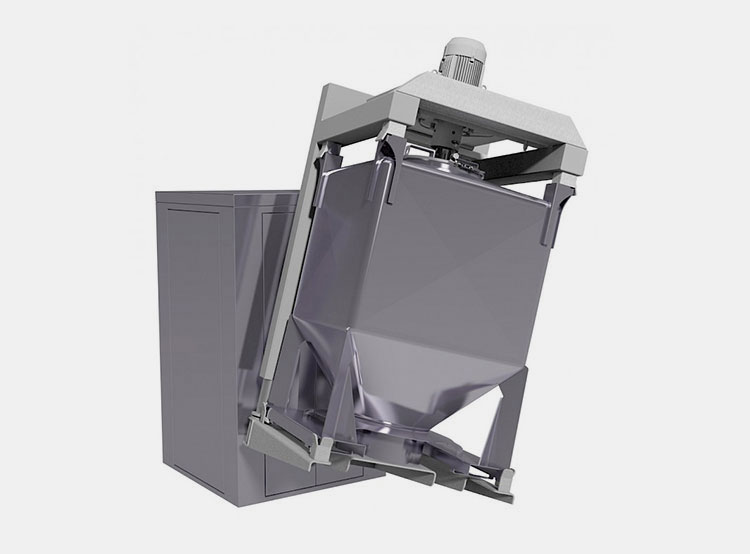
Paddle Blender VS Ribbon Blender: What Is The Different?
Paddle Blender VS Ribbon Blender: What Is The Different?
In the world of industrial manufacturing, the blending process can’t be ignored! Side by side, the major options such as paddle blender and ribbon blender are also considered popular tools due to versatility and efficiency.
Both of them possess distinctive properties and are suitable for various uses. In this article, paddle blender VS ribbon blender: what is the difference, you are going to explore the key variations between these two equipment.
Let’s start it!
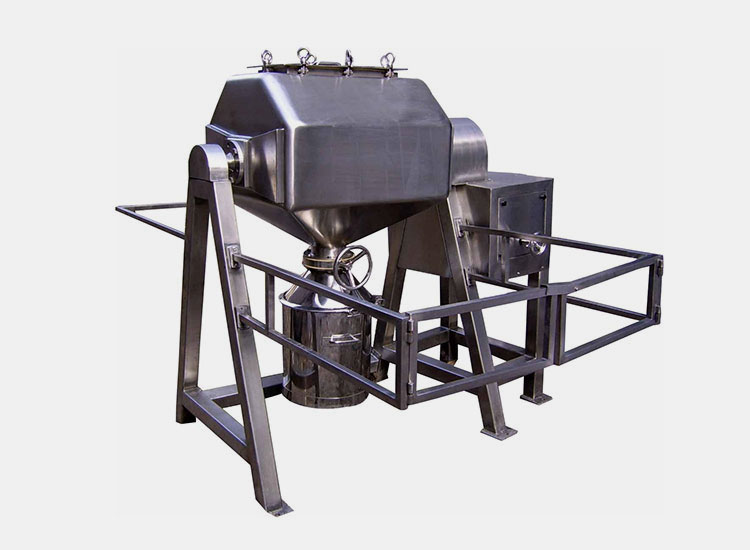
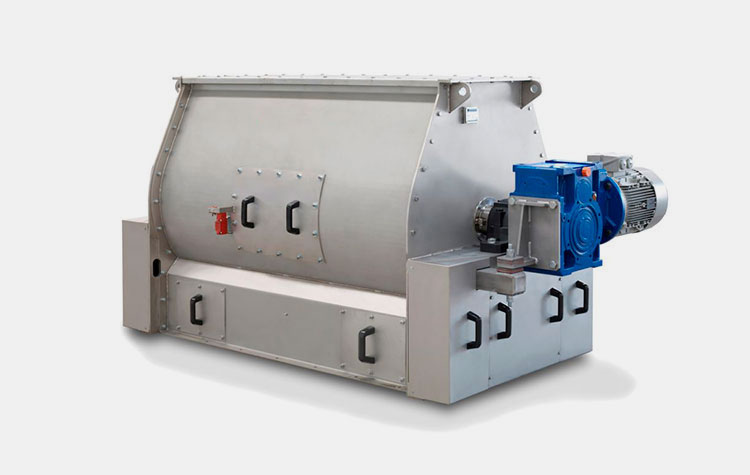
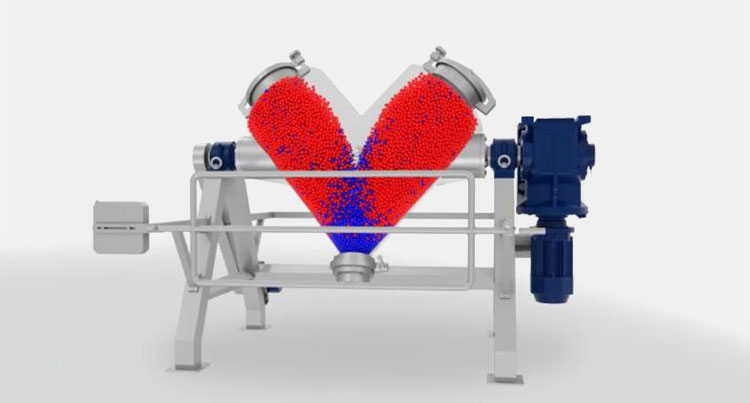
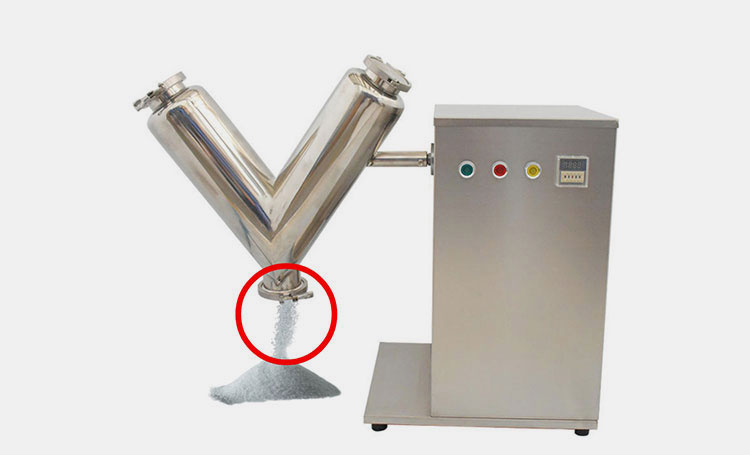
1.What is a paddle blender?
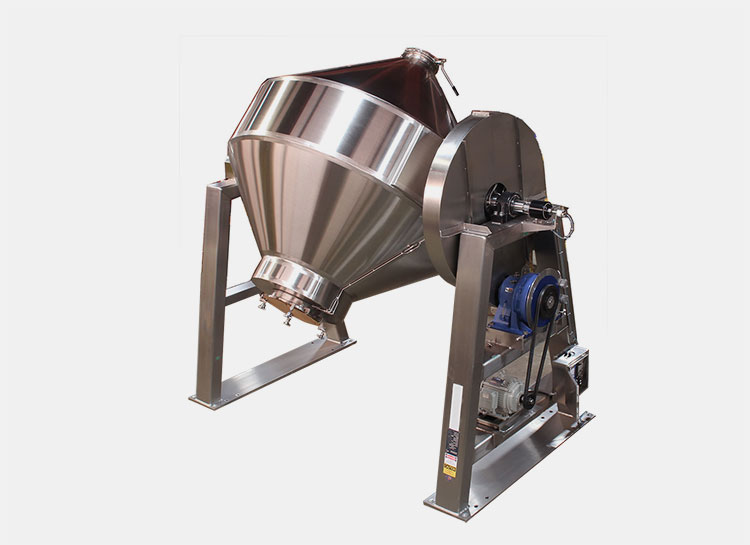
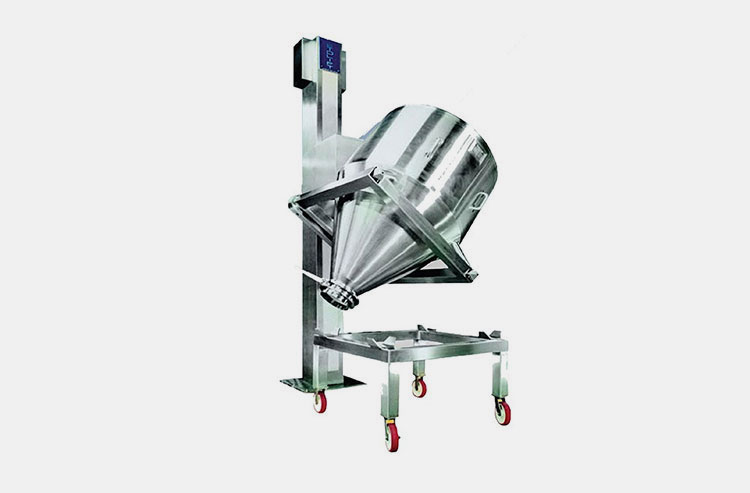
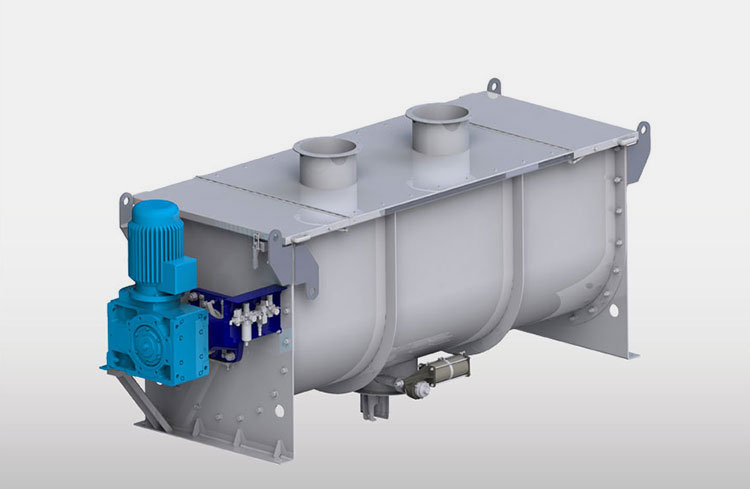
Paddle Blender- Picture Courtesy: PreMix
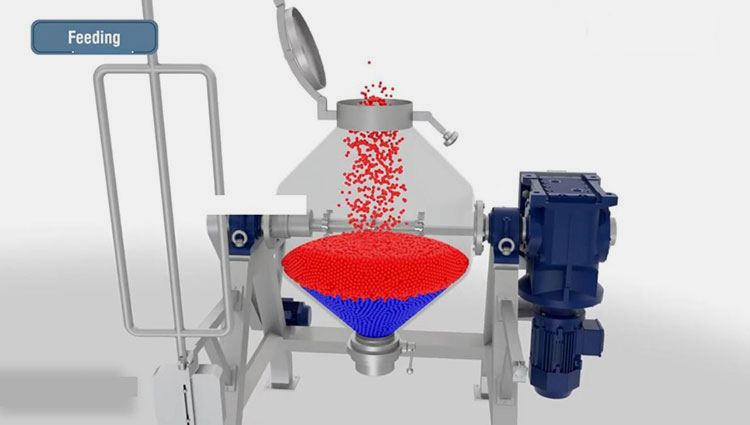
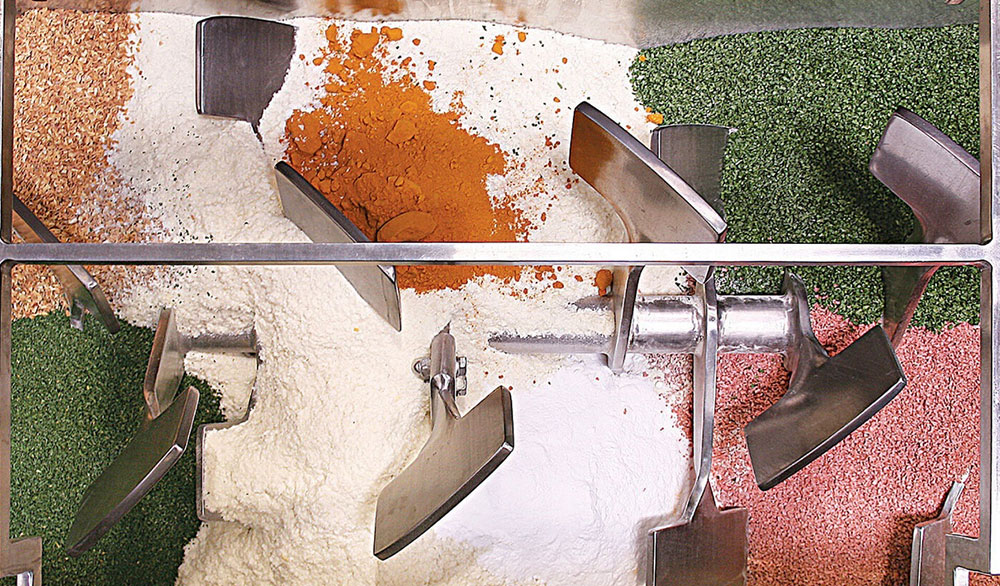
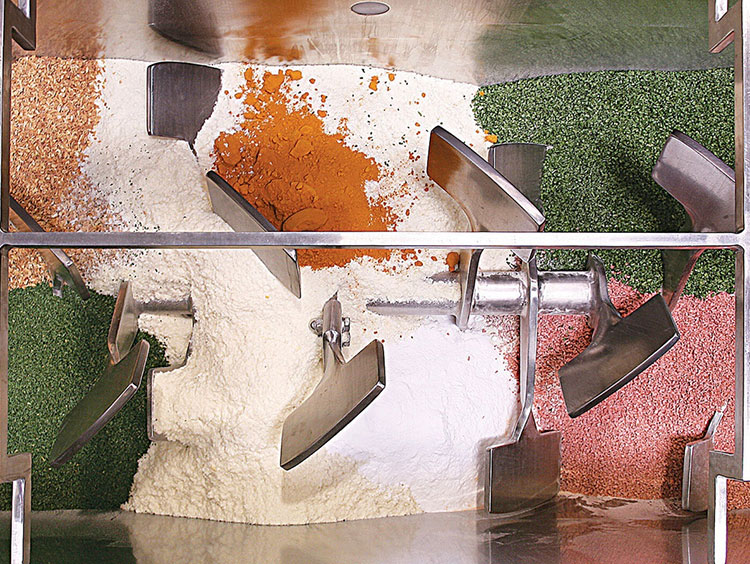
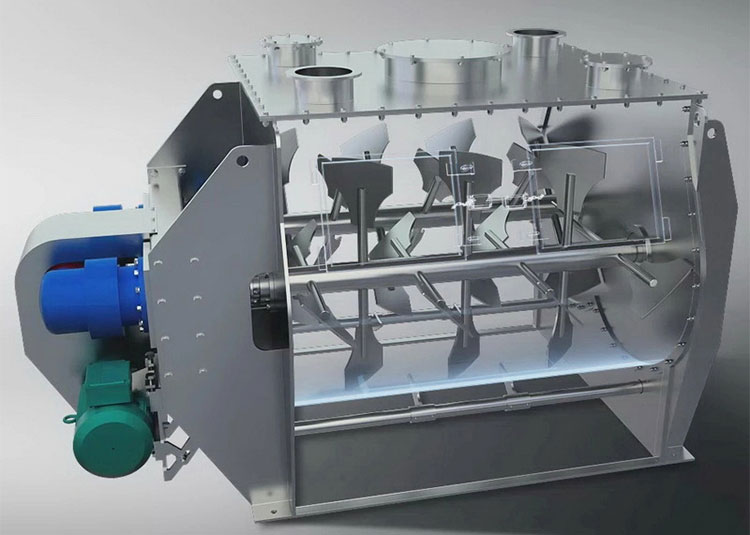
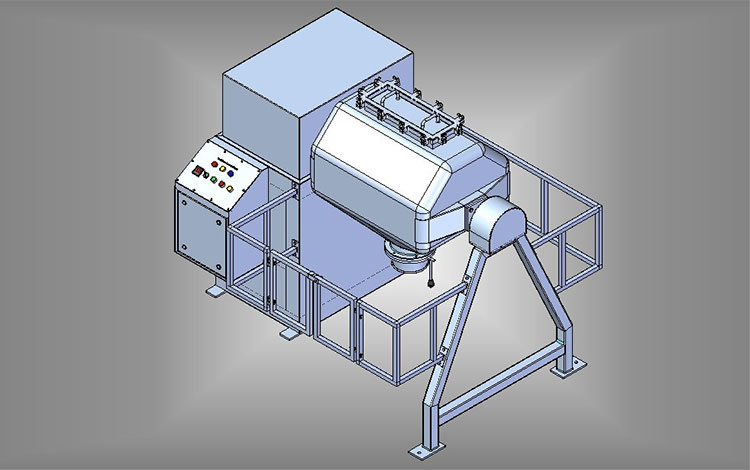
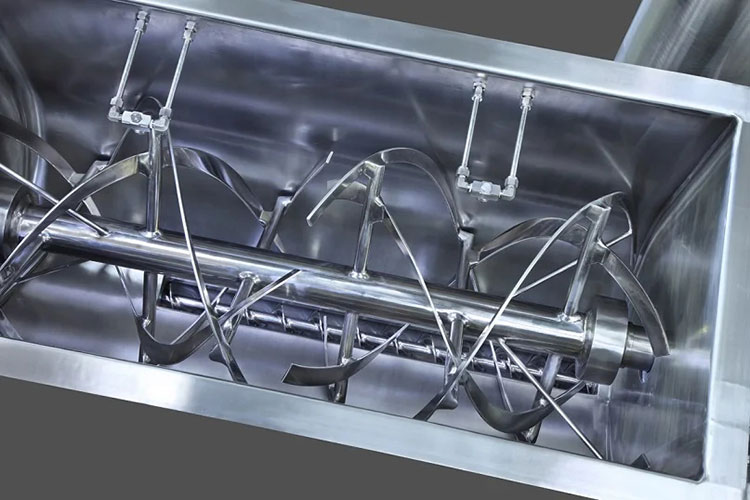
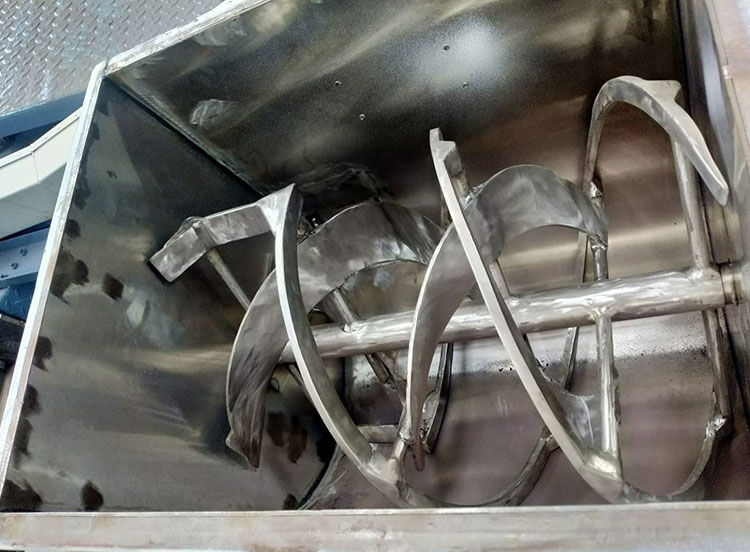
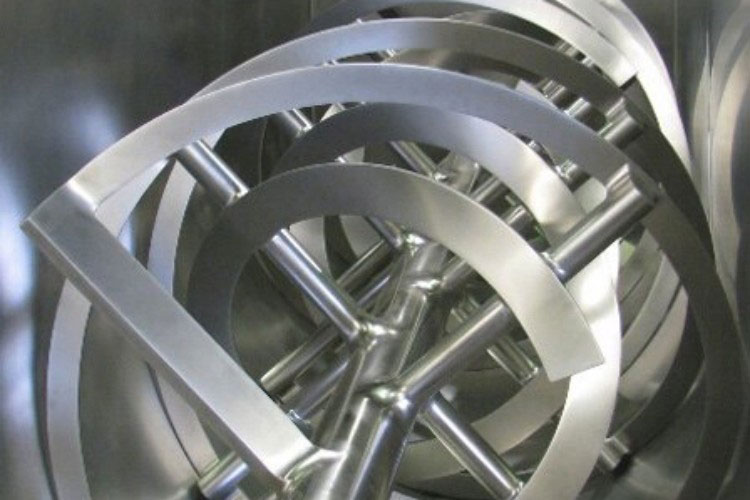
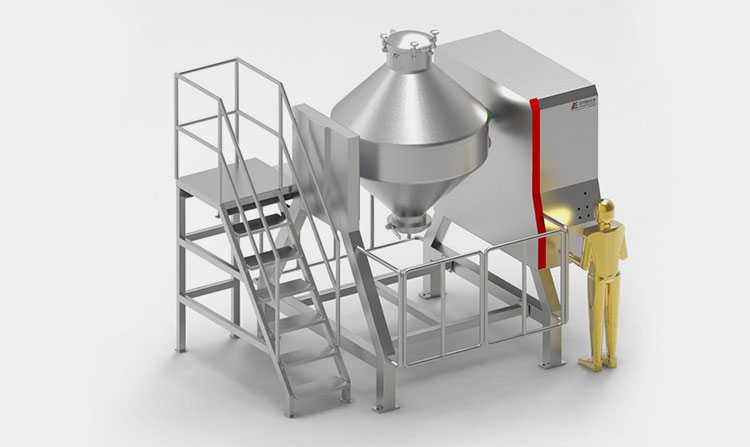
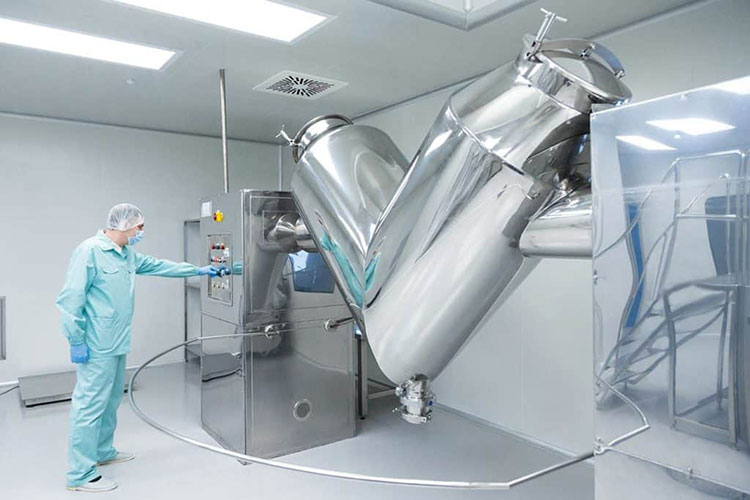
A paddle blender is a subcategory of connective mixer, whose name is derived from the shape of its impeller, which is in the paddle form. A paddle blender is also called a mass mixer or non-gravity blender. It performs mixing by the agitation of the materials. It is composed of a stationary container and an automatically rotating impeller.
In this type of blender, the mixing intensity is very high, resulting in the suspension of the material in the air and the formation of a turbulent mix. It creates a fluidized zone for effectively mixing the raw feed.
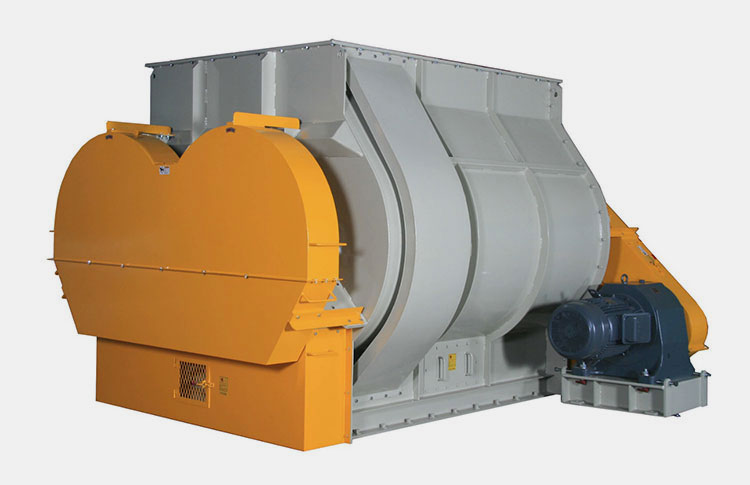
2.What is a ribbon blender?
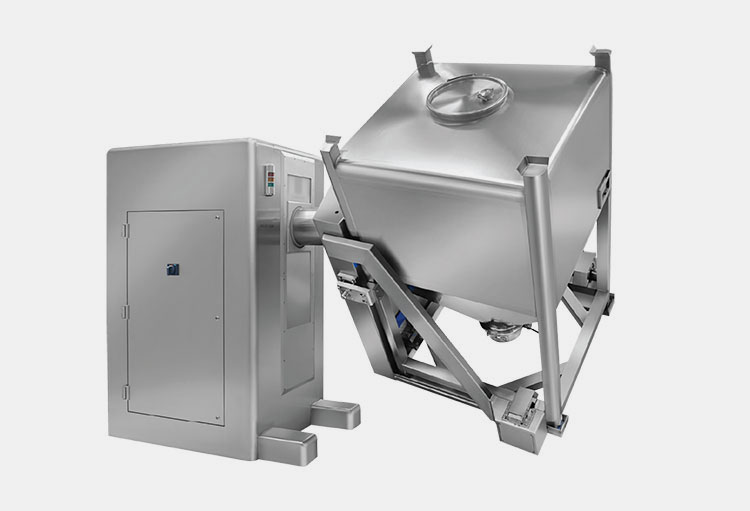
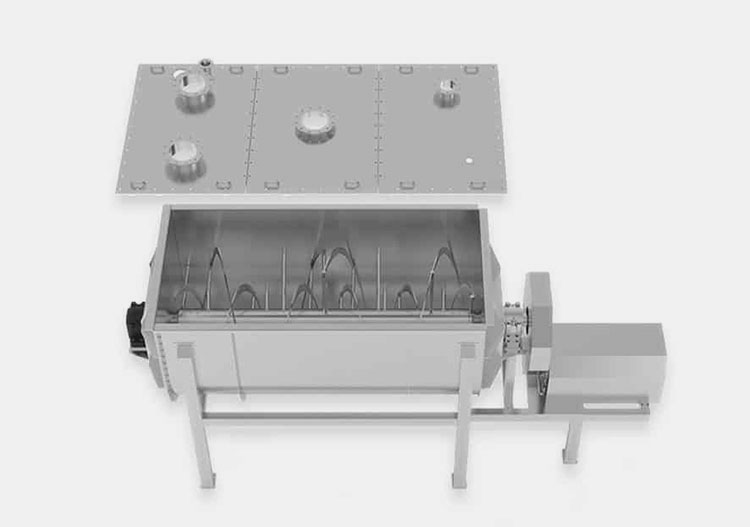
Ribbon Blender- Picture Courtesy: GIMAT srl
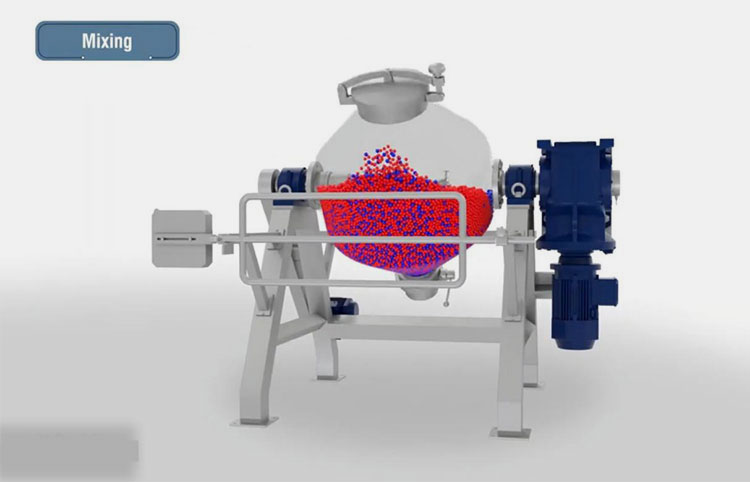
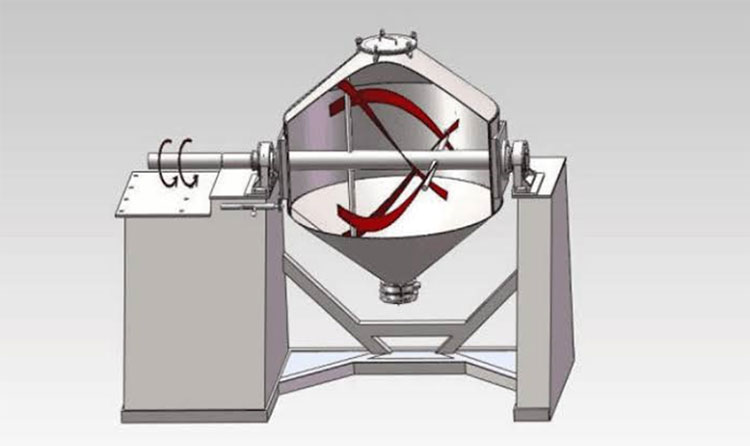
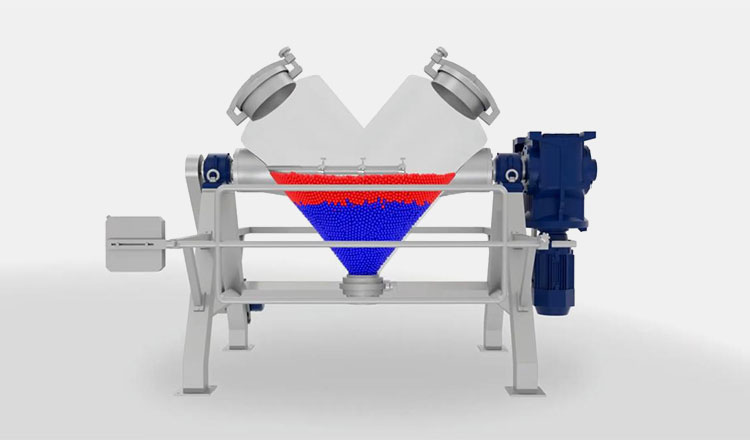
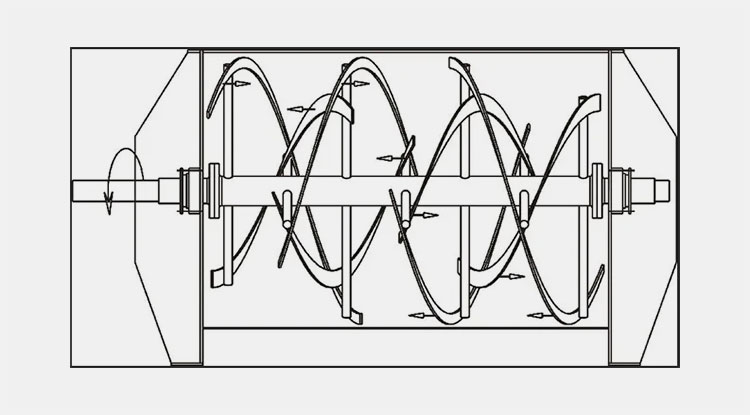
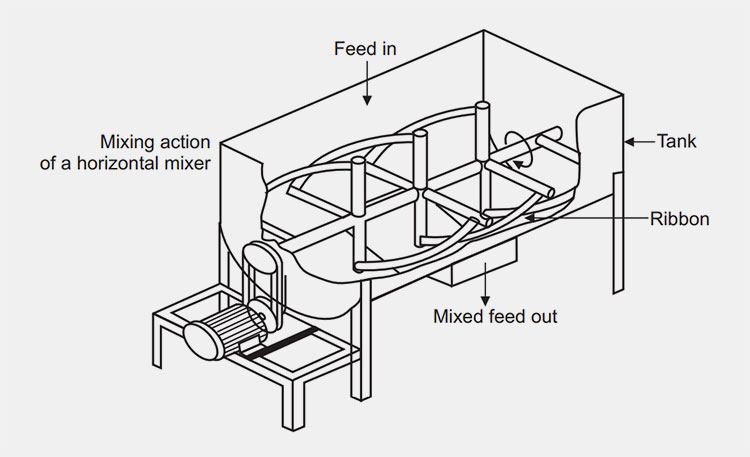
A ribbon blender is a well-renowned mixer, commonly used in industrial settings. Its role is well-established for mixing dry powders, granules, and low-moisture pastes. It has one to three mobile agitators, also known as ribbons, for scattering the materials in the blend. These ribbons rotate back and forth to intermingle the mixture.
The ribbon blender has a straightforward and durable construction and is best for mixing dry particles with decent blending efficiency.
It is a smart-sized industrial equipment and has inner and outer helical ribbons to disperse feed both in inward and outward directions for smooth mixing.
3.Paddle Blender VS Ribbon Blender: What Is the Different?
Paddle and ribbon blenders are increasingly utilized in the manufacturing unit for attaining the ideal mixing effect. Each blender type has its specific set of advantages and the differences between paddle and ribbon blender lies in its design, working, and applications. Let’s discuss their differences in selecting a suitable blender for specific applications.
Design
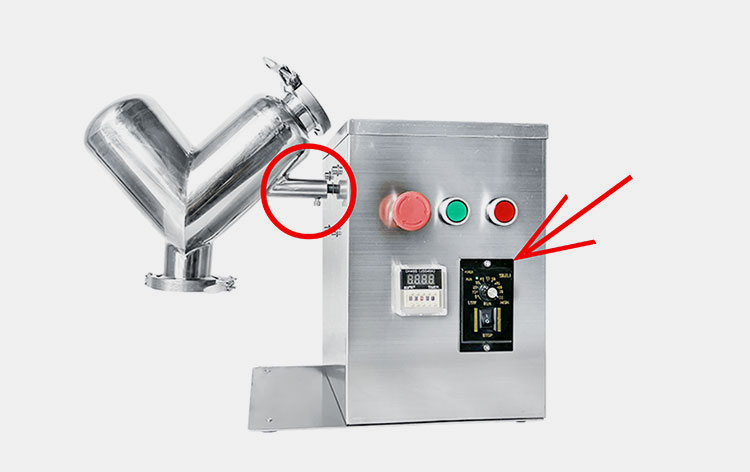
Paddle Blender Design
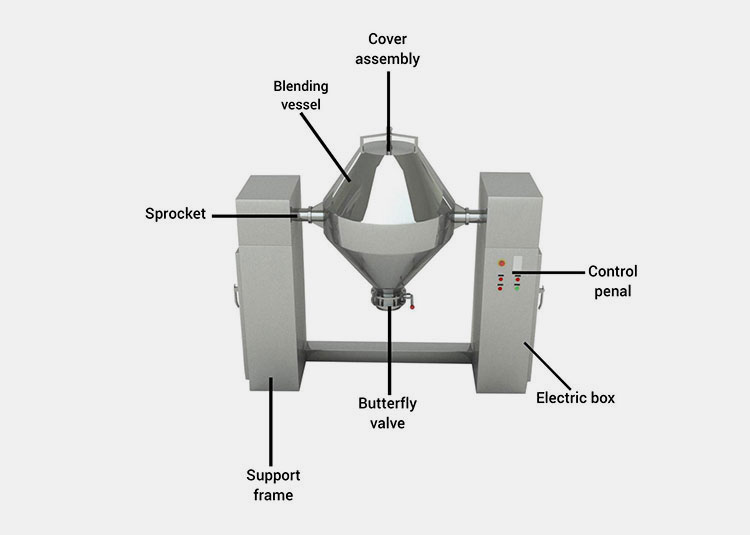
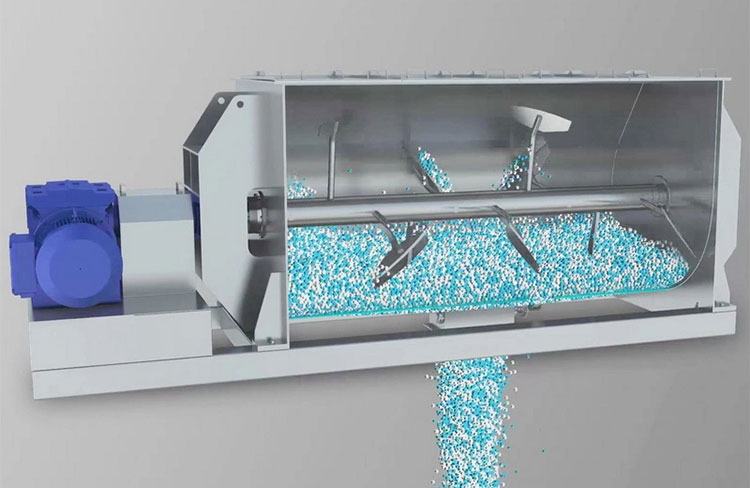
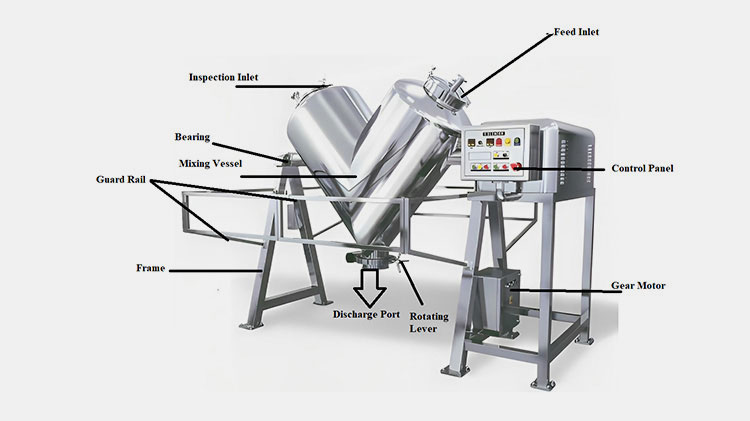
A paddle blender is a substitute for a ribbon blender because its design is quite identical to that of the latter. The main mixing vessel in this machine is a cylindrical U-shaped vessel.
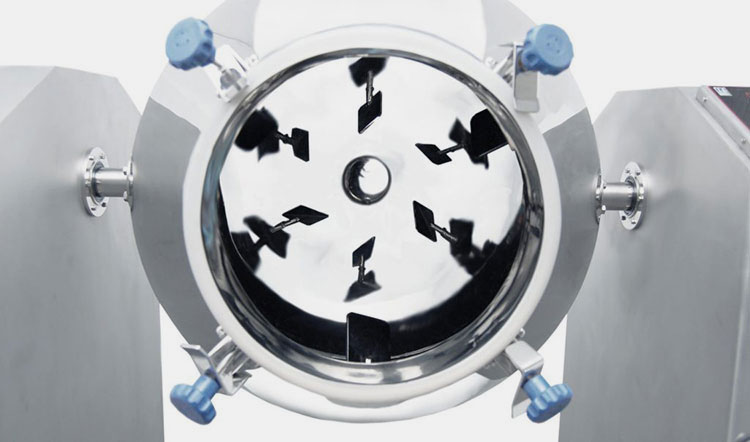
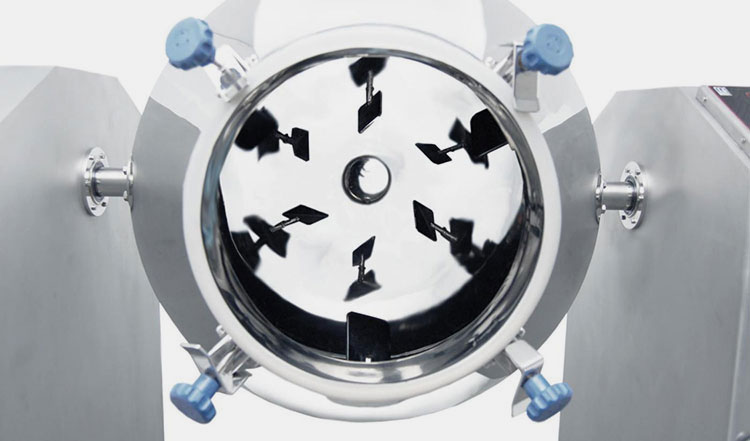
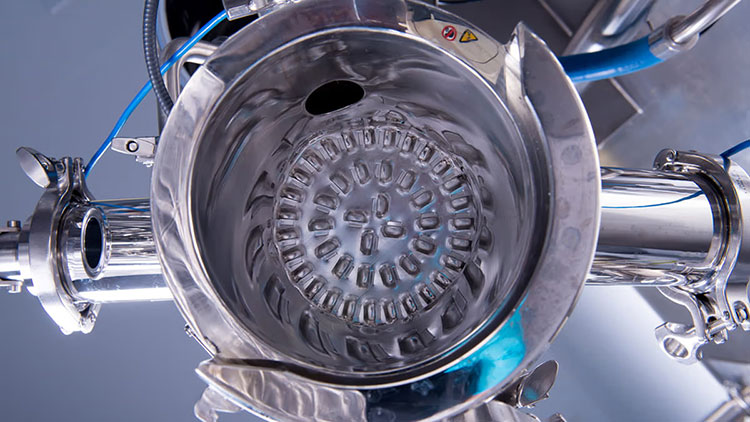
It has a centrally fixed agitator, that has several shafts having radial arms. Multiple short paddles are mounted on these radial arms. These paddles are responsible for agitating the material in the mixing drum.
They are typically arranged in the V or star-shaped configuration. The rotation speed of the paddle blender is provided by the transmission line (motor and drive system). At the bottom portion, a discharge gate or vent is present to allow complete offloading of products.
Ribbon Blender Design
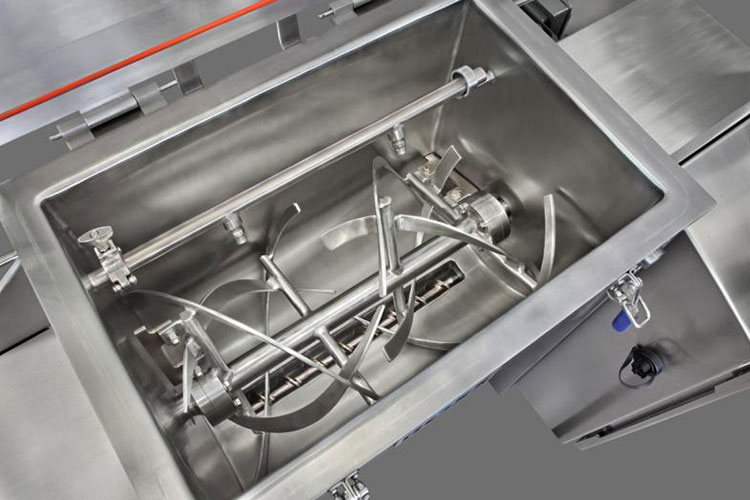
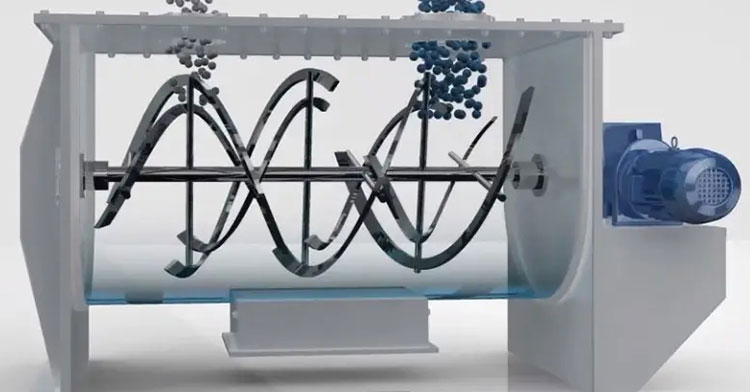
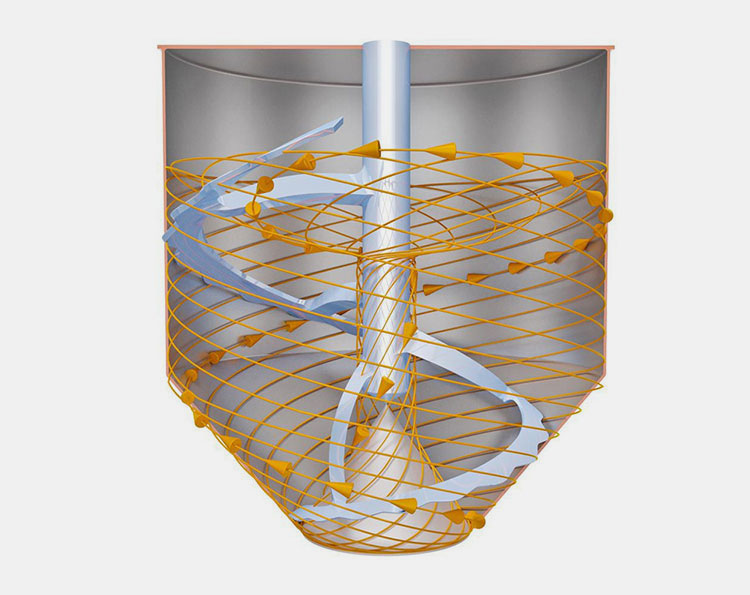
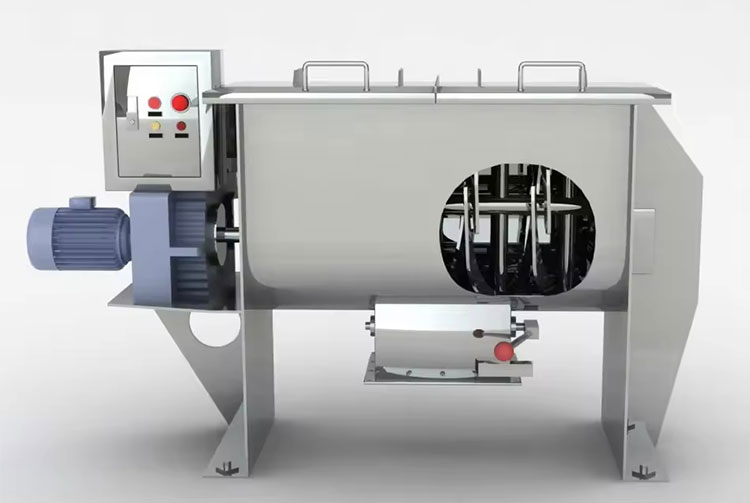
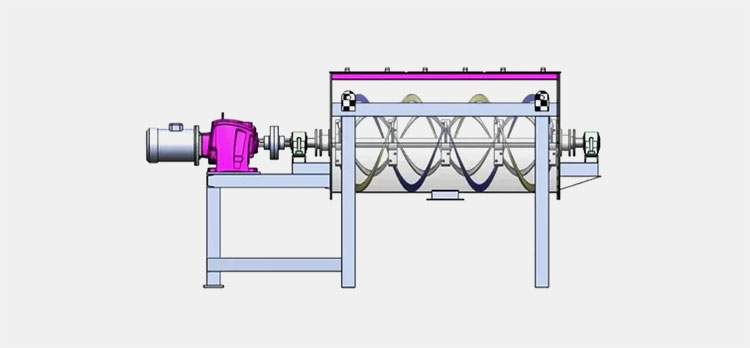
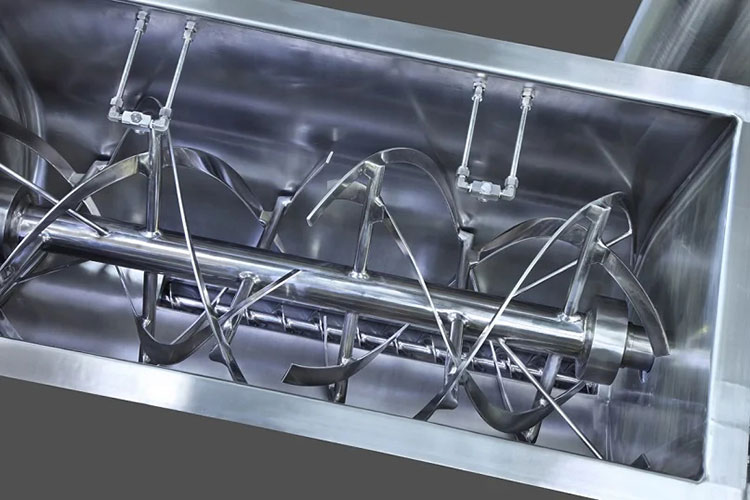
Ribbon blender has a U-shaped shell or trough, either in the horizontal or vertical orientation. An agitator shaft is located centrally inside the mixing vessel. This shaft has mounted helical blades, slanting in various directions, and bears resemblance to metal ribbons. The design of this blender is similar to that of stands of DNA due to its helical blades.
The ribbon blades come in two parts- outer and inner. Outer and inner helical blades are effective in mixing materials in counteracting directions. It is also powered by a motor, gearbox, and coupling. A sealed discharge valve is located at the bottom end to prevent material leakage during operation.
This blending machine is built to accommodate accurate gap tolerances in the walls of the mixing vessel. Moreover, in some cases, it is even engineered with soft material wipers that prevent product accumulation on the edges.
Working
Paddle Blender Working
The laminar flow of different materials, either solid or semi-solid is produced by the paddles fixed on agitators. It has a connective mixing mechanism, which occurs with the loading of materials from the top inlet port. Upon loading, the paddles force the feed in radial and tangential directions. Unlike the ribbon blender, there is no axial movement of paddles lest blades are pitched.
Blades have a larger surface area when compared with the container, so they are easily rotated near the walls of the mixing vessel for even mixing. With the rotation of the shaft and paddles, the materials are lifted and fall, causing a fluidized mixing bed, thus ensuring contact of every particle with the other. This leads to uniform blends, preventing clumps and inconsistencies.
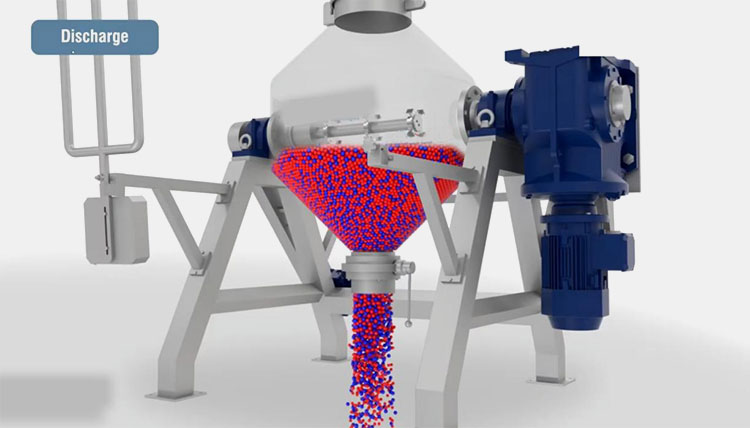
The materials after thorough blending are removed from the discharge port- customized with different types of valves.
Ribbon Blender Working
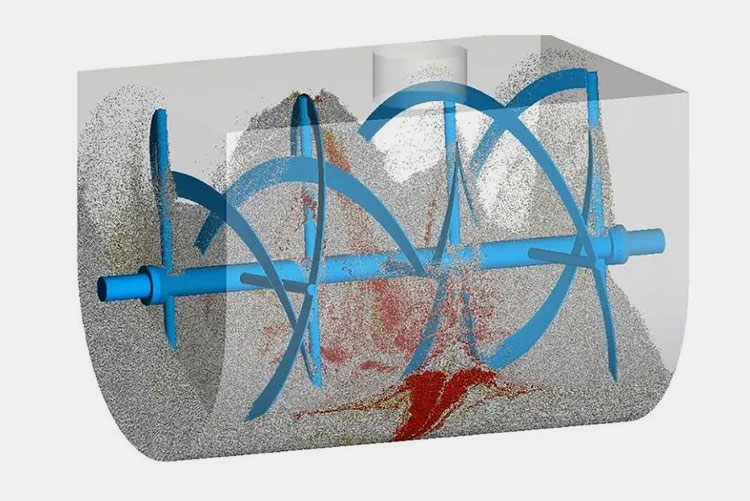
The working principle of the ribbon blender is based on connective mixing. It works on the triple-action approach. The double helical construction of the agitator, consisting of inner and outer ribbon blades, moves in reverse directions. This counter-action movement is integral in achieving successful mixing efficiency.
The outer blade is constructed to transfer feed from the edges of the mixing trough to the center, whereas, the inner ribbon has a role in the movement of particles from the middle to opposite edges of the mixing vessel. These opposite inclinations and directions of helical ribbons create a consistent convection flow and shear mixing.
The blades move axially and radially and are responsible for cutting, rolling, and rotation. The product mixture is unloaded from the discharge spout or vent present at the bottom of a ribbon blender.
Types
The paddle blender is available in several different types, for instance:
Types of Paddle Blender Based on Configuration
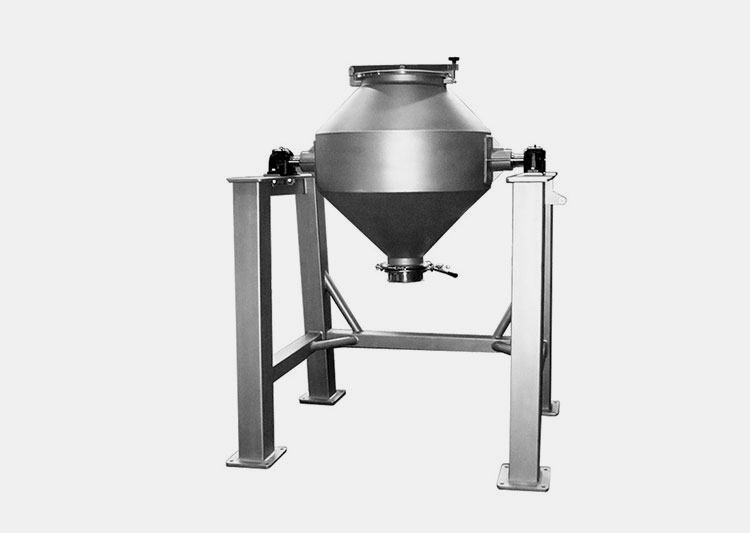
Vertical Paddle Blender
Vertical Paddle Blender
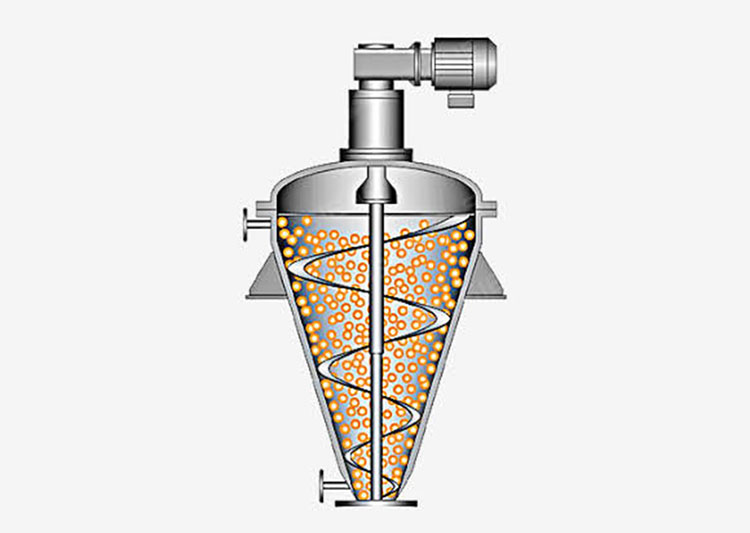
The mixing trough in this type of paddle blender is typically cylindrical and vertical. Moreover, this vessel is designed in a vertical configuration. Therefore, the materials are moved from the bottom to the top direction for homogenous mixing.
It has a central vertical shaft furnished with blades. It occupies a smaller space but more headroom. It is ideal for smaller batches due to its smaller capacity.
Horizontal Paddle Blender
Horizontal Paddle Blender- Picture Courtesy: Habrotek
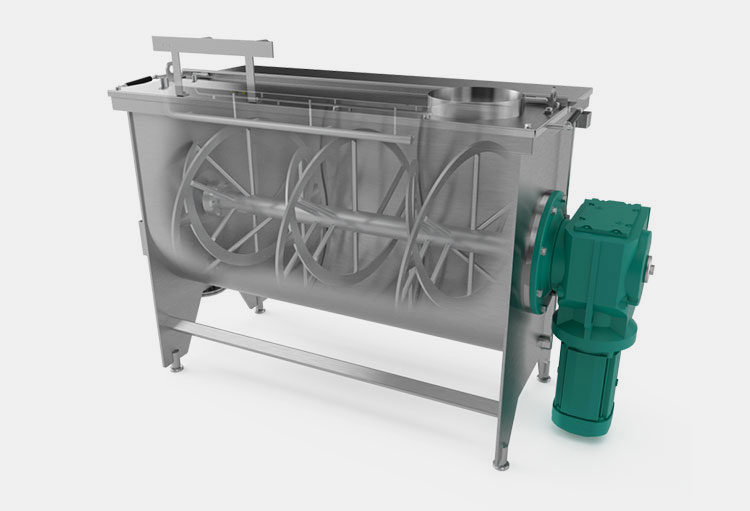
In this type of paddle blender, the mixing vessel has a U shape and is designed in a horizontal configuration. It has a horizontally attached shaft that accommodates different paddles. The movement of feed in the horizontal paddle blender is in the lateral and radial directions.
It has a higher footprint but could be installed in rooms having low ceilings. It can process larger batches.
Types of Paddle Blenders Based on Design
Single-Shaft Paddle Blender
Single-Shaft Paddle Blender- Picture Courtesy: Fragola Spa
It consists of a single shaft that runs along the length of the mixing vessel. It is the core component of the single-shaft paddle blender and paddles are fixed at particular angles around it. The shaft is connected to a drive system that provides the necessary mechanical energy for rotation.
The function of paddles is to raise and fold the mixture within the mixing trough, thus generating a tumbling action for consistent mixing. It requires more time to accomplish smooth mixing.
Double-Shaft Paddle Blender
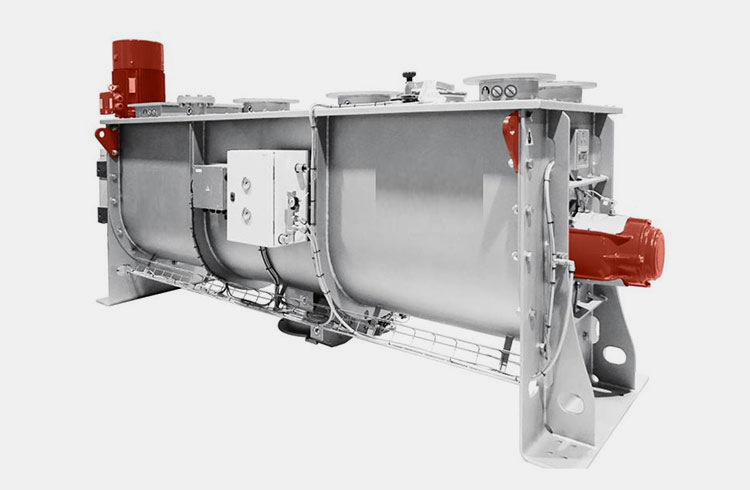
Double-Shaft Paddle Blender- Picture Courtesy: IDAH
It constitutes two parallel horizontal shafts; each is supported by paddles. These paddles present at two shafts rotate in opposing directions, consequently producing an intermeshing feat that improves the mixing efficiency. It is larger than a single-shaft paddle blender because it is fitted with a double shaft.
Mixing action is rapid because of intermeshing action. Moreover, it performs more intense mixing, attaining a high rate of homogeneity.
There is diversity in the types of ribbon blender, for instance:
Types of Ribbon Blender Based on Configuration
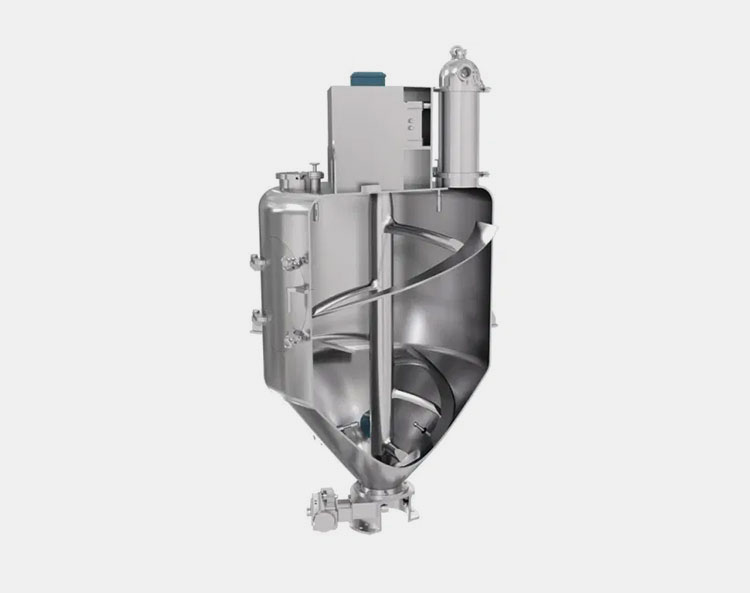
Vertical Ribbon Blender
Vertical Ribbon Blender- Picture Courtesy: PreMix
It has a vertically located mixing vessel and a middle vertical shaft. There are numerous helical ribbons found on the central shaft. The materials are pushed to the top, ultimately cascading down, producing a smooth mixing action. It occupies less ground space but more headroom.
Gravity assists in the working of a vertical ribbon blender. A consistent blend of light and fine materials is obtained due to this blender. However, it has a smaller working capacity.
Horizontal Ribbon Blender
Horizontal Ribbon Blender- Picture Courtesy: GIMAT Srl
This type of ribbon blender has a horizontal configuration with a horizontally tailored mixing vessel. It has a horizontal shaft with helical ribbons. These ribbons relocate feed in all directions from bottom to top and left to right. This leads to back-and-forth blending.
It needs more floor space for installation but less floor height. It has a larger mixing capacity and is routinely utilized in continuous or batch processing.
Types of Ribbon Blenders Based on Design
Single Ribbon Blender
Single Ribbon Blender- Picture Courtesy: WAM Inc.
This blending machine features only one helical ribbon supported on the middle shaft. This ribbon rotates inside the mixing trough and shifts feed in a single direction, normally propelling it towards the edge of the vessel, and resulting in the tumbling and folding of materials.
It is ideal for basic mixing jobs but it is harder to achieve complete blending of materials with different densities. Its single-direction rotation might result in a less uniform mixture.
Double Ribbon Blender
Double Ribbon Blender- Picture Courtesy; Cybernetik
It is comprised of two helical ribbons- outer and inner- fixed on the core shaft. These ribbons spin in an opposing way, with the outer ribbon transferring materials in the direction of the discharge port, while the inner ribbon conveys feed in the reverse direction. This produces more intricate and effective mixing action, resulting in even and swift mixing.
It is a standard mixing option for most of the industrial mixes. Its bi-directional spinning offers quicker and more consistent mixing.
Triple Ribbon Blender
Triple Ribbon Blender- Picture Courtesy: MIXSYS
This type of ribbon blender is equipped with three helical ribbons- one inner, one in the middle, and one at the outer end, each having different rotational directions. These ribbons are positioned in such a way as to boost the contact of materials and ribbons for efficient mixing.
Triple ribbon blender provides the most complicated and absolute mixing among three ribbon blender designs. These ribbons spin in numerous directions, increasing the mixing performance and minimizing dead spots. It is very suitable for blending particles with varying densities.
Suitable for types of materials
Abrasive Powders- Picture Courtesy: Kennametal
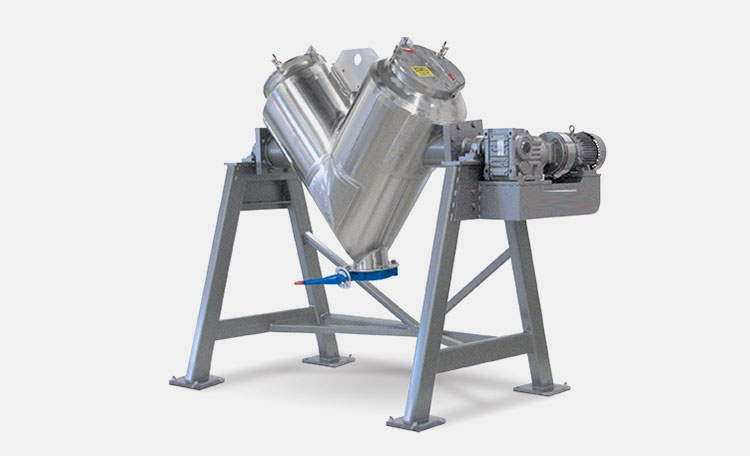
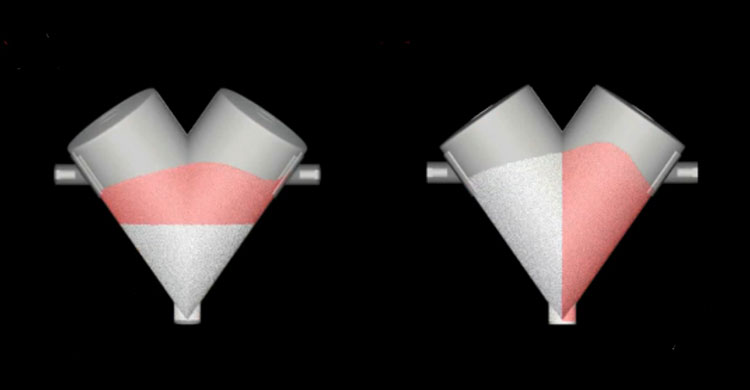
A paddle blender is usually used for mixing friable feed and mixing small batches with 15% of the total mixing capacity. Paddle agitators can easily process abrasive feed more capably than the ribbon blender. It is ideal for processing heavy-duty applications, for instance, wet materials (soups, batters, pastes) and heavy metals.
Its design and impellers are particularly customized to process viscous and pasty-like feed efficiently. The paddle blender is excellent for blending fragile and rough formulations because of its gentler movement of paddle-style agitation.
Free-flowing Powders- Picture Courtesy: Fresh Fruit Turkey
A ribbon blender is normally used for mixing low- and medium-duty feed, such as free-flowing and dry materials. It has long-twisting ribbons that are a great choice for getting rid of larger agglomerates and clumps. Its helical ribbon screws spin at a particular angle, making it a perfect fit for effective mixing of dry components.
It cannot mix small batches of materials effectively because, in its mixing tank, dead spots are developed, thus leading to incomplete and uneven mixing of some portions of smaller batches and also product segregation.
In the ribbon blender, the ribbon agitator construction causes pinching points near the periphery of mixing tank walls, as a result of delicate mixture compresses. However, the paddle impeller has a smaller surface area at the edge and offers delicate blending action with minimal heat.
Heat Transfer
Heat Transfer by Paddle Blender- Picture Courtesy: Elrich Machine
Heat transfer is much superior in the paddle blender than the ribbon blender. Its enclosed cylindrical design and sealed topside have a larger surface area for heat transfer, which improves its mixing efficiency if heat transfer is needed for the desired blending performance.
In contrast, heat transfer is also an issue in the ribbon blender, especially if product heating is needed, because of its open gap in the upper portion and empty spaces between the mixture and the top of the mixing vessel, which makes it inefficient in heat transfer during mixing.
Loading of Feed
Loading of Feed in Ribbon Blender- Picture Courtesy: Chemical Processing
One of the major limitations of the paddle blender is that it is not efficient in loading larger loads directly into the mixing vessel because of its cylindrical type shape and typically requires larger conveyors for introducing the feed into the mixing trough.
On the other hand, the bulk batch of raw materials is directly fed into the mixing vessel in the ribbon blender because of its wide open top and U-shaped trough. Hence, it does not need conveying for loading materials.
Speed
Speed of Ribbon Blender- Picture Courtesy: ROSS Mixers
The paddle blender is capable of rotating at high speed, making it suitable for mixing products that require quick mixing.
Ribbon blender usually works at a slow speed, which is perfect for processing fragile items. The paddle blender has a short mixing cycle because of its faster tip speed than the ribbon blender.
Maintenance
Maintenance of Ribbon Blender- Picture Courtesy: Chemical Processing
When the maintenance features of the paddle and ribbon blender are compared, it is discovered that the paddle blender is easier to maintain because of its design construction. It is convenient to readjust and reposition the paddle blades. Thus, less effort is required in cleaning the paddle blender between batches.
However, more time is required for cleaning and maintaining the ribbon blender machine. Ribbon blades are difficult to reposition and disengage because they run across the entire length of the mixing vessel. Manufacturers face more trouble in cleaning the ribbon blender between the blades, as products tend to stick between the helical ribbons.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both paddle and ribbon blenders are widely popular blending machines in the market and have their fair share of merits and demerits. The paddle blender stands out in the efficient mixing and blending of cohesive and abrasive materials. Conversely, the ribbon blender is perfect for mixing dry powders and granules. By learning about the remarkable features of each blender, businesses can opt for the superior solution that not only fulfills the precise mixing demands but also attains top-notch blending mixture in the manufacturing industry. To select which blender is most suited to your productions, contact our leading experts. We, Allpack have years of experience in powder blending and can offer you cutting-edge solutions that will exceed your expectations.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide

Paddle Blender VS Ribbon Blender: What Is The Different? Read More »


































 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours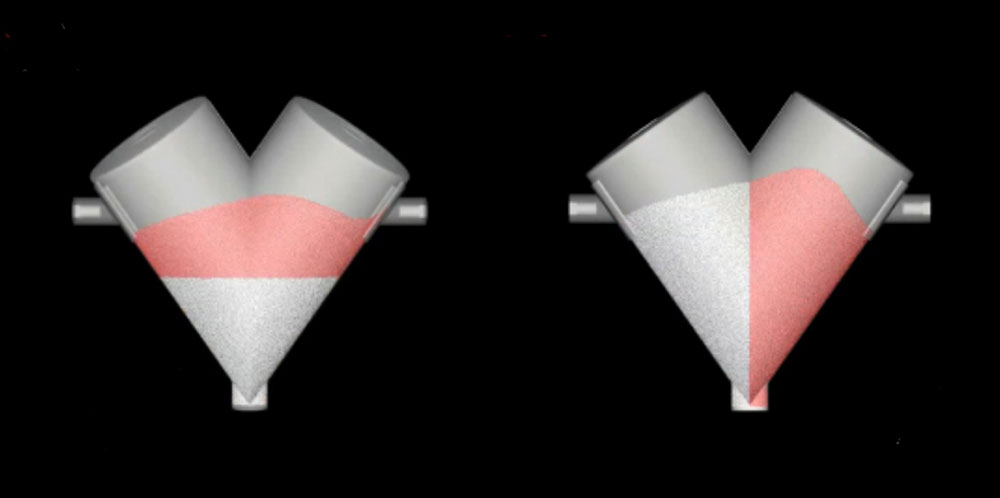

































































































 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours