liquid |
| 2 | Role | It is crucial for knowing the factors responsible for liquids flow, thus they can be controlled | Density is essential for determining the possibility of particles' floating and sinking when laid inside fluids |
| 3 | Application | Viscosity can be only applied to fluid substances | While as, density is applicable to liquid, solid and gas |
| 4 | SI Unit | The SI unit of viscosity is poiseiulle (PI) | the SI unit of density is kg/m³ |
| 5 | Example | Water 0.01, honey 0.421 and Oil 0.1 | Water 997, Wax 960 and Air 1.23 |
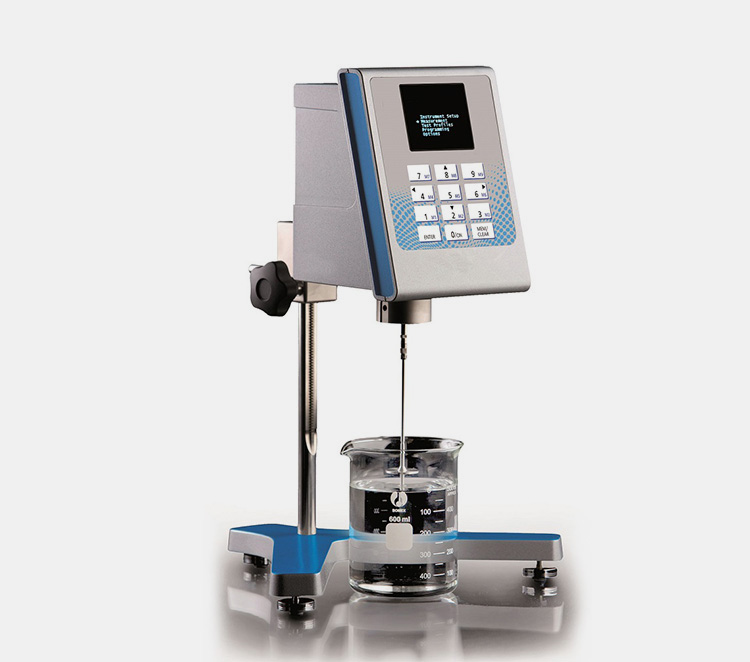
| 6 | Pictures | 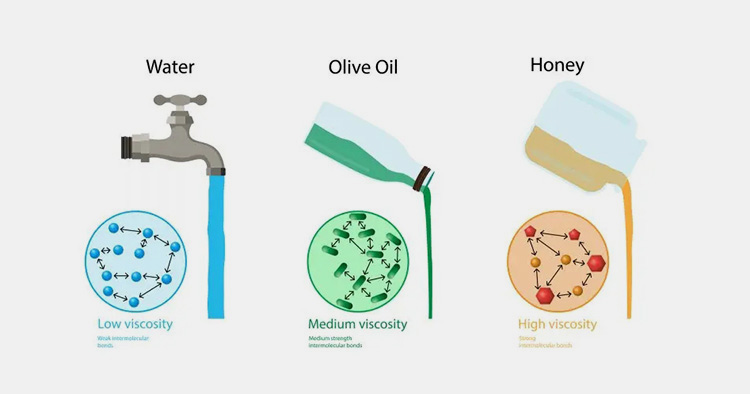 |
 |
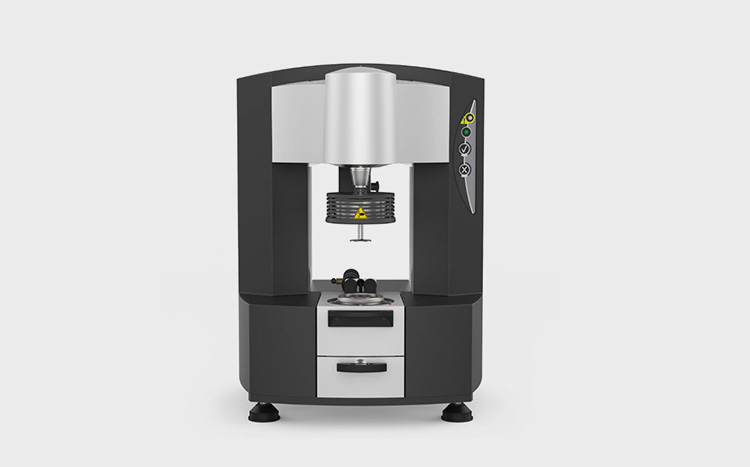
11.Viscometer Vs Rheometer- Elaborate?
Viscometer and rheometer are innovative applications brought for measuring the viscosities of diverse fluids. Both are excellently accomplishing their tasks in respective spheres which can be analyzed in the following table:
| No | Factors | Viscometer | Rheometer |
| 1 | Definition | An instrument employed to gauge the viscosity of a fluid is called viscometer | Rheometer is an apparatus utilized for scaling the way in which liquids flow against applied force |
| 2 | Benefits | It helps in assessing flow properties and toughness of fluids | It is capable of processing small sample size and variate the temperature required |
| 3 | Categories | It can be divided into four categories namely capillary tube viscometer, falling ball viscometer, rotational viscometer and falling piston viscometer | Rheometer has two types including controlled-strain and controlled-stress rheometer. |
| 4 | Application | Newtonian liquids can be measured while using viscometer | In contrast, rheometer is used for measuring non-newtonian fluids |
| 5 | Example | Water, honey and alcohol etc. | Shampoo, paint and grease etc. |
| 6 | Pictures |  |
 |
Conclusion
Whether is it medical field, research laboratories or business firms, the processing of fluids cannot be overlooked. In the same way, it is also necessary to take care of the responsible formulations. For this, the help of viscosity chart can be taken to avoid mistakes and carry on smooth processing. If you found this viscosity chart an informative piece of writing, you can get further relevant knowledge by visiting our site or contacting us through our link for asking any query.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide