Quality Control VS Quality Assurance
Do you struggle to produce quality products? Do you have difficulty identifying the defects in your product? Are you having trouble differentiating quality control and quality assurance? What comes first-quality control or quality assurance? You are not the only person having these queries.
To achieve the highest quality standards, both quality control and quality assurance have an integral role. These quality approaches have significance in the realm of quality processing. Neither is optional and one cannot achieve quality control without quality assurance and vice versa. A healthy balance of both the activities assures effectiveness of the quality management system.
In this blog post, we will probe deep into the complexities of quality control and quality assurance and discuss the key differences between these approaches. Let’s have a read to know all the answers regarding this pivotal quality management tool.
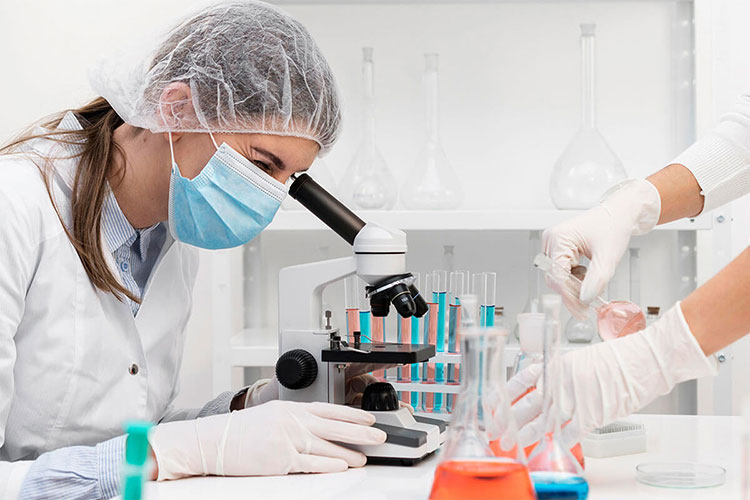
1.What is quality control?
Quality Control- Picture Courtesy: Innopharma Technical Services
It is a methodical approach employed in various industrial settings to distribute standardized goods or services. It incorporates systematic procedures and measures to ensure that the product or service being created fulfills a business’s preset threshold for quality.
In the quality control process, testing and inspection are carried out to ensure the product satisfies the demand for quality. It can be considered a fine-tuning inspector, responsible for thorough checking of every batch and making sure that goods meet precise requirements.
Quality control also identifies the faults in the product and fixes these issues before products are delivered to the market. It ensures that no substandard goods get to the buyer. Moreover, it verifies that rules are followed during product manufacturing.
This quality control checking is performed by going through a comprehensive checklist, which directs product tests, such as design, features, dimensions, color, texture, appearance, working, barcodes, information labeling, and packing.
2.What is quality assurance?
Quality Assurance- Picture Courtesy: Source of Asia
Quality control is an orderly approach used by different manufacturing sectors to ensure that preset quality constraints are sustained and fulfilled. Rather than, inspecting faults in the final product, its objective is to boost the accuracy and precision of the manufacturing and designing process to prevent weaknesses in the product.
It ensures that goods are perfect from the beginning. It is a broad-spectrum activity employed throughout the whole production operation to assure goods are created “right first time”.
It shapes the entire manufacturing process and includes rules, techniques, and processes founded and upheld by the business to guarantee the quality of its goods and services is constantly perfect and conforming to organizational and global regulations. It aims to perfect the development process.
3.Quality Control VS Quality Assurance: What do you know about history?
History- Picture Courtesy: ISO TRACKING
Whether utilizing a tool, product or performing any experiment; its quality defines its excellence. So the concept of quality related to studies and performance has been hooked to industrial settings since early times. When quality control and quality assurance came into play the roles are described below:
Quality Control- 1920s
In the 1920th, quality control was implemented in industrial practices that era was known as the Industrial Revolution and better methodologies were developed to ensure better quality. The primary aim was to meet the correct and precise criteria for the final product to produce quality and consistent batches.
Quality Assurance- 1950s
To ensure the product’s quality, in 1950s the systematic establishment of procedures and relevant documentation was highlighted and focused included in quality assurance. Quality assurance meant to verify the primary functions of the industrial procedures and framework assuring that they’re up to the mark.
4.Quality Control VS Quality Assurance: What is primary focus?
Primary focus
Quality Control (QC)
Quality control is usually considered a reactive process and is implemented in response to a developed product or service. It reacts by detecting and fine-tuning remaining errors or flaws in the final product. The quality control team notifies the development team to make modifications to the product because it has defects.
Quality control aims to check and detect weaknesses and imperfections in the end product before it is distributed in the market. Using quality control activities, inspectors discover and give precedence to remaining flaws.
Quality Assurance (QA)
On the other hand, quality assurance is a proactive activity. It incorporates vital guardrails to keep the manufacturing process on track and ensure the product is manufactured under pre-defined quality rules.
Organizations constantly establish and refine their quality assurance procedures to enhance the quality of the manufacturing process. It builds the foundation to decrease product flaws from the start and impacts the working of developers and operators.
The objective of quality assurance is to prevent errors or bugs from being incorporated into the product. It guarantees product quality by ensuring the production process complies with established standards and protocols.
5.Quality Control VS Quality Assurance: What skills do you need?
Skills- Picture Courtesy: Catalyst Life Science
For balancing quality management, different key skills are required for quality control and quality assurance. See below to learn about technical skills.
Quality Control (QC)
To be a quality control analyst, you must know technical skills like operating various instruments, data preparations, and interpretation. It includes testing on raw materials, testing the prepared products, and laboratory assays. The major instruments included are HPLC, spectrometry, microscopy, pH meter, density, etc. to assess the minor deviation from the desirable goals and record the data.
Quality Assurance (QA)
In quality assurance, you must know the preparation and running of the audit relying on international regulatory guidelines. For example, ISO, FDA, cGMP, etc. hence ensuring that your system is adhering to the right path. The skills required are extensive knowledge of quality assurance measurements, running computer software, quality management, communications, preparation and maintaining the documentation and SOPs of industrial setups.
6.Quality Control VS Quality Assurance: Where it can work?
Operational sectors- Picture Courtesy: News Medical
Every manufacturing industry that is more concerned with its quality and assurance discipline is associated with quality control and quality assurance practices. For example:
Quality Control (QC)
In the manufacturing sector where you need to ensure that the formulated medicines or products to confirm that they are without any defects or errors before it is delivered for marketing. The quality control testing is considered a significant tool for its measurement and documentation.
It can work with the manufacturing of medicines, cosmetics, food, beverages, nutraceuticals, herbal, veterinary, etc. sectors to monitor and ensure the presence of defects as well as ensure a uniform delivery of the produced batches.
Quality Assurance (QA)
Quality assurance is never ignored when there’s quality control. It is mainly implemented in order to inspect the sustainable methodologies of quality control departments. Therefore, quality assurance is required in developing and monitoring the processing implementation in manufacturing, packaging, laboratories, healthcare, food, medicines, software, and various related industries to improve the user satisfaction.
7.Quality Control VS Quality Assurance: How to get started?
Method Onset
Quality Control (QC)
Quality control only starts when there is a manufactured good or developed service to inspect and test. It can take place before and after the product's first release, usually at the last stages of manufacturing. It happens within a shorter time frame.
Quality Assurance (QA)
In contrast, quality assurance processes transpire during the entire fabrication process, from preparation to implementation. It is a continuous process rather than a single stage, taking place at every stage of production to authenticate and enforce the product quality. It starts before production and is consistently implemented while the product is being manufactured.
8.Quality Control VS Quality Assurance: How it can work?
Workflow
Quality Control (QC)
One of the main distinguishers between quality control and quality assurance is their core on execution. Quality control typically concentrates on the service or commodity being produced. It inspects and fixes errors or problems that persist after development. It assesses the result of the making process.
Quality control principally involves testing and inspecting teams of the organization. Generally, a smaller team consisting of individuals, who can carry out tests is engaged in quality control. It has dedicated personnel, responsible for final product inspection.
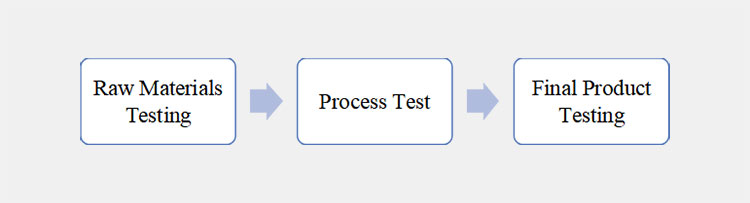
There are the following working phases involved in quality control processing.
Working phases of QC
Raw Materials Testing
Before manufacturing of any drug, you should know that the raw ingredients used are compliant to the quality standards and don’t possess any unwanted microbial or foreign contaminants. For that basic tests are performed by QC.
Process Test
Once you get that the raw materials are the best fit for manufacturing the product, the next step is process testing which involves testing in processed product to ensure the drug to be formed will be compliant to all essential specifications.
Final Product Testing
The finished product is now again sent to quality control test to ensure that it meets all elementary standards set for your product. If they are corrected, so the batch is considered as passed and sent to the final procedures. Quality control has the right to reject the batch if it doesn’t meet the criteria required for drug final stages so it can’t be released for sale.
Quality Assurance (QA)
Conversely, the focus of quality assurance lies on the processes and practices to uphold the quality standard during development and design. It is associated with the creation and upholding of methodical designing processes to guarantee constant quality in the product.
However, quality assurance is primarily an organization-wide activity, it encompasses every member of the company from the marketing to the development side, from planning to the design team. It involves top executives as well as the frontline workforce. It is cross-functional, involving all the teams and departments of the company.
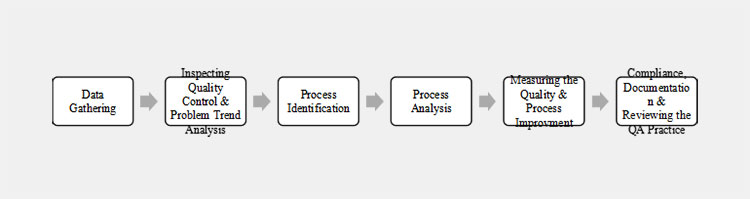
There are the following basic phases involved with QA practices
Phases of QA practices
Data Gathering
The primary working steps of QA is to establish quality goals and specified standards based on user’s needs under best practices and gather the data.
Inspecting Quality Control & Problem Trend Analysis
QA receives the data from QC to identify the pattern of defects and underlying issues related to the deviation and inspect the quality of the performance.
Process Identification
This is the main step where QA establishes the quality procedure related to all activities and instrumentation used in the industry and specifies the policies for production activities. Also, the mapping out the steps involved in manufacturing and production setups involved in raw materials, bulk, and finished products with assessment and identification closely.
Process Analysis
To monitor and assess the procedures followed in quality control for its entire work cycle and implementation of tools such as QMS or quality control management for tracing the services.
This is the prime task of QA to conduct the training and create SOPs for personnel to ensure the best possible services.
Measuring the Quality & Process Improvement
Regular consideration of quality performance with the help of key performance indicators or KPIs. Conduct and identification of those risk issues that could affect the operational procedures and quality of the product. Also, it develops the corrective and preventive actions or CAPA to minimize the non-conformities.
Compliance, Documentation & Reviewing the QA Practice
Conduct and plan the internal audit and assess the quality system via inspecting the reviews. This is the responsibility of quality assurance to maintain the documentation, review files, updating or regulate the changes via inspecting the procedures and audit.
9.Quality Control VS Quality Assurance: How to prepare documentation?
Documentation
For the preparation of the documents, the quality control and quality assurance testing are done on the following parameters, such as, tests, assessments of raw materials, finished products, and instruments. For example:
Quality Control (QC)
When performing quality control testing, you need to prepare the check sheets and manage and filling the control chart such as histogram, Pareto chart, stratification, and scattering diagrams for estimating the results and deviation.
Also, SOPs, test reports with deviation logs etc. are the documentation prepared when you’re performing the QC test. Quality control includes procedures to complete the testing of the finished products, such as product sampling, beta or canary testing, defect inspection, and amendment.
Quality Assurance (QA)
This is relatively a broad subject that encompasses with various management systems, for instance, sourcing, planning, documentation, skill enhancement, product certification, audits, supply chain management, design inspection, and ongoing improvements.
It also consists of the creation and implementation of Standard Operating Procedures or SOPs, pieces of training, preparation of audit reports, monitoring checklists of the quality control unit, a compilation of records, and assessment of quality documentation that must specified with international regulatory guidelines including inspecting quality control, risk management, manuals.
10.Quality Control VS Quality Assurance: What is the time frame?
Time Impact
Quality control has an instant effect but is a more time-consuming and lengthy process as it involves testing the batches in its entire process life to ensure the product is free of faults before it reaches the hands of consumers.
Quality Assurance (QA) involves planning, processing, documentation and inspection to minimize the errors or downtime of the operational flow therefore, the time frame seems to be less than QC. Thus, it has a long-term effect on the entire manufacturing process and organization, as it is involved in the continuous improvement of product quality standards.
11.What are the Certification of Quality Control and Quality Assurance?
Certifications of quality control and quality assurance- Picture Courtesy: NACPT Pharma College
There are several lists of certifications associated with QC and QA related to its specific roles, for example:
American Society for Quality (ASQ) certification
For quality, the ASQ offers certain certificates and training that are required by industries in quality management. For example:
- Certificate of Quality Process Analyst or CQPA: this is the special certificate that supports the quality of workers and operational protocols.
- Food Safety and Quality Auditor or CFSQA: it offers auditing of food, inspecting and ensuring the safety mechanism.
- Manager of Quality Organization Excellence or CMQ/OE: it is the certificate ensuring the strategy planning, processing, and leadership.
- Certificate of Quality Engineering: it is required to ensure that the workflow or control system is compliant with regulatory requirements.
- Certificate of Calibration Technician or CCT: is required to ensure the equipment is maintained, calibrated, and repaired.
- Software Quality Engineer or CSQE: it is mainly emphasized with software working principles and operational practices with assuring quality throughout the lifecycle of processing by the help of testing and verifications.
12.What Comes First: Quality Control or Quality Assurance?
Quality Assurance Onset
Quality assurance usually comes before quality control in the quality management process. The former is comprised of planning, designing, and incorporating mechanisms to satisfy quality standards. Quality assurance usually takes place from the beginning of manufacturing of the product, whereas, quality control is implemented after the development of the product.
Nevertheless, quality assurance processes happen during the complete product or service lifecycle from pre-planning and manufacturing through distribution and post-retailing. Quality control executes periodic procedures in the lifespan. It occurs at certain points in the product development cycle to validate product quality.
13.Is Quality Control Higher Than Quality Assurance?
Quality Control VS Quality Assurance
Both quality control and quality assurance work under the broader umbrella of quality management systems. The latter unifies quality control and quality assurance for quality management. However, quality control is not higher or more important than quality assurance, and vice versa
Quality assurance covers every facet of maintaining and improving quality, comprising the execution of quality control procedures. Although quality control can be viewed as a component of the general quality assurance framework, quality control is a separate activity with a specific goal and outcome that is solely focused on inspecting faults in the end product instead of improving process quality.
14.Can A Business Have Quality Control Without Quality Assurance or Vice Versa?
Incorporation of Quality Control
No, it is not feasible to have quality control without quality assurance or vice versa because both are essential in maintaining quality standards. Integration of both activities is vital in having a balanced quality management system.
Both these processes complement each other and are reliant on each other to be effective. Without effectual quality assurance, quality control will be flooded with errors and flaws, several of which will remain uncorrected and go into the hands of customers.
Conversely, without thorough quality control, the company cannot test the work efficiency of its latest product and determine if it is well-received by clients.
15.The Key Differences Chart
| Points | Quality Control | Quality Assurance |
| History | Established in the industrial revolution in the 1920s. | Implemented in the 1950s to maintain documentation and policies. |
| Primary Focus | Reactive as well as detect flaws and errors. | This is proactive ensuring the process goes without errors. |
| Skills | Testing, instrumentation, analysis of data, interpretation. Such as HPLC, spectrometry, density testing etc. | Maintaining documentation, software, and communication. |
| Operational Sectors | Pharmaceuticals, foods, nutraceuticals, chemicals, R&D etc. | Broad applications in healthcare, manufacturing, packaging, clinical etc. |
| Onset | From raw materials to its finished product. | Begins with the initial steps of production till its marketing. |
| Work steps | Inspection, testing, and final records. | The maintenance, consistency and improvement of the workflow. |
| Documentation | Spreadsheets, charts, log and bar diagrams etc. | Preparation of SOPs, audit record, reporting, etc. |
| Time Frame | Lengthy process but immediate results. | Continuous processing and have a longer impact. |
Conclusion
In simple terms, quality control and quality assurance, are fundamental in delivering the highest-quality good or service to the customer. They both achieve quality goals, ultimately helping to deliver business success. Quality assurance establishes the basis for quality and prevents things from straying the quality standard path while quality control checks that the foundation has been constructed rightly and measures the efficiency of the product. The former improves the product, whereas, the latter fixes the issues in the final product. Together, they strive to consistently manufacture top-quality products. Still confused about these activities, then contact Allpack customer care to get a quick response to your queries.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide