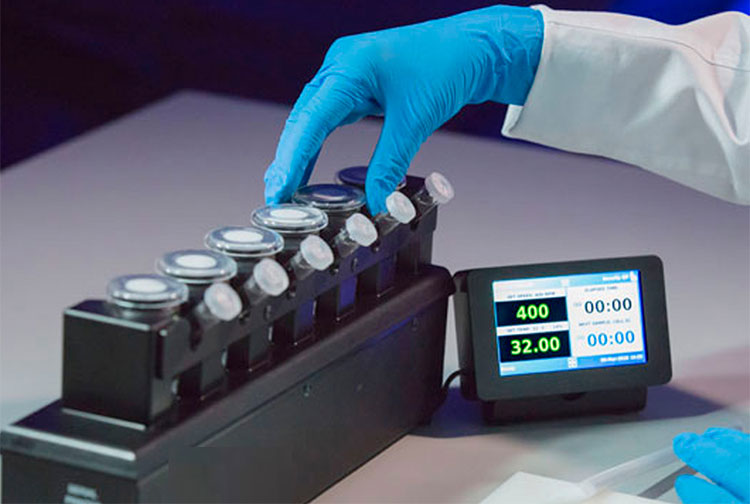
Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester: The Complete Buying Guide In 2025
Everyone prefers a non-invasive mode of drug delivery! Drug transdermal formulations are the world’s renowned and accepted route of drug delivery as they release the medication through your skin. Isn’t that amazing? How is it confirmed that drug transdermal medication works effectively? Are drug-transdermal products absorbing inside the skin? How is it estimated?
The drug transdermal diffusion tester is a promising device that ensures the quality of your product. How it works? What benefits it offer? There are plenty of queries that will be knocking on your mind; this article is here to answer all about the device. Have a look at the enlisted questions and detailed answers below:
1.What is a drug transdermal diffusion tester?
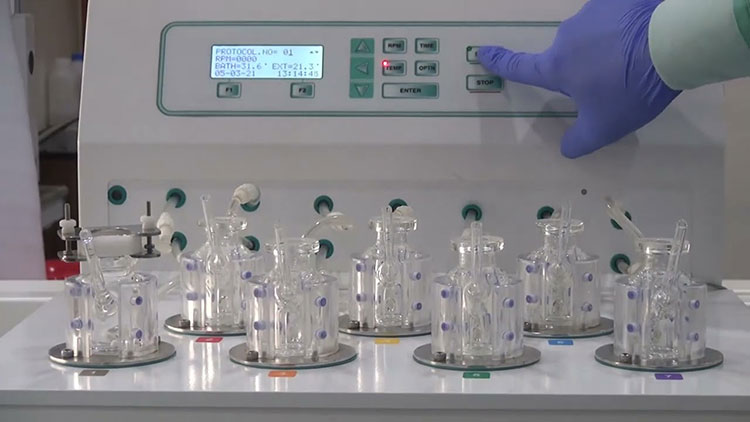
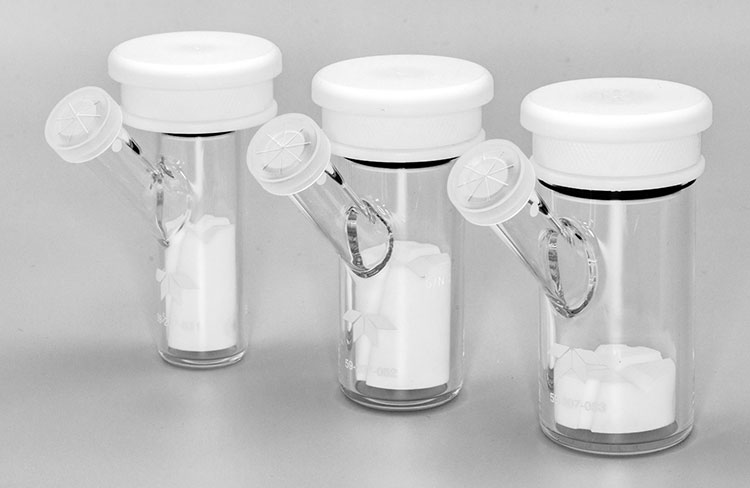
Allpack Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester
It is a form of pharmaceutical testing equipment that estimates the drug release profile of semi-solid tropical or transdermal medications in vitro. This apparatus measures the quantity, rate, and diffusive extent of active ingredients that penetrate through skin or membrane at a given time point.
A drug transdermal diffusion tester has a central role in measuring the potency and release behavior of transdermal delivery systems, such as transdermal patches, gels, creams, and ointments. It facilitates analysts in assessing the permeability potential of drugs and optimizing tropical drug formulations.
The data outcomes supplied by the drug transdermal diffusion tester allow researchers to predict the rate at which active pharmaceutical ingredients flow into systemic circulation when administered to the skin.
2.When does a drug transdermal diffusion tester come into use?
History of Transdermal Drug Delivery System- Picture Courtesy: The Canadian Encyclopedia
Humans have been applying different medicinal and cosmetic substances to the skin for treating disorders and for beauty purposes, respectively. The skin became a route for drug delivery at the beginning of the 20th century.
To carry out systemic research into in vivo and in-vitro association, T.J. Franz developed a drug transdermal diffusion tester in 1975. Since its invention, this tester has become a major instrument for evaluating the permeability and stability of transdermal products.
3.What is the role of a drug transdermal diffusion tester in drug formulation?
A drug transdermal diffusion tester is a standard and well-utilized instrument in formulation development and quality control approaches to characterize the permeation of tropical semi-solid dosage. Now let’s read about the integral role of a drug transdermal diffusion tester in drug development:
Formulation Optimization
Formulation Optimization- Picture Courtesy: Elerctrolab
Pharmaceutical and cosmeceuticals have intricate makeup, in which several ingredients interact with each other and skin tissues. So, with the use of a drug transdermal diffusion tester, developers can test different combinations of ingredients- such as solvents, excipients, penetration enhancers, and many more- to discover ideal formulation components that boost drug bioavailability and then fine-tune in preparation accordingly.
Role in Permeation Studies
Role in Permeation Studies- Picture Courtesy: Teledyne Hanson
A drug transdermal diffusion tester assesses the permeation pattern of drug components that pass through the skin layer and go into blood circulation. It helps in gauging whether a drug has the potential for skin administration.
Safety Evaluation

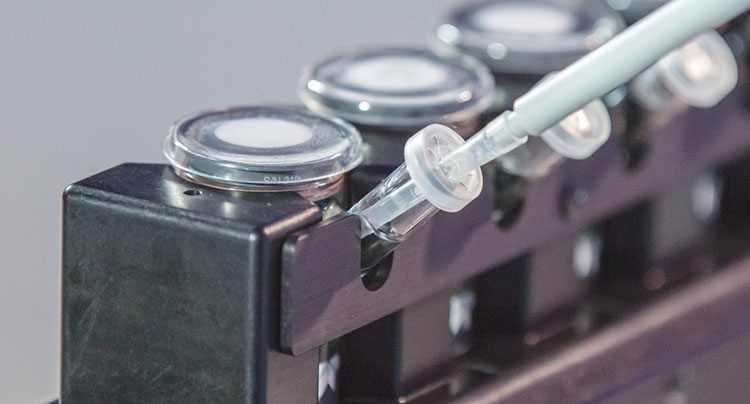
Safety Evaluation- Picture Courtesy: Teledyne Hanson
Tropical medications are smeared on the skin and provide localized and systematic effects. However, in some cases, these medications cause adverse reactions and irritate the skin. Therefore, a drug transdermal diffusion tester evaluates the safety profile of tropical drugs in vitro by determining the potential antagonist effects of core ingredients.
Role in Bioequivalence Studies
Role in Bioequivalence Studies-Picture Courtesy: Vitronic
Using a drug transdermal diffusion tester, analysts study the release profile, efficacy, and absorption pattern of several generic and branded medications. It helps in comparing the amount of drug delivered by both formulations over time. It shows that generic and innovative drugs are bioequivalent to each other.
Compliance with Drug Regulations
Compliance with Drug Regulations- Picture Courtesy: Teledyne Hanson
Transdermal drugs are subjected to drug regulations so, they must be evaluated through tests to establish that they fulfill safety criteria. Hence, the data produced by a drug transdermal diffusion tester provides evidence of the effectiveness of preparation and is needed by drug authorities when applying for drug approval.
Non-Invasive Testing
Non-Invasive Testing- Picture Courtesy: Femto Scientific
This apparatus is highly popular for non-invasive studies, as it offers noteworthy perceptions about the behavior of a drug in the human body without requiring human or animal models. It stimulates the skin environment and predicts therapeutic outcomes of formulation in the body, thus conserving time and resources.
4.What important information is provided by the drug transdermal diffusion tester?
Data by Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester- Picture Courtesy: Teledyne Hanson
A drug transdermal diffusion tester is benchmarked in testing tropical and transdermal dosage forms because it assists manufacturers in determining a multitude of pivotal facets of drugs. The basic information provided by a drug transdermal diffusion tester includes:
| Flux | It is the number of drug molecules penetrating through the barrier layer or membrane into the circulatory system per unit of time. It helps estimate the rate of drug absorption. |
| Total Quantity of Permeated Drug | It is the cumulative amount of the drug going across the membrane during specific time intervals. The effectiveness of the drug delivery method and bioavailability of formulation is estimated through this parameter. |
| Lag Time | It is a time interval between the administration of formulation and the duration required by drug molecules to attain the steady-state concentration in the receptor system. This metric aids in developing rapid or extended-release medications. |
| Steady-State Diffusion | The active ingredients attain a steady-state diffusion stage after the lag phase, at this stage the diffusion occurs constantly. Steady-state diffusion aids in predicting therapeutic levels of drugs over time. |
| Permeability Coefficient | A drug transdermal diffusion tester also provides estimates of the permeability coefficient, which is the rate at which active ingredients penetrate the barrier membrane. It determines how speedily the drug will permeate the skin in real time. |
| Skin Retention | The quantity of formulation that is retained in the skin tissues is called skin retention. The information obtained from the drug transdermal diffusion tester is utilized for measuring the skin retention rate. This is necessary to predict the effect of local tropical medications as their components stay on the skin over a specific time point. |
| Membrane Integrity and Stability | This instrument mimics skin physiology and allows researchers to study the diffusion rate of the drug through intact and compromised membranes. It can gauge the integrity of the membrane utilized in the studies and ascertain the precision and dependability of permeation outcomes. |
5.Where is a drug transdermal diffusion tester utilized?
A drug transdermal diffusion tester is originally invented to assess the permeability and stability of various dermatological medications. Different manufacturing and research sectors utilized this instrument because it establishes associations between skin, drug, and preparation. Some of the primary sectors where a drug transdermal diffusion tester is utilized include:
Pharmaceutical Industry
Transdermal Patches- Picture Courtesy: News-Medical
A drug transdermal diffusion tester is a well-accepted assay in the pharmaceutical sector that reliability determines the release kinetics of tropical remedies in-vitro and ex-vitro. It screens different combinations of active substances, excipients, and enhancers to discover suitable components that offer desired drug permeation and absorption.
Quality Control Inspections
Quality Control Inspections- Picture Courtesy: Amarin Technologies
Quality control of tropical and transdermal preparations is integral in determining their therapeutic efficacy, the number of undesired effects, and their compliance with pharmacopeial regulations. Therefore, due to its simplicity, a drug transdermal diffusion tester is routinely used in quality control inspections to evaluate the toxicity and stability of dermatological drugs.
Academia
Academic Research- Picture Courtesy: ERCO Pharma
This sector is in continuous pursuit of formulating dermatological therapies with better effectiveness and limited skin irritation problems. So, to analyse drug permeation rates and dermato-pharmacokinetics of various skin-related formulations, researchers use estimation tools like drug transdermal diffusion tester. They also shed light on release patterns of novel drug delivery systems, for instance, nanoparticles, liposomes, and biofilms, to name a few.
Cosmetic Sector
Cosmetic Skincare Patches- Picture Courtesy: Cosmetics & Toiletries
Cosmetic and dermatological products, such as lotions, creams, gels, serums, etc. come with positive benefits, for example, hydration, skin brightening, anti-aging properties, and healing effects for skin disorders. A drug transdermal diffusion tester models physiological conditions, consequently, it directly compares different cosmeceutical products, assesses their safety potential, and evaluates their intended effect.
Veterinary Industry
Veterinary Tropical Medications- Picture Courtesy: VetMedics Compounding Pharmacy
The utility of a drug transdermal diffusion tester goes beyond the scope of the pharmaceutical industry and extends to the veterinary sector. This apparatus analyses the diffusion rate, release kinetics, absorption rate, and performance of veterinary formulations for treating skin diseases in pets and livestock.
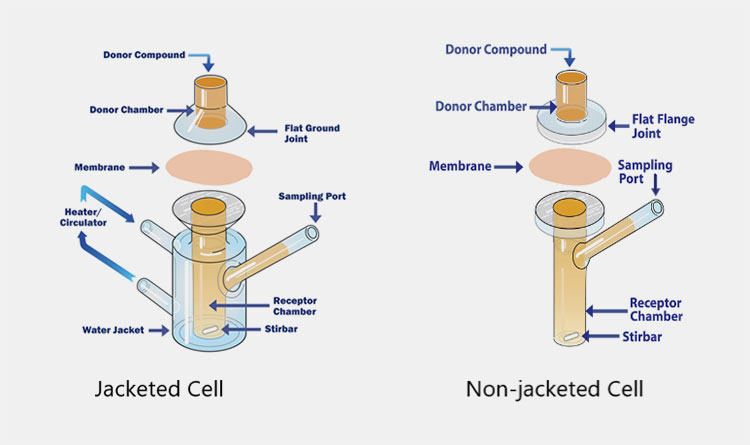
6.What are the design and parts of a drug transdermal diffusion tester?
A drug transdermal diffusion tester is comprised of several parts that team up to mimic a controlled physiological setting for investigating drug permeation across biological or artificial membranes. A list of basic components and design elements of a drug transdermal diffusion tester is discussed below:
Parts of Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester- Picture Courtesy: PermeGear
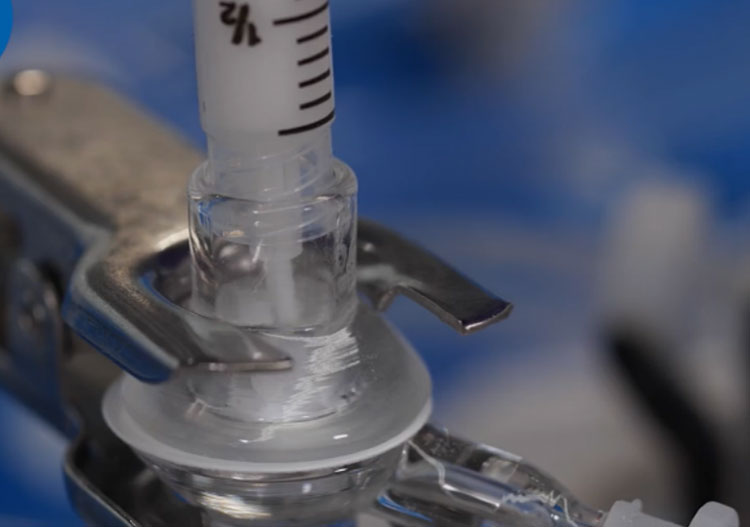
Components of Diffusion Cell
Picture Courtesy: Copley
| Donor Chamber | It is known by different names, such as cell cap, cell top, donor chamber, or donor compartment. It is manufactured from a permeable material and retains the drug vehicle, for instance, patches or ointment. |
| Joint | The top portion of the cell body or receptor chamber and the mating downward part of the donor compartment are collectively termed joint. |
| Membrane | An inert and highly permeable barrier is present between the donor and receptor compartment. It behaves like a conduit through which permeation occurs. Several membrane types are used to conduct transdermal drug estimations, such as human skin tissues, animal tissues, synthetic membranes (PVDF, Supor Polyethersulfone, and Strat-M Membranes), and human skin equivalents. It is put in the center of the joint and kept in place by a clamp. |
| Heater/Water Circulator | This part is integral in keeping the temperature under the required range by circulating hot water or other liquid around the apparatus. |
| Water Jacket | It is also termed a heating jacket and is a glass compartment enclosing the receptor chamber. It flows liquids- such as water- to keep the temperature of a drug transdermal diffusion cell under a range of 32-37°C. |
| Sampling Port | It is present in the receptor compartment and provides a suitable outlet through which aliquot is extracted at a particular time point for evaluation. |
| Receptor Chamber | It is the innermost component present in the lower part of the diffusion cell. The diffused drug is collected in this chamber. It is loaded with appropriate solvents, for instance, phosphate buffer saline to dissolve the drug. |
| Stir bar | This magnetic stirrer or stirring bar is present in a receptor compartment that constantly stirs the solution. It ensures the homogenous distribution of active substances in the receptor liquid. The stirring speed is usually in the range of 200 to 2000 RPM. |
| Cell Clump | It is also known as a membrane holder and is made of metal, which serves the purpose of securing the membrane between two chambers. It guarantees precise diffusion appraisals by offering a leakage-proof tight seal. |
| Insulation | Insulation is an essential component located in a non-jacketed drug transdermal diffusion tester and reduces heat loss or gain, while the machine is running. It helps increase the heating efficiency of a heating block by averting heat transfer between the system and surroundings. |
| LCD Screen Panel | It is present in advanced versions of the drug transdermal diffusion tester and has a role in displaying real-time data- for example, temperature, stirring velocity, sampling interval, and elapsed time. It acts as a control interface using which operators program and modify operational settings. |
| Heating Block | A heating block is designed with heating elements and temperature control systems to provide heating to the system for keeping a constant temperature. It is typically found in the non-jacketed drug transdermal diffusion tester. |
7.What is the working principle of a drug transdermal diffusion tester?
The working principle of a drug transdermal diffusion tester is grounded on the mechanism of in-vitro diffusion. This is the movement of active material (permeant or drug) across the barrier (modelling skin behavior) from the area of higher concentration gradient to the area of lower concentration gradient.
A drug transdermal diffusion tester follows the diffusion principle by introducing a drug vehicle (a drug with a medium like water, alcohol, or propylene glycol) to one side of the barrier and calculating drug movement into the receptor compartment.
Let’s take a look into the various steps involved in the working of a drug transdermal diffusion tester:
Preparation of Diffusion Cell Apparatus
Preparation of Diffusion Cell Apparatus- Picture Courtesy: Sigma-Aldrich
First, the receptor fluid is filtered with a vacuum filtration flask. This fluid is a lipophilic or hydrophilic substance that behaves similarly to the bloodstream. Then, the stirring system for every cell in the drug transdermal diffusion tester is switched on.
After that, the membrane is positioned- shiny side up between the donor and receiving compartments, and this arrangement is secured by a metallic clamp. Next, the lower compartment- receptor chamber in case of jacketed drug transdermal diffusion tester- is loaded with receptor buffer,
A syringe loaded with a receptor fluid is inserted into the sampling port to prevent the formation of air bubbles.
A fixed amount of drug or permeant is incorporated into the vehicle medium and then this preparation is introduced in the donor chamber. The arrangement of the diffusion cell apparatus is kept at 32°C and 37°C to replicate ambient skin temperature.
Drug Diffusion
Drug Diffusion- Picture Courtesy: Teledyne Hanson
After a while, the active components in the donor chamber pass through a barrier and are collected inside the receiving chamber. This drug diffusion is dependent upon membrane permeability, characteristics of the drug vehicle, and fluidity of the receptor buffer.
Sampling and Evaluation
Sampling and Evaluation- Picture Courtesy: sigmaaldrich
The quantity of permeant accumulated in the receiving chamber is measured in short intervals by the sampling port. A device or syringe is inserted in the sampling port to extract the receptor fluid. Sampling must be repeated approximately 5-6 times to attain reliable calculations.
After sampling, the samples are dispensed in vials and then permeant is detected by chromatographic or spectroscopic methodologies.
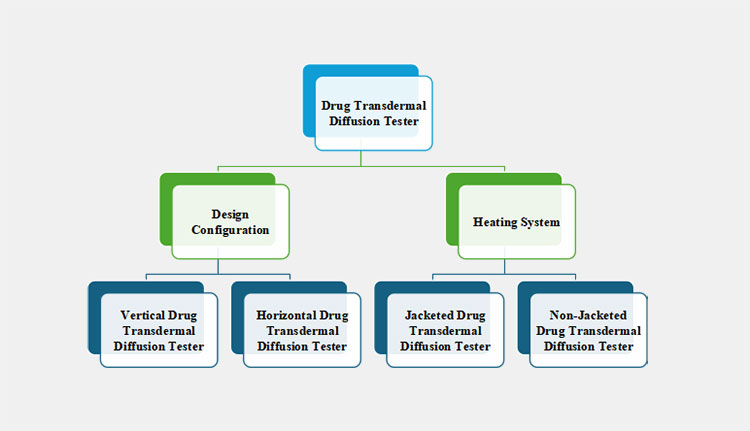
8.What are available types of drug transdermal diffusion testers?
A drug transdermal diffusion tester is categorized into two diverse categories, based on design structure and the presence of a heating jacket. These kinds include:
According to the Design Configuration
There are two primary types of drug transdermal diffusion testers when classified based on design configuration.
Vertical Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester
Vertical Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester- Picture Courtesy: Copley
In this kind of drug transdermal diffusion tester, the donor chamber is situated above the barrier membrane, while the receptor chamber is positioned under the membrane. The drug vehicle is kept against the membrane via gravitational force.
This design configuration is identical to applying the drug to the skin. It has better sealing properties, as the drug stays smeared on the membrane. In vertical drug transdermal diffusion tester, sampling is carried out from the lower portion of the machine, preventing the chances of disturbing membrane-drug arrangement.
Stirring is more consistent due to the placement of the stirrer in the receptor compartment.
Horizontal Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester
Horizontal Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester- Picture Courtesy: Logan Instrument Corps.
It has a horizontal configuration in which donor and receptor chambers are positioned side-by-side. The membrane is positioned sideways between these compartments. Thus, it is also called a side-by-side drug transdermal diffusion tester. The diffusion of drugs occurs laterally through the membrane and there is no role of gravity in this setup.
The drug vehicle in this design type is more prone to evaporation due to increased exposure of the drug to the air. It is more difficult to perform sampling in a horizontal drug transdermal diffusion tester because of the horizontal alignment of membrane and drug preparation, which can alter the drug-membrane setup. Due to its horizontal orientation, it is difficult to stir receptor fluid.
According to the Heating System
There are two kinds of drug transdermal diffusion testers depending on their temperature control systems.
Jacketed Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester
Jacketed Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester- Picture Courtesy: Logan Instrument Corps.
It has a double-walled insulation chamber that circulates a temperature-controlled liquid. The latter can be heated or cooled to maintain a uniform temperature range within the diffusion cell. The receptor compartment and heating jackets are manufactured at the same time by hand blowing, hence they do not separate.
Due to its intricate design, it is more expensive than its counterparts. However, it is preferred in studies of the pharmacokinetics of transdermal and topical formulation because it closely models the physiochemical changes in the skin by providing precise control of temperature.
Non-Jacketed Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester
Non-Jacketed Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester- Picture Courtesy: Teledyne Hanson
It has a more straightforward design, as it does not consist of a heating jacket and usually relies on ambient temperature for drug diffusion. The non-jacketed drug transdermal diffusion tester is dependent on a heating block, water bath, or temperature-regulated surroundings to keep the temperature under the required threshold.
Due to its simple design, it is less pricey than the jacketed drug transdermal diffusion tester. It is commonly found in laboratories.
9.What are the common medications marketed by examining on drug transdermal diffusion tester?
Transdermal Medications- Picture Courtesy: Aspercreme
A variety of medications are sold as a transdermal drug delivery system after studying their characteristics by a drug transdermal diffusion tester. Their names and uses are described in the table below:
| Drug | Use | Marketed Name | Application Time |
| Nicotine | Smoking Abstinence | Nicoderm CQ® | 24 hours |
| Hormones
Estradiol Testosterone |
Menopausal symptoms
Hypogonadism |
Vivelle-Dot®
Androderm® |
2 times per week
24 hours |
| Fentanyl | Pain Management | Duragesic® | 3 days |
| Clonidine | Hypertension | Catapres-TTS® | 7 days |
| Scopolamine | Motion Sickness
Nausea |
Scopace® | 3 days |
| Rivastigmine | Alzheimer's disease
Dementia |
Exelon® | 24 h |
| Lidocaine | Postherpetic Neuralgia | Lidoderm®
Dermalid®
|
up to 3 times daily for no more than 12 hours |
| Buprenorphine | Chronic Pain
Opioid Dependence |
Butrans® | 7 days |
| Methylphenidate | Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) | Daytrana® | 9 days |
| Selegiline | Depression | Emsam® | 24 hours |
| Rotigotine | Parkinson's Disease Restless Legs Syndrome | Neupro® | 24 hours |
| Diclofenac | Localized Pain
Arthritis |
Flector® | 12 hours |
| Nitro-glycerine | angina | Minitran®
Nitro-dur® |
12-14 hours |
10.What are the precautions for a drug transdermal diffusion tester?
Precautions For Drug Transdermal Diffusion Tester- Picture Courtesy: Teledyne Hanson
A drug transdermal diffusion tester is an exceptional equipment for assessing the permeation rate of the skin-administered formulation. However, necessary precautions must be adopted to guarantee the safety of the operator and experiment during the run. So, here are some essential precautions for operating a drug transdermal diffusion tester:
- First, carry out some preliminary experiments to prevent manifestation of personal errors, if you are not skilled enough to conduct permeation studies.
- During membrane setup, gently handle the membrane and do not overstretch or break it by puncturing.
- The skin specimen must have a larger size so that its fringes are securely positioned in the diffusion cell around the opening.’
- The skin membrane should not extend into the receiving compartment as otherwise, it could hinder the stirring of receptor buffer.
- If you are going to use membrane later, then it is best to freeze it at -80°C.
- Uniformly distribute drug vehicles to donor chambers because failure to do so would cause a disparity in outcomes.
- The tester should have consistent temperature throughout the run because temperature changes influence the diffusion estimates.
- Do not disturb membrane setup during sampling and pipetting because it could lead to discrepancies in results.
11.What are the technical issues and solutions relevant to a drug transdermal diffusion tester?
A drug transdermal diffusion tester is a sophisticated instrument, designed to minimize errors but even then, some occasional technical issues find their way into this equipment and reduce the efficiency and reproducibility of test estimations. That’s why, we are penning some technical issues and solutions to minimize your unease.
Temperature Deviations
Temperature Deviations- Picture Courtesy: LABOAO
From time to time, unexpected inconsistencies occur in the temperature control of the drug transdermal diffusion tester, contributing to poor estimations of permeation rates because temperature impacts the movement of formulations across the membrane.
Solutions
To address this issue: you should check the working performance of the insulation, heating block, and water jacket. Also, regularly calibrating the heating mechanism alleviates the issue of temperature fluctuations. Monitoring of real-time temperature assessment must be done using an LCD screen. It is recommended to use an external temperature sensor to verify temperature stability.
Variances in Membrane Characteristics
Variances in Membrane Characteristics- Picture Courtesy: Teledyne Hanson
In certain cases, characteristics of the membrane deviate from batch to batch, resulting in inaccuracies in the determination of diffusion rates and variable results.
Solutions
To solve this problem, it is suggested to procure membranes from reputable and standardized sources so that there would not be any inconsistencies in the properties of membranes. It is ideal to pre-test the thickness, hydration, and quality of the membrane before carrying out formal tests. The high variability associated with biological membranes is minimized with artificial membranes.
Presence of Air Bubbles
Presence of Air Bubbles- Picture Courtesy: Teledyne Hanson
Air is entrapped under the membrane layer or in the cell body, disrupting expected drug diffusion patterns and leading to imprecisions in permeation estimates.
Solutions
To rectify the problem of air bubbles, operators should degas the fluid by introducing a vacuum. Care should be taken when assembling the diffusion cell apparatus, especially setting the membrane to avert the buildup of air bubbles.
Evaporation from Donor Chamber
Evaporation from Donor Chamber- Picture Courtesy: Teledyne Hanson
Sometimes, the drug vehicle evaporates from the donor chamber, producing drug concentration changes and impacting the diffusive behavior of formulation.
Solutions
This technical issue is resolved by properly sealing and covering the donor chamber using paraffin films or other sealing materials, which prevent the vaporization of the formulation vehicle. Secondly, perform the permeation analysis in controlled humid surroundings to cut down evaporation possibility. Periodically monitor volume changes in the donor chamber to identify any minor evaporation incident.
Insufficient Stirring
Insufficient Stirring- Picture Courtesy: Teledyne Hanson
At times, there is an event of irregular stirring in the receptor compartment, causing non-uniform mixing of receptor liquid that leads to the formation of concentration gradients and errors in diffusion rate calculations.
Solutions
To remedy this predicament, modify the stirring velocity to correctly mix receptor fluid without creating turbulence. Carefully place the stirrer in the receptor chamber to prevent mixing dead zones. Regularly schedule calibration of the magnetic stirrer to make sure it is correctly working.
Conclusion
Let’s conclude this enlightening blog post about a drug transdermal diffusion tester by stating that this instrument is a great way to standardize in-vitro transdermal drug testing protocols. It assesses the permeability behavior of tropical and transdermal drugs using different model membranes. It is known for its real-time stimulation of skin physiology, thus providing systematic insights into the in-vitro-in vivo association of formulation. Consequently, you can achieve consistency, producibility, and excellence in your testing procedures by adding a drug transdermal diffusion tester in your labs and institutes. We, Allpack are here to guide you in the choice of a superior machine for your test procedures. Get in touch with us at your earliest convenience.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours