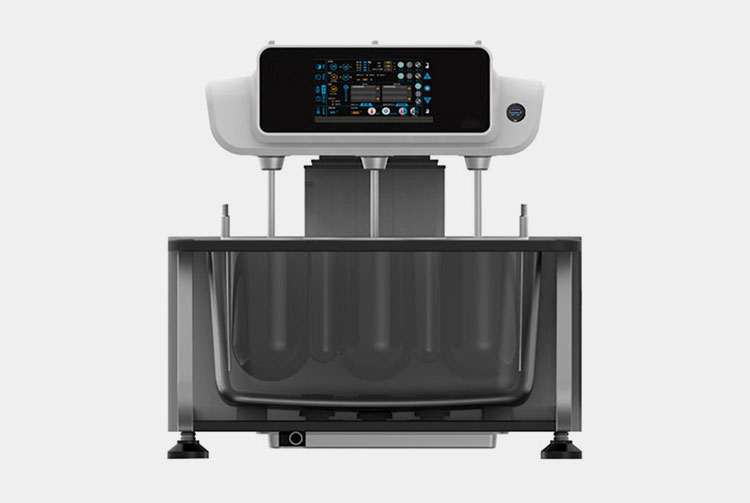
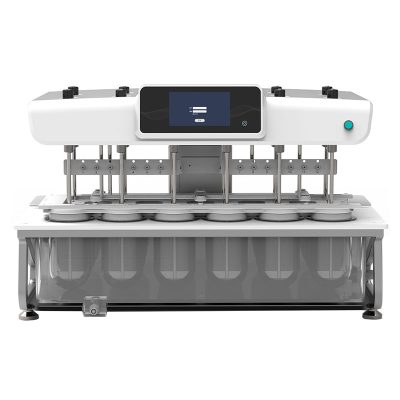
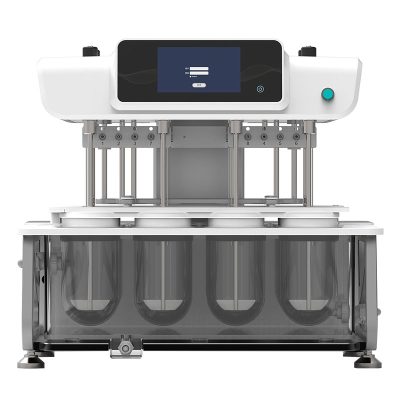
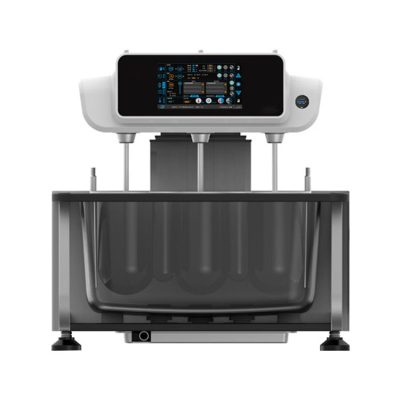
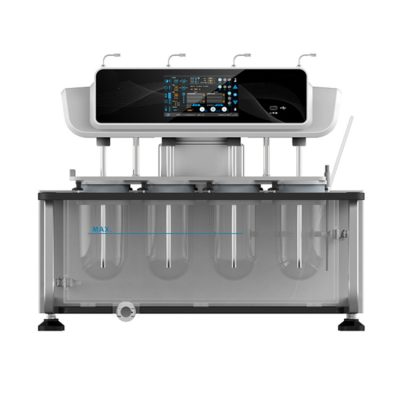
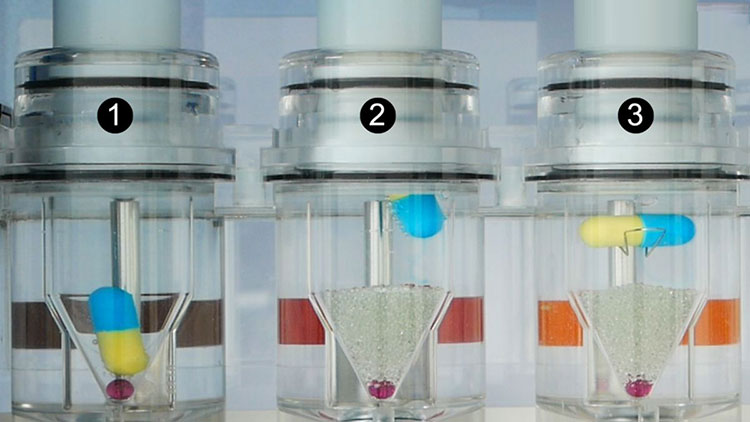
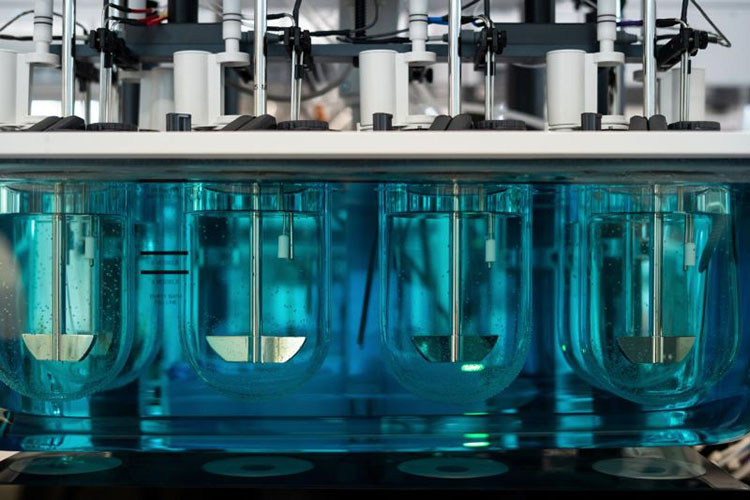
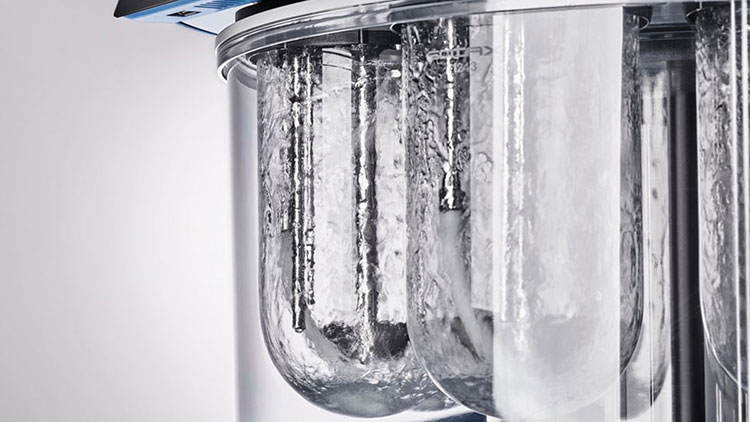
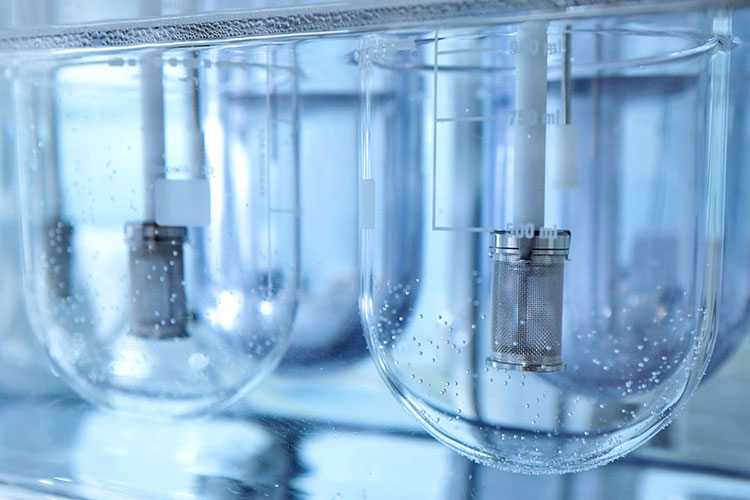
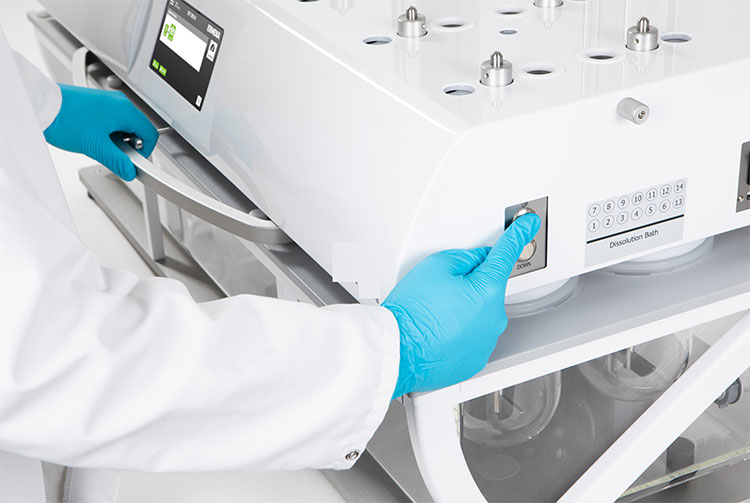
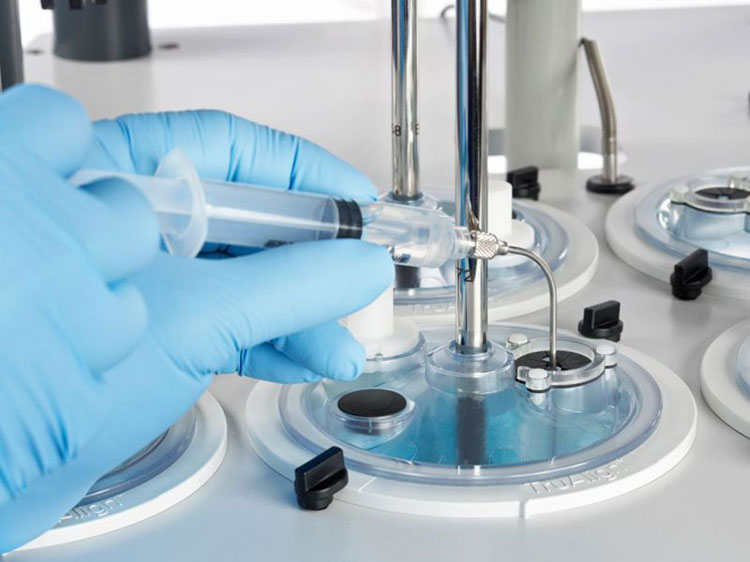
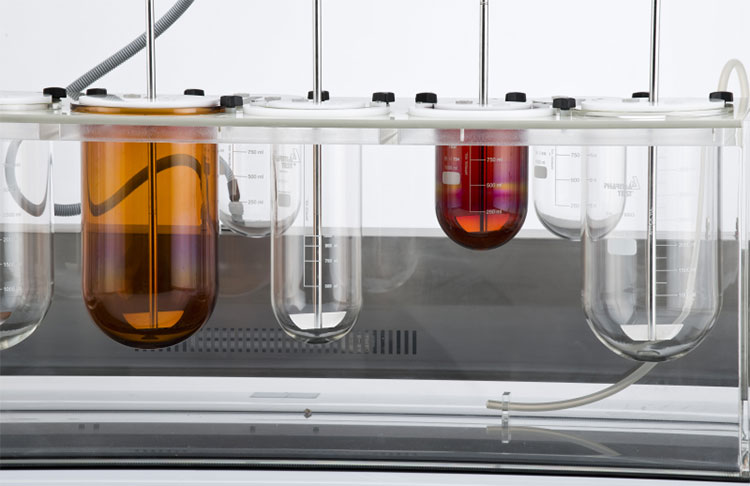
Dissolution Tester
Allpack APK-A series dissolution testers are used for detecting velocity and extent of pharmic dissolution from tablet, capsule etc in prescriptive menstruum, which have been widely used in food and cosmetics industry to perform the necessary dissolution test. All the dissolution testers adopt the mechanical structure of the lifting column lifting and lowering drive. The appearance are beautiful, the working performance is stable and reliable, the circuit part adopt the most novel circuit design, and the clock control module adopts the advanced program preset chip, which can be preset during the test. The single-segment time control and the multi-segment time reminding program have high automation degree, convenient operation, superior performance and high precision of test data.All Allpack dissolution testers can be applicable to the laboratories of pharmaceutical inspection departments, hospitals, scientific research departments and major pharmaceutical companies.
Allpack Dissolution Tester
12 Cups APK-12A Automatic Medical Digital Tablet Dissolution Tester for Pharmacy
Allpack APK-12A Dissolution tester is equipped with eight vessels and poles, allowing for the simultaneous testing of multiple samples and significantly improving testing efficiency.With the automated up and down movement of the testing head, the operation becomes more convenient, enhancing user experience.The basket units and paddle units made of imported stainless steel (SUS316L) ensure the durability and reliability of the product.The magnetism-pumped circular water current ensures even heating within the system, maintaining temperature balance during testing.
Automatic Head Movement
Stainless Steel Material
Automated Control and Parameter Presetting
APK-8A Laboratory Dissolution Testing Equipment Fully Automatic Tablet Dissolution Tester
Allpack APK-8A Dissolution tester is used to determine the dissolution properties of solid drug preparations. With 8 cups 8 paddle 4 column structure, can perform 2 batch test at a same time, one blank test, one standard test. The rotate basket and plasm haulm are made of imported SUS316L. Automatically and intelligently control temperature, rotary speed and time. The preset and real-time data can be displayed alternately in time. This dissolution tester can do auto-test, auto-diagnose and auto-alarm.
Easy operation and stable performance
Micro processor and LCD Display
Water circulating in the bath to keep the temperature conformity with magnetic pump
APK-6N Automatic Pharmaceutical Drug Dissolution Tester for Tablet & Capsule
Allpack APK-6N Dissolution tester is used to test dissolution speed and degree of tested medicament from solid preparation. This dissolution tester has eight vessels and six poles, with six vessels and six poles in back and other two vessels at front.The head part of the instrument can be artificially turned over smoothly and flexibly. The basket units and paddle units are made of imported stainless steel (SUS316L).The magnetism-pumped circular water current can heat the system evenly, and the bath liquid can achieve an equal temperature.
Test by self and alarm automatically
Time can be preset at many points
Automatic temperature control, automatic time keeping
Pharmaceutical testing equipment APK-8N Dissolution Tester For Drug
Allpack APK-8N Dissolution tester is used to examine the dissolving speed and degree of solid preparations like drug tablets or capsules in the specified solvents. It can automatically alerts users to any faults or deviations, ensuring timely action. The built-in diagnostics help identify and address issues promptly. The dissolution tester can perform automated testing, reducing manual intervention. With high-precision real-time constant temperature control, fast temperature rise, small temperature drift, over temperature protection and temperature calibration functions.
More accurate speed, stable operation
Low energy consumption and high reliability
The head moves up/down automatically
APK-1B Dissolution Tester Pharmic Intelligent Lifting 8 Vessels LCD Fully Automatic Tablet Dissolution Tester
Allpack APK-1B Dissolution tester is used to check the dissolution rate and degree of drugs from tablets, capsules and other solid preparations in the specified solvent. The dissolution tester adopts classical modeling design and is featured by high cost performance, stability, reliability, simple operation and durability.The machine has friendly human-computer interface, with simple and convenient operation.All the working parameters can be preset and saved automatically, without the need to set repeatedly when the instrument is started next time.
Self-inspection fault alarm and over-temperature protection
Quality and performance meet the requirements of Chinese Pharmacopoeia
Accurate rotating speed, steady operation and low energy consumption
The Buyer's Guide
Drug Dissolution Apparatus: The Complete Buying Guide In 2025
Are you worried about medicine quality and stability? Do you want to maintain batch-to-batch consistency? Do you want to recognize batches with unsuitable bioavailability? These queries concern everyone in the formulation sector.
The oral dosage form is one of the widely employed ways to administer drugs to patients. The rate at which medication is dispersed in the body is a pivotal facet of the pharmaceutical sector. Hence, the drug dissolution apparatus is an important analytical device that performs quality control processes at every step of production.
In this article, we will delve deep into basic aspects that make drug dissolution apparatus integral in the industry. This piece of writing aims to provide sufficient knowledge about this device.
1.What is a drug dissolution apparatus?
Allpack Drug Dissolution Apparatus
The drug dissolution apparatus measures the quantity of drug ingredients that enter into the medium per unit of time under consistent conditions.
It is important in drug development and stability analysis since it offers information about drug release mechanisms. Drug dissolution apparatus is part of routine procedures during the product formulation cycle. It is an analytical tool needed for final-release studies of dosage forms to conduct product quality control evaluation and ensure batch-to-batch consistency. It aims to detect products with undesired bioavailability because dissolution is correlated to bioavailability.
2.Why is a drug dissolution apparatus required?
The drug dissolution apparatus is a central in-vitro instrument, offering crucial information about the dissolution profile of dosage forms. It determines the uniformity in drug release that in turn ensures the potency and safety of medications. Let’s discuss why the drug dissolution apparatus is needed in the manufacturing and developmental sectors.
Optimization of Developmental Process
Optimization of Developmental Process- Picture Courtesy: Agilent
In pharmaceutical development, the drug dissolution apparatus aids in the choice of the suitable formulation and process type. By assessing the dissolution pattern of various formulations, scientists can evaluate to ensure an appropriate drug delivery approach.
Establishing In Vivo–In Vitro Correlation (IVIVC)
Establishing In Vivo–In Vitro Correlation (IVIVC)- Picture Courtesy: World Atlas
Dissolution data generated by the drug dissolution apparatus is critical in establishing the relation between drug dissolution in laboratories under controlled conditions and drug bioavailability in a physiological environment. This IVIVC allows researchers to predict drug kinetics in vivo without conducting lengthy human and animal drug trials.
Improvement in Drug Performance
Improvement in Drug Performance- Picture Courtesy: Agilent
The dissolution rate is influenced by diverse types of factors, such as particle size, type of ingredients, and developmental process, so researchers strive to study dissolution behavior changes and use the dissolution data to make vital alterations in the drug formula to improve its performance.
Predicting Therapeutic Efficacy
Predicting Therapeutic Efficacy- Picture Courtesy: SOTAX
Drug dissolution apparatus is a gold standard when it comes to evaluating and predicting drug therapeutic efficacy using dissolution data. It produces scientific data regarding the timing of dissolution that envisages bioavailability and onset of action. This predictive model aims to identify potential problems like poor dissolution rate that could negatively impact the performance and effectiveness of the drug.
Ensuring Batch-to-Batch Consistency
Ensuring Batch-to-Batch Consistency- Picture Courtesy: JAMP Pharma Manufacturing
Drug dissolution apparatus offers noteworthy insights into the effectiveness of dosage forms in different batches. It measures the uniformity in dissolution rate for each batch and guarantees there is consistency between batch-to-batch. This ensures that drug products developed across various batches and conditions will deliver the same therapeutic response.
Compliance with Regulations- Picture Courtesy: Copley Scientific
Dissolution testing is a requisite part of the approval process of drug standardization authorities, such as the FDA and EMA. So, manufacturers use drug dissolution apparatus to fulfill important approval protocols and ensure that dosage forms are manufactured according to stringent predefined specifications.
3.What are the types of drug dissolution apparatus?
Different pharmacopeias (Japanese; JP, US; USP and European; Ph. Eur.) agree on four types of drug dissolution apparatus, while according to USP, there are seven types of drug dissolution apparatus. We will detail all seven kinds of drug dissolution apparatus one by one.
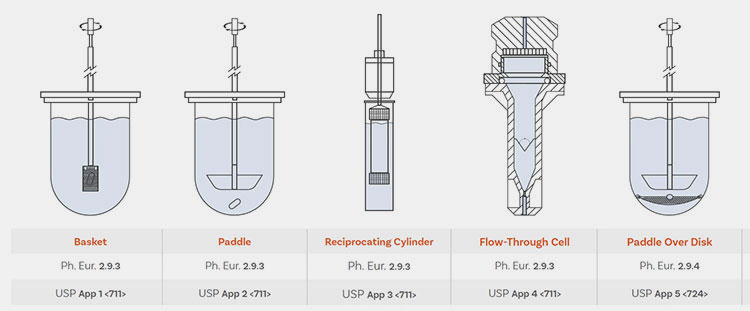
Types of Drug Dissolution Apparatus- Picture Courtesy: Antech
Basket Apparatus (USP Apparatus I)
Basket Apparatus (USP Apparatus I)
This apparatus was the first drug dissolution apparatus employed for studying dissolution profiles in 1970. Till today, it has remained the most common apparatus, accounting for a bulk proportion of dissolution testing across the world alongside apparatus II.
It is constructed with a cylindrical basket, vessel (manufactured using glass or other non-reactive material), motor, drive shaft, and vessel cover. The latter is integral in minimizing the evaporation of the sample; however, it has an adequate opening for positioning of thermometer and extraction of samples.
It is well-suited to analyze dissolution patterns of capsules, tablets, chewable, and extended-release drugs. However, it could not be used to evaluate pills that disintegrate into finer powers, as they may escape from the basket.
It does not give repeatable results, due to its inconsistent agitation. Particles stick to the basket, causing clogging.
Paddle Apparatus (USP Apparatus II)
Paddle Apparatus (USP Apparatus II)
It is usually the first-choice method for scrutinizing the rate of dissolution. The paddle-type apparatus has the same design as that of the basket-type apparatus, except for the stirring component, which is substituted with a paddle (three-blade stirrer) for a basket. This change is to prevent the migration of fine residues into various dissolution regimes.
The paddle is pivotal in agitating the dissolution medium. This apparatus is comprised of a vessel, drive shaft (holding paddle), motor (rotates paddle), water bath, and cover.
Sinkers or wire helix are attached with dosage type- capsules- to hold them down in a stable position, as otherwise they will float away. It is highly suitable for oral dosage forms (tablets and capsules) and suspensions.
Apparatus I and Apparatus II are popular because of their simple design, convenient operation, and robustness; however, they have certain limitations, for instance, it is difficult to realistically induce changes found in the gastrointestinal tract. They also have shaft positioning issues and wobbling.
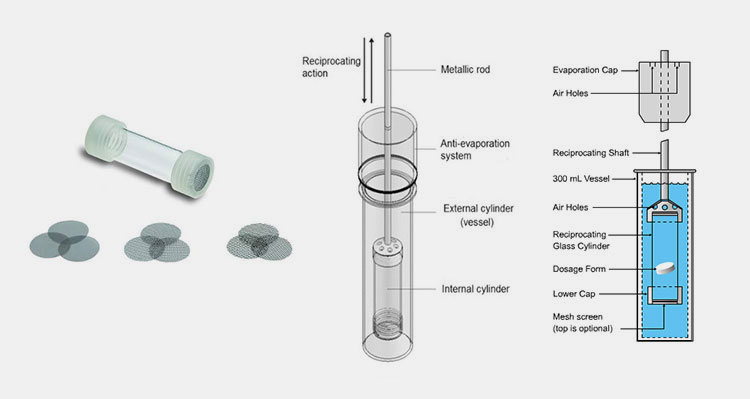
Reciprocating cylinder Apparatus (USP Apparatus III)
Reciprocating cylinder Apparatus (USP Apparatus III)
It is also called bio-dis apparatus. It was first adopted in 1991 for accessing the dissolution behavior of extended-release tablets. The reciprocating cylinder apparatus is designed with a pair of cylindrical glass vessels having flat bottoms, a pair of glass reciprocating cylinders, screens- placed on top and bottom of glass cylinders to keep the dosage form in place, motor and drive unit to oscillate the cylinders up and down in the vessel carrying dissolution medium.
It takes about 6 days to run tests. It easily mimics mechanical and physiological changes that impact the release of drugs in the digestive system by altering the media makeup, agitation speed, and dissolution time; the inner sample-containing reciprocating cylinder is changed between outer vessels to aid these analyses. However, it is difficult to maintain sink conditions in this type of drug dissolution apparatus.
Flow-Through Cell Apparatus (USP Apparatus IV)
Flow-Through Cell Apparatus (USP Apparatus IV)- Picture Courtesy: SOTAX
This apparatus features with reservoir, (offers fresh medium), a pump for dissolution liquid, a flowthrough cell, and a water bath. The dosage form is placed on a support in the middle of the cell, the latter is submerged in a water bath, heat exchanger, or heating jacket.
In this system, the medium is taken from the reservoir and circulated to the cell having dosage form. There are two types of flow-through cell apparatus- open systems and closed systems. In an open system, fresh dissolution liquid is circulated to the cell every 30 minutes and then sample fractions are extracted from the system.
Conversely, in a closed system, the dissolution liquid is propelled into a circle but is not substituted with fresh medium.
Flow-through apparatus maintains consistent sink conditions, thereby, exposing samples to a continuously circulating dissolution medium. It is run at various temperatures and flow rates; thus, it has flexibility in processing quantities of dissolution medium and types of dosage forms, such as low-solubility, modified- and extended-release tablets, capsules, powders, suppositories, and medical devices like implants.
Paddle-over-Disc Apparatus (USP Apparatus V)
Paddle-over-Disc Apparatus (USP Apparatus V)
It is a modified version of a paddle-type apparatus, as it also contains a stainless steel disc in addition to a paddle. This disc assembly is featured in the paddle-over-disc apparatus to accommodate transdermal patches. The patches are placed in such a way that their release side is collateral to the paddle blade.
It is essential to keep a length of 25±2 mm between the lower end of the paddle and the upper part of the disc. To ascertain faster drug release, it is imperative to prevent dead zones between the disc and the lower end of the vessel.
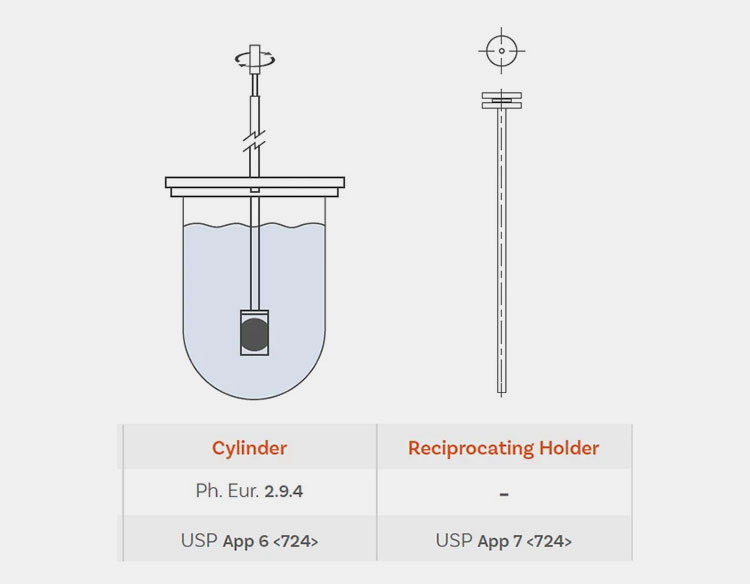
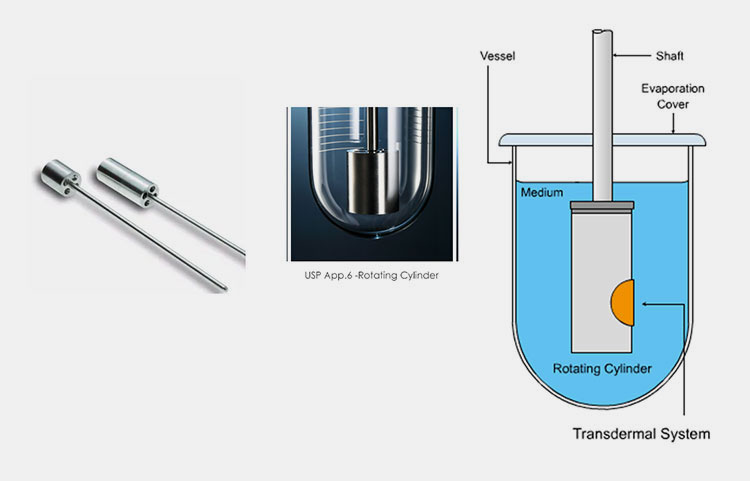
Rotating Cylinder Apparatus (USP Apparatus VI)
Rotating Cylinder Apparatus (USP Apparatus VI)
It is identical to a basket-type apparatus in its design and working, except, in its construction, the basket and shaft are substituted by a stainless steel cylinder. The drug product (transdermal patches) is put into a cylinder and the latter rotates in the vessel- loaded with dissolution liquid. A cuprophan is utilized in a rotating cylinder apparatus to withdraw the drug that is dissolved in the medium. However, cylinder size limits the kinds of transdermal patches for testing.
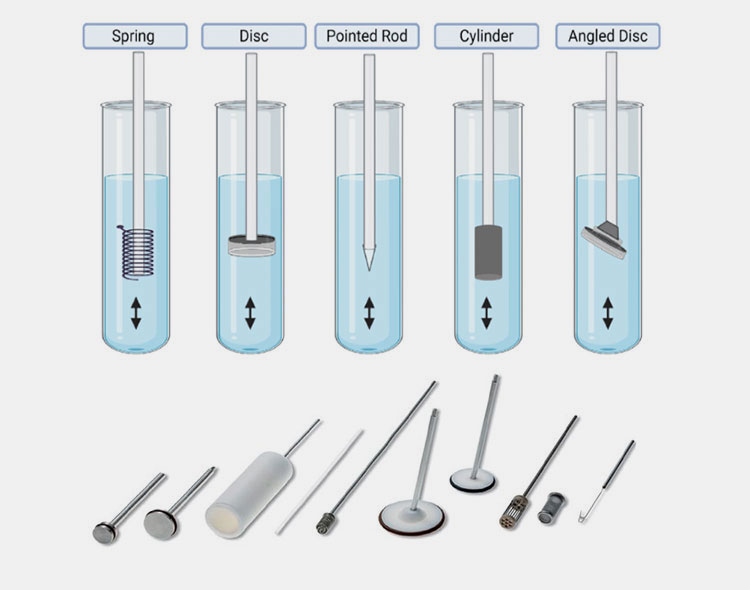
Reciprocating Holder Apparatus (USP Apparatus VII)
Reciprocating Holder Apparatus (USP Apparatus VII)
It is also termed a reciprocating disc or reciprocating cylinder. It is infrequently employed in the testing of oral solid dosage but is well-matched to low-volume assessment studies, including evaluation of the effect of media variation. There are many types of reciprocating holder apparatus, which originated from a sample oscillating holder. This part can be a disk, cylinder, spring, or acrylic rod in different variants of this apparatus.
It has an assembly comprising containers (flat-bottom cylindrical) manufactured using glass or other inert substances, motor, and drive components. The motor and drives reciprocate the sample holders and containers vertically in the test medium. This reciprocating movement promotes mass transfer between dissolution fluid and sample.
This apparatus is suited to the identification of small differences in the drug release profile of poorly soluble or extended-release medications.
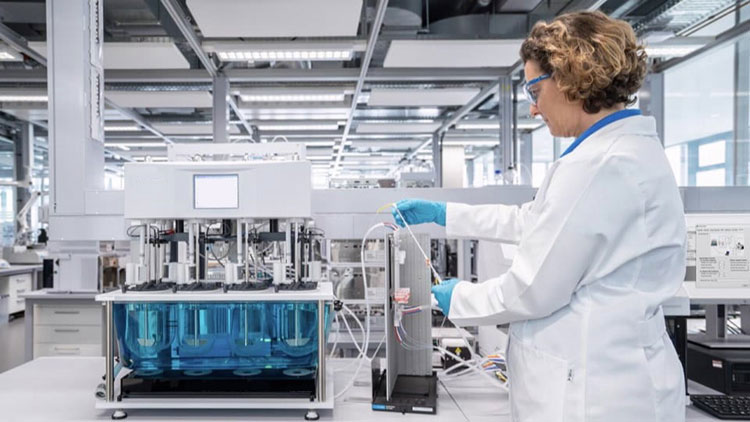
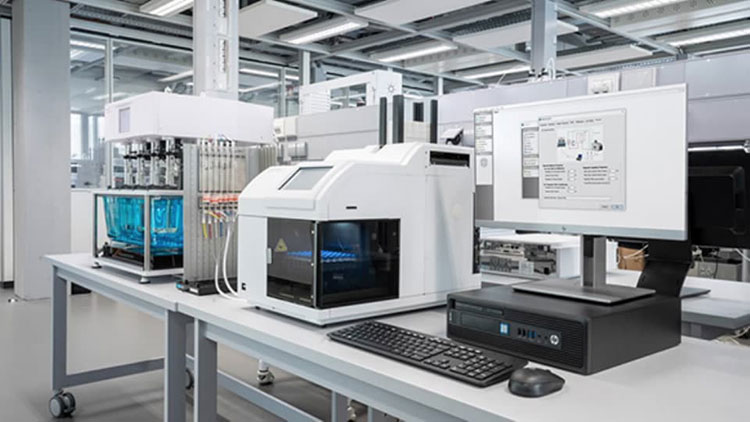
4.How does the drug dissolution apparatus work?
There are multiple stages in the working of the drug dissolution apparatus. The working of the drug dissolution apparatus is subdivided into three main steps- pre-run, dissolution-run, and post-run. For your understanding, we are penning the basic sequence of steps that happen earlier, during, and afterward the evaluation testing.
Working of the Drug Dissolution Apparatus- Picture Courtesy: Eurofins
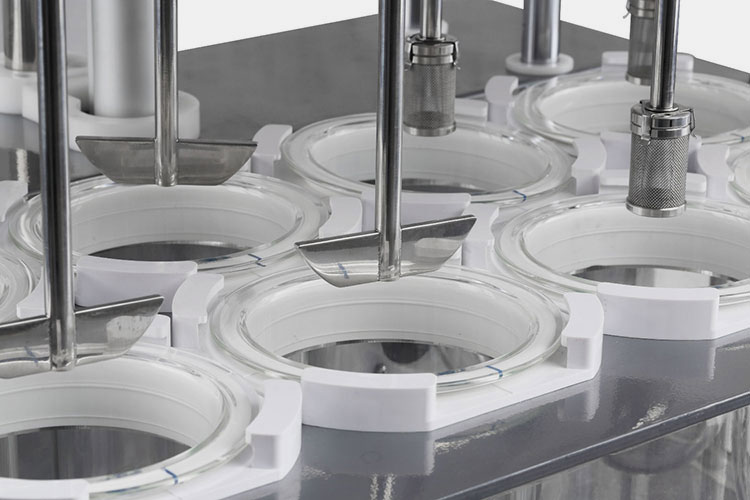
Assembly Set-up
Assembly Set-up- Picture Courtesy: OSTICK+WILLIAMS
First, the drug dissolution apparatus is completely and thoroughly cleaned using mild detergent and wet cloth. Then, the dissolution vessel and stirring or oscillating system- paddles, baskets, reciprocating cylinder, and reciprocating discs are assembled.
Media Preparation
Media Preparation
The dissolution medium is prepared following standard practices and is introduced in each vessel assembly. This medium is a liquid that imitates the physiochemical changes in the gastric tract. Then, the vessel assembly containing the medium is gently placed in the water bath or heat exchanger.
Dosage Form Introduction
Dosage Form Introduction
In the next step, the sample or dosage type is centrally positioned with the vessel assembly in such a way that it does not come in contact with the sides of the agitating apparatus. Then, a stirring mechanism is attached to the vessel.
The stirring or agitation system, such as baskets, paddles, reciprocating cylinders, etc. allows the sample to continuously interact with dissolution fluid.
Sample Withdrawal and Filtration
Sample Withdrawal- Picture Courtesy: Pharmaceutical Processing World
Samples are extracted from the dissolution liquid at preset intervals (5, 10, 15, 20.25, 30. 45, 60) using sampling or drain ports to inspect the quantity of formulation dissolved in the medium. Before sample analysis, the dissolution medium is filtered to eliminate the undissolved residues in the sample.
Sample Analysis and Cleaning
Sample Analysis and Cleaning
After the dissolution run, the samples are evaluated using methods like UV spectrophotometry or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to estimate the quantity of dissolved product. The dissolution data is plotted in the form of a curve between the time and percentage of drug dissolve.
Finally, the drug dissolution apparatus is cleaned to prevent contamination between testing batches.
5.What are the primary applications of drug dissolution apparatus?
Data acquired from the drug dissolution apparatus direct the selection of excipients and manufacturing strategies to increase the bioavailability and absorption of the drug products. Consequently, this apparatus has proven its worth in formulation development areas. Here are some primary applications of drug dissolution apparatus:
Pharmaceutical Industry
Tablets and Capsules
This industry is the main area in which drug dissolution apparatus is an essential part of routine testing. It helps in differentiating drug ingredients, excipients, as well as formulations based on their capability to boost bioavailability. The information gathered from the drug dissolution apparatus is integral in developing pharmacokinetic profiles to speed up drugs to market.
Moreover, bioequivalence studies of generic and branded drugs heavily depend upon the conclusions drawn from dissolution testing.
Biotechnology Industry
Nanoparticles in Biotechnology- Picture Courtesy: BBC
Engineering of different kinds of biopharmaceuticals is carried out in the biotechnology industries, so the drug dissolution apparatus is a crucial instrument, that studies the release profile of different proteins and enzymes for their respective delivery systems like liposomes and nanoparticles. It also tests the release rate of biological molecules from implants.
Cosmetic Industry
Cosmetic Capsules- Picture Courtesy: bellaweb.it
The use of transdermal patches and soft gelatin capsules is widespread in the cosmetic industry; hence, cosmetic developers estimate the dissolution extent of active substances in the cosmeceutical by the drug dissolution apparatus.
Nutraceutical Industry
Nutraceutical Capsules- Picture Courtesy: Nested Naturals
Dissolution testing is a fundamental procedure to assure the quality and safety of nutraceuticals, such as probiotics, prebiotics, antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and hormones. Therefore, the drug dissolution apparatus helps researchers envisage the in vivo absorption and efficacy pattern of nutraceutical supplements.
Veterinary Industry
Veterinary Capsules- Picture Courtesy: Cat in the Box LLC
This industry involves the engineering of drugs for pet and veterinary care, consequently, to test the dissolution kinetics of veterinary medications, the drug dissolution apparatus is vital to formulation protocols. It estimates the consistency in the release of therapeutics and establishes a drug profile that is ideal for clinical efficacy.
Forensic Industry
Forensic Drug Analysis- Picture Courtesy: Bruker
In this industry, the drug dissolution apparatus compares the release profiles of suspicious forged products to original products for detecting counterfeited pharmaceuticals. This instrument also studies adulterated products to identify the incidence of impure and foreign materials.
6.What are common testing conditions for drug dissolution apparatus?
Testing Conditions for Drug Dissolution Apparatus- Picture Courtesy: Agilent
The testing conditions for the drug dissolution apparatus are imperative to attain precise and repeatable results. Here are a few common testing conditions:
| Dissolution Medium | Different varieties of media, such as stimulated gastric fluid (SGF), stimulated intestinal fluid (SIF), phosphate buffer, and other buffer media are frequently utilized for assessing dissolution profiles. SGF and SIF are usually used for their ability to imitate biophysical changes in the stomach and small intestine, respectively. |
| Volume of Dissolution Medium | Generally, about 500-1000 ml of dissolution medium is used for conducting the analysis. |
| Standard Temperature | The temperature of the drug dissolution apparatus is about 37°C ± 0.5°C to mimic physiological temperature. |
| pH | The standard pH of the dissolution medium is about pH 1.2, pH 4.6, and pH 6.8. |
| Sink Conditions | Sink conditions are retained in the drug dissolution apparatus to ensure that the quantity of dissolved product does not affect the dissolution rate, allowing a more precise evaluation of the intrinsic release rate. |
7.What is the rotational speed of the basket and paddle drug dissolution apparatus?
Rotational Speed of Basket and Paddle Drug Dissolution Apparatus- Picture Courtesy: Scientz
The purpose of the rotational speed of the basket or paddle apparatus is to induce forces similar to that of peristaltic movement exhibited by the stomach and small intestine. However, the original forces observed within the stomach offer a higher level of mixing than those generated by a basket or paddle.
The standard rotational speed of basket-type drug dissolution apparatus is 100 RPM, which is usually used for drugs that are released more gradually or require a higher level of agitation. This drug dissolution apparatus uses 50 RPM for immediate-release drugs.
The rotational speed range for paddle-type drug dissolution apparatus is about 25-75 RPM. It has a drive speed of 50 RPM for capsules and 25 RPM for suspensions.
8.How can you extend the lifespan of the drug dissolution apparatus?
Maintenance of Drug Dissolution Apparatus- Picture Courtesy: Agilent
Prolonging the lifespan of the drug dissolution apparatus is vital for acquiring maximum advantage out of investment. For this, it is essential to consistently maintain, appropriately use, and, strictly comply with manufacturing protocols. Some of the key strategies to ensure the maximum working life of the instrument are:
| Regular Maintenance
|
Visually evaluate various components of the drug dissolution apparatus, like stirring systems, vessels, and water baths. Thoroughly check for evident wear and tear, corrosion, break lines, cracking, etc. Immediately replace damaged components to avoid severe malfunctioning of the equipment. |
| Routine Calibration
|
Train operators to routinely calibrate machine components like temperature sensors, speed regulators, and drive systems. Also, check the alignment of parts of the instrument daily. |
| Cleaning
|
Disassemble various parts for deep cleaning to avoid cross-contamination. It is necessary to wash and rinse the drug dissolution apparatus to prevent product accumulation on different parts. It is recommended to use non-abrasive cleaning agents to avert the degradation of delicate parts. |
| Correct Storage Procedure | Store delicate components, such as baskets, paddles, and cylinders in a clean and dry setting to avoid rusting, warping, and wear and tear. Cover the apparatus to safeguard it from external agents, for instance dust, or debris. |
| Proper Handling | Follow best practices as recommended in the operational manual provided with the apparatus. Always set the correct parameters for rotational speed and temperature. Running the instrument at incorrect settings could lead to burnout of motors, bearings, or mechanical stress. |
9.How to troubleshoot basic problems associated with drug dissolution apparatus?
A drug dissolution apparatus is a machine that, like others is prone to errors, which significantly impact the evaluation and analysis of testing results. However, with basic skills and knowledge, these common problems are easily troubleshooted. Some prevalent problems of the drug dissolution apparatus along with their solutions are mentioned below for your information.
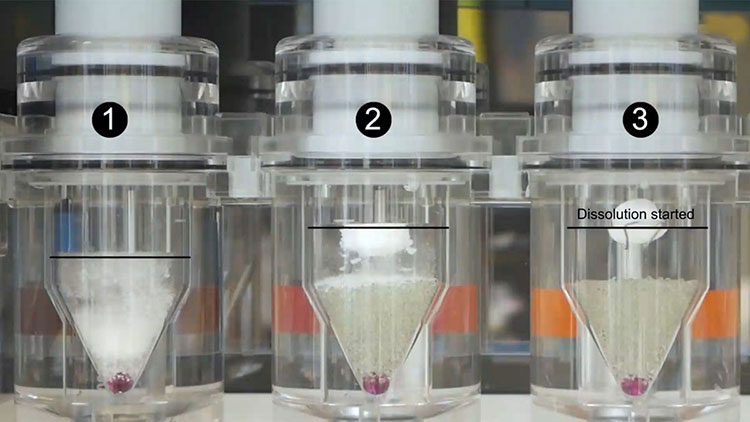
Air Bubble in Dissolution Medium
Air Bubble in Dissolution Medium- Picture Courtesy: SOTAX
The entrapping of air while mixing the dissolution medium or during the rotation of the equipment leads to its adherence to the dosage types or apparatus, disrupting the dissolution process.
Troubleshooting
It is advised to degas the medium before running the apparatus with the use of various methods, for instance, vacuum filtration, heating, or helium spraying. After putting the testing sample, make sure to visually inspect the medium for bubbles.
Variability in Test Results
Variability in Test Results- Picture Courtesy: Full Spectrum Lab Services
There is a huge inconsistency between the test results of different batches or they do not align with the standard dissolution profile.
Troubleshooting
To reduce the test variability, first, check the calibration status of the apparatus, particularly its rotational speed, temperature, and shaft positioning. Properly position the paddle or other stirring mechanisms at the required height (25 ± 2 mm for paddles and baskets) and in the center. Ensure every vessel in the equipment is completely cleaned and free of blemishes. Verify there is no wobbling of baskets or paddles and they are not touching the vessel. Degas the liquid before starting.
Deviation in Temperature Reading
Deviation in Temperature Reading- Picture Courtesy: Erweka
It is observed that the temperature of the dissolution liquid fluctuates from the standard 37°C ± 0.5°C, contributing to variable outcomes.
Troubleshooting
It is suggested to follow these instructions to solve this issue, such as verifying that the heating system is operating correctly. Fill the water bath at the proposed level. Calibrate the temperature probe using a standardized thermometer. Dissolution vessels should be appropriately insulated to keep the temperature of the apparatus at a specified range.
Inconsistent Sampling
Inconsistent Sampling
Sometimes, the sampling probe is not functioning properly, leading to inconsistency in sample collection or incomplete sampling at planned interludes.
Troubleshooting
This problem is solved by ascertaining that there is no clogging or blockage in the sampling ports. Check the proper working performance of the sampling timing system to ensure samples are taken at the right intervals automatically. Inspect the sample extraction tubing for blockage or air bubbles and ensure that it is particle-free.
Vessel or Water Bath Leakage
Vessel or Water Bath Leakage- Picture Courtesy: Pharma Test
If there is leakage in the water bath or vessel, it could cause incorrect temperature control or medium volume level.
Troubleshooting
The solutions for this problem, include: inspection of seals or O-rings on the water bath or vessel for damage and replacing them if required. Properly align dissolution vessels in the water bath or heating jacket to prevent leaks.
Conclusion
The drug dissolution apparatus has evolved continuously to address the limitations of dissolution testing. It has gained importance for checking the impact of changes in drug formulation during development, scale-up, and post-approval. There are multitudes of the drug dissolution apparatus, each with a specific set of features and advantages. The choice of using the right type of equipment is typically based on the properties of dosage forms. Investing in the latest model of the drug dissolution tester is the right decision that decreases issues like test variability, inhomogeneity in mixing, and poor prediction of In vitro-in vivo correlation. If you are overwhelmed regarding the selection of the drug dissolution apparatus, then feel free to get in touch with our sales expert. We, Allpack, are here to address your purchase problems.
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp:+86 18171018586