How To Solve The Phenomenon Of Agglomeration Of Particles In The Dryer?
Are you tired of severe agglomeration problems during the drying step? Does your product degrade during drying?
Unintended agglomeration in the drying process could lead to a host of issues and it is challenging to address this problem. It is essential to control the particle size of bulk solids, as that contributes to the success of processes and products. This facilitates better processing and better outcomes, finally resulting in high-quality end products.
It is a question in every manufacturer’s mind, “how to solve the phenomenon of agglomeration of particles in the dryer”. So, this is the perfect blog to get the answer to this question. By reading this blog post, you will be able to take the necessary steps to mitigate this problem and attain the desired output. Let’s explore this topic.
1.What is the Agglomeration of Particles?
Agglomeration of Particles
Agglomeration of particles is a natural phenomenon in which particles of solid stick with each other. It is a particle size enlargement process that combines finer particles into bigger cohesive units. With agglomeration, the newer entity is obtained with a larger particle size.
This process is utilized to enhance the properties of bulk solids, such as reduced dust generation, improved flowability, minimal segregation, and decreased sticking. Moreover, it is easier to handle, store, and transport granular particles than fine materials.
However, unwanted agglomeration of particles can result in uncontrolled product accumulation, caking, bridging, and clumping.
2.What are the Causes of Particle Agglomeration in the Dryer?
Agglomeration of particles can happen due to a variety of reasons in the drying process and having a basic understanding is imperative in mitigating this issue. Let’s discuss different reasons for particle agglomeration one by one:
High Ambient Moisture

High Ambient Moisture and Agglomeration- Picture Courtesy: Feeco International
If there is too much humidity in the surroundings of the dryer, it impedes the drying efficiency of granular particles, causes high moisture accumulation on surfaces, and boosts the rate of agglomeration. Also, if there are different temperature zones in some drying units, then water content condenses on the materials during the cooling stage, resulting in a high rate of particle clustering.
Particle Stickiness

Particle Stickiness- Picture Courtesy: Feeco International
Another reason for agglomeration in the dryer machine is the high moisture presence on the exterior of particles. Uneven evaporation of moisture from the surface causes some regions of the material surface to retain stickiness, leading to the cohesivity of particles. Moreover, due to the high heat in the dryer, the materials soften and stick with each other before their complete drying.
Particle Size Distribution
Particle Size Distribution- Picture Courtesy: Organic Plant Boost
Fine particles have more tendency to stick with each other due to their higher surface area-to-volume ratio. This increases the area for binding of molecules and promotes surface forces. Besides this, smaller particles stick to bigger particles more quickly.
Furthermore, there is a high chance of massing in the dryer when particle size distribution is non-uniform. The irregularly contoured and sized particles have more contact points, increasing the chances of particle bonding.
Insufficient Airflow
Insufficient Airflow- Picture Courtesy: Inora Pharmaceutical Machinery Co., Ltd.
Owing to non-uniform or inadequate airflow in the drying vessel, the materials have uneven drying rates, consequently, some particles retain moisture level, while others dry quickly. These moist particles tend to adhere together, resulting in agglomeration.
Particles remain separated during the drying phase because of low airflow. This increases their chances of contact and cohesivity.
Inadequate Drying Time
Inadequate Drying Time- Picture Courtesy: Gansons
Rapid drying of the surface of particles may be a reason for agglomeration in the drying chamber. For example, the internal core of particles stays wet, while the exterior of particles is swiftly dried. This differential drying results in stickiness and agglomeration of particles.
Also, if the drying time is short or the drying cycle is prematurely discontinued, then residual moistures in the materials foster agglomeration during the post-drying stage.
Presence of Binders
Presence of Binder- Picture Courtesy: Pyropower
Binders or other additives- for instance, gums and starches- incorporated in some formulations have inherent cohesiveness.. Although these binders are necessary for the formation of a product, however, they promote agglomeration due to the contact between particles at the drying stage.
Presence of Electrostatic Charges
Presence of Electrostatic Charges- Picture Courtesy: Silica Specialist
The particles in the bulk solids can acquire electrostatic charges in the dryer, particularly when air velocity is high. The force of attraction is increased between the particles due to the accumulation of electrostatic charges, leading to particle clumping and agglomeration. Moreover, if equipment is not properly grounded, it can lead to an uncontrolled buildup of charges, further promoting adhesivity issues.
3.How To Solve the Phenomenon of Agglomeration of Particles in The Dryer?
The stickiness of particles contributes towards its agglomeration that in turn causes undesired product buildup and accumulation of fine particles in the dryer device. Here are some suggestions to solve the phenomenon of agglomeration of particles in the dryer.
Optimize Drying Variables
Optimize Drying Variables- Picture Courtesy: GEA
Since different kinds of drying parameters influence the agglomeration of particles in the dryer, it is vital to fine-tune them to optimize the efficiency of the drying process. Controlling humidity and temperature during the drying phase results in minimizing stickiness, in turn decreasing agglomeration.
The temperature should be optimal for effective drying and it should not vary significantly to prevent non-uniform drying and particle adhesion.
Maintaining a lower rate of humidity leads to less moisture buildup, decreasing the chances of condensing and agglomeration. Modifying airflow patterns like cross-flow or opposing flow also increases the drying quality and minimizes the chances of bridging between particles.
In addition to this, high air speed is responsible for keeping the particles in motion and reducing their stagnancy, therefore, reducing their clumping and agglomeration.
Equipment Design and Maintenance

Equipment Design and Maintenance- Picture Courtesy: Servicon
Equipment design has a significant contribution to the agglomeration in the dryer, so it should be designed in such a way as to properly distribute airflow, prevent regional hot spots or cold spots, and ensure optimal drying. Furthermore, the dryer should have gentle handling to avoid undesired stress on the materials that could otherwise cause agglomeration.
The equipment should be leakage-proof and airtight because if even a small amount of water vapor enters the dryer, then it could promote adhesion and agglomeration. Also, tightly close the lid of the dryer to reduce air exposure because the latter causes oxidization of particles, changing their surface properties and contributing to lumping.
The dryer should have convenient access for cleaning and maintenance, which improves the cleaning and upkeeping quality, hence reducing the likelihood of product accumulation.
Particle Pretreatment
Particle Pretreatment- Picture Courtesy: FEECO International
It is a valuable approach to prevent the possibility of particle agglomeration in the dryer. If the characteristics of particles are altered before drying, then their massing is averted. By reducing the size of particles through grinding or milling, the surface area of particles is increased, which reduces the odds of clumping.
Similarly, the removal of bigger particles by sifting, screening, or classification will increase the uniformity of the batch and curtail the probabilities of agglomeration by reducing the chances of fine particles bonding with larger particles. Moreover, the shape of particles is changed to reduce their packing densities and contact points, which leads to less risk of stickiness of particles.
Process Optimization
Process Optimization- Picture Courtesy: iFormulate
It is a strategy to tweak attributes of the drying process to reduce the particle agglomeration in the dryer and to maintain the product quality. The feed rate of particles is adjusted to ensure their uniform flow in the dryer and to prevent overcrowding, which can be the root cause of aggregation. It is advised to gradually and steadily load the materials to prevent unexpected surges that can lead to non-uniform drying and clumping.
It is necessary to optimize the drying time so that particles have sufficient time in the dryer for complete drying; however, avoid providing excessive residence time as it can result in agglomeration.
Prevention of Electrostatic Charges
Prevention of Electrostatic Charges- Picture Courtesy: Marubeni Europe
As already established, electrostatic charges are an integral contributor to the agglomeration of particles in the dryer. Therefore, manufacturers utilize different strategies to prevent the buildup of electrostatic charges in the dryer, for example, these charges are dissipated by following proper grounding procedures for equipment like conveyors, dryers, etc.
Different kinds of static eliminators, for instance ionizing bars or blowers are utilized in the dryer to discharge ions into the surrounding air, hence; neutralizing the electrostatic charges. Also, the accumulation of electrostatic charges is minimized using anti-static additives in the dryer machine.
Gradual Drying of Particles
Gradual Drying of Particles- Picture Courtesy: Pilotech
Gradual drying involves slow and careful drying of material and is an integral approach to prevent particle clumping. In this process, moisture is removed in a controlled manner, which decreases the perils of particle stickiness. The moisture is vaporized evenly from the exterior and center of particles, thus preventing adherence to sticky surfaces.
It is recommended to first set the temperature at lower settings and then increase gradually to avoid agglomeration. This process prevents the formation of a tacky outer layer on particles, which is the leading cause of agglomeration. With the decrease in moisture, the temperature is slowly raised in the dryer to remove residual watery content from the particle core. This reduces the incidence of sticky conditions that result in particle binding and cohesivity.
Use of Additives
Use of Coating Agents- Picture Courtesy: Feeco International
One of the oldest methods to prevent the agglomeration of particles in the dryer is the use of additives that act as anti-caking agents or coating agents in the dryer. They are a separator or barrier, consequently averting the chances of the buildup of crystal bridges between particles during the drying. Silica, starch, cellulose, or other anti-caking agents are added both before or during the drying to minimize moisture absorption and surface cohesivity.
The coating agents are usually hydrophobic and modify the characteristics of particles like reducing their surface tension, altering their viscosity, and decreasing their adherence with each other by reducing the forces of attraction between particles.
Agitation and Other Mechanical Methods
Agitation and Other Mechanical Methods- Picture Courtesy: FEECO International
This is a suitable approach routinely utilized in the dryer device to bar the agglomeration by disrupting the particle contact point and increasing rates of uniform drying. Mechanical agitators are pivotal in deterring the settling of particles and their clumping. Baffles and other agitators are ideal for improving particle motion, thereby reducing the contact duration between moist particles and breaking up clumps.
In some dryers, such as rotary and drum dryers, stirring and rotation have an impact on the motion of particles, which reduces clumping. The materials tumble with rotation and roll over each other, thus reducing their contact with each other for a longer duration.
Vibrating dryers and pulsating air increase the dispersal of particles and avert particle agglomeration by breaking the weak bonding between agglomerates. In some cases, ultrasonic waves are also utilized to disrupt the bridging between particles and improve their dispersal.
Fluidized Bed Drying Approaches
Fluidized Bed Drying Approaches
Fluidized bed dryers are highly popular in industrial settings to prevent particle agglomeration. In these dryers, particles are fluidized in the air or gas, remain under constant motion, and establish a fluid-like behavior. This continual movement hinders the stickiness of particles.
The air is directed upward through a particle bed that lifts and moves particles continuously, hence preventing the likelihood of particle bonding and adherence. It promotes particle separation, and reduces the interaction between particles, thus preventing particle agglomeration.
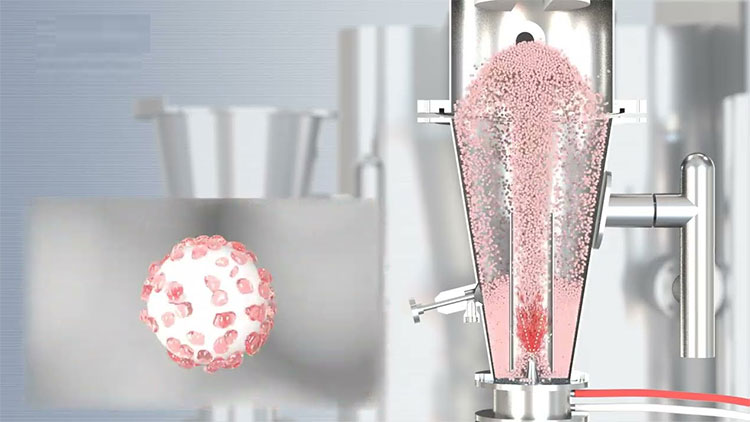
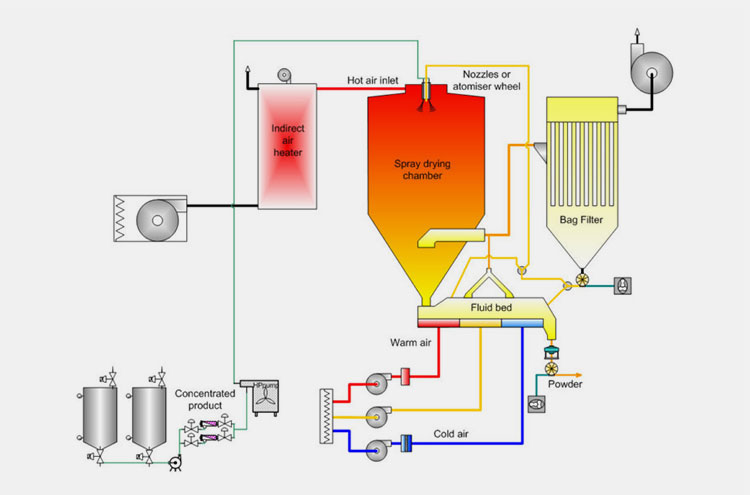
Spray Drying Techniques
Spray Drying Techniques- Picture Courtesy; European Pharmaceutical Manufacturer
Spray drying is one of the preferred techniques in the manufacturing sector for eliminating moisture from slurries, pastes, and granules. The materials are atomized and transformed into fine mist, and moisture is vaporized from droplets with a hot gas. It is advised to design spray nozzles with a smaller size, as smaller droplets have increased chances of quick and uniform drying, which decreases the opportunity for moist droplets to cluster.
Furthermore, it is suggested to use a two-stage drying process to control the rate of agglomeration. Moisture is quickly reduced to prevent a sticky phase in the first drying stage. In the second drying stage, minimal temperature is applied to ascertain complete drying and to prevent material cohesivity.
Use of Hybrid Approaches
Use of Hybrid Approaches- Picture Courtesy: Spray Drying Nozzles
These hybrid approaches incorporate several techniques to tackle the agglomeration challenge in the dryer. They present synergistic advantages and are exceptionally effective in intricate situations. Sometimes, they involve the utilization of a fluidized bed dryer and sprayer dryer consecutively, which allows rapid drying, even particle distribution, and minimal agglomeration.
Connective drying is also used with fluidization to improve heat transfer and decrease the likelihood of particle cohesion and stickiness. Additionally, integrating the drying step with other methods like filtration and grinding boosts the process's effectiveness and hinders agglomeration.
Conclusion
Agglomeration is a beneficial process in industries for improving the handling of particles but sometimes it leads to undesired effects like caking and bridging. It reduces the efficiency of the dryer and results in poor-quality products. Various manufacturers do their best to solve the phenomenon of agglomeration. So, to facilitate these manufacturers this blog post “How to Solve the Phenomenon of Agglomeration of Particles in The Dryer” is compiled. Hopefully, you have learned about the combination of different techniques to prevent agglomeration by modifying the surface properties of particles and optimizing drying parameters. If you have more queries in mind, then call our customer care. We, Allpack are ever ready to guide and serve you.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours