ISO VS GMP
Are you involved in the manufacturing sector? Do you want to produce quality goods? Do your industrial regulations include compliance with quality assurance standards? Are you confused about the differences between ISO and GMP? Do you have questions regarding the scope and objectives of ISO and GMP?
The answers to the above-mentioned questions and more will be detailed in this enlightening blog: “ISO VS GMP”. ISO and GMP are similar in various aspects, such as maintaining records, training of operators, calibration of equipment, and product quality tests. Here we will focus on the differences between ISO and GMP so that you can understand the requirements of these regulations and implement them in your business. Let’s start reading.
1.What is Meant by ISO?
ISO
ISO stands for International Organization for Standardization and is an international body formed from national standard agencies. Its purpose is to create and publish a variety of proprietary, industrial, and commercial protocols.
ISO was created in 1947 in London, United Kingdom. It provides a regulatory framework for running an organization and audits its activity. It is a globally accepted standardized quality management protocol valid for every type of production. It has been reported on ISO website that approximately 1.2 million organizations in 170 world countries have been ISO certified.
It focuses on different facets of seamlessly establishing and managing businesses and is committed to continuously improving quality across every procedure and level of organization. It deals with the requirements of managing and fulfilling customer demands.
2.What is Meant by GMP?
GMP- Picture Courtesy: Angstrom Technology
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices. Sometimes, it is also called cGMP or current Good Manufacturing Practice. GMP regulations uphold a special place in fulfilling the quality assurance protocols and developing quality-compliant products.
It encompasses every facet of the manufacturing process to protect against any catastrophic hazards that degrade the product quality, safety, and potency. It guarantees that products are optimized for their expected use and adhere to marketing or clinical trial regulations.
In 1941, after substandard and contaminated sulfathiazole tablets adversely affected about 300 people, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) revised manufacturing protocols significantly, leading to the establishment of GMP. These regulations were first finalized in the 1960s and the FDA published its GMP standards in 1963 to prevent contamination of pharmaceuticals and drug formulation errors and ascertain product reliability.
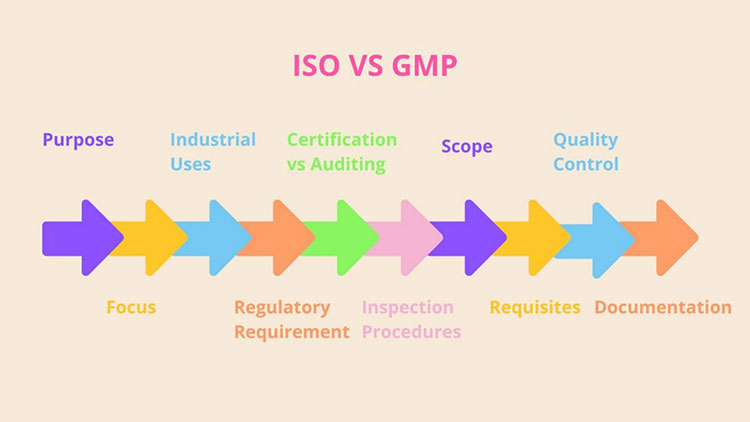
3.What are the Differences between ISO and GMP?
Both ISO and GMP certifications are crucial to quality assessment approaches and by adhering to these regulations, manufacturers and developers can attain fineness in product formulation and provision of services in far and wide productions. They are vastly different from each other, serve immensely diverse objects, and are applicable in dissimilar settings. Let’s look into detail of key differences between ISO and GMP one by one:
Differences between ISO and GMP
Purpose
Purpose- Picture Courtesy: Meet Recruitment
The main purpose of ISO regulations is to increase operation performance quality, effectiveness, and, consumer trust in diverse industries. Its primary job is to make a structural framework and process-centric methodology to establish quality assurance.
GMP is specially devised to ensure every regulated industry- producing health-related and beauty-related products- conforms to quality standards in manufacturing, processing, packing, handling, and storage. It is product-oriented and deals with the shortcomings of products that adversely affect the well-being of humans.
Focus
Focus- Picture Courtesy: Alcimed
ISO and GMP differ significantly in their focus. ISO is related to the organization's general management and is strongly focused on customer opinions- both external and internal. It includes standards for satisfying customer demands, fulfilling their expectations, and gaining customer trust. It is more committed to enhancing the management of the business. It usually mandates organizations to devise quality policies and goals.
It is usually focused on running the business in the right way, although one of its goals is to manufacture the right quality product, it has other objectives, such as establishing responsibilities of top management for quality assurance.
ISO advises companies to inspect, revise, and boost their quality system for leading perfection in other non-production areas.
Alternatively, GMP is dedicated to guaranteeing the safety, security, durability, quality, traceability, recognition, and sterility of consumable goods. It is responsible for protecting the health and safety of consumers, especially patients from adverse reactions and other possible harms. By GMP guidelines, organizations are obligated to document their every manufacturing step.
GMP is more deeply concerned with product quality and gives more emphasis to standardized manufacturing practices.
Industrial Uses
Industrial Uses- Picture Courtesy: Moravek
ISO and GMP are widely diverse in their industrial applications. ISO is valid for every organization, whether production, healthcare, laboratories, construction, trade, or others, and is not unique to any facility or production line.
On the contrary, GMP protocols are exclusively implemented in industries- regulated by drug and food regulatory agencies, for instance, the medicinal, biotechnology, nutraceutical, veterinary, medical instruments, food, beverage, and, beauty industries.
Regulatory Requirement (Voluntary or Mandatory)
Regulatory Requirement- Picture Courtesy: Single Use Support
Acquiring the ISO certification is completely voluntary and organizations usually get a competitive edge over their competitors and customer trustworthiness by adhering to this certification.
It is noteworthy that there are no legal ramifications of not obtaining ISO certification. Still, for successfully operating an organization this certification is a must. The firms are free to adopt ISO regulations to show their clients that they are committed to quality.
However, laws and guidelines are an absolute must for pharmaceutical and food companies. The governing bodies, especially FDA and EMA dictate and review compliance with the GMP standards. GMP standards are enforced by law and are a must for production approval licenses. Companies must adhere to GMP to legitimately produce, market, and sell their consumable goods.
Certification vs Auditing
Certification vs Auditing- Picture Courtesy: PharmOut
Organizations interested in implementing ISO certification must undergo auditing through third-party bodies that are qualified to inspect and audit different patron businesses. ISO-accredited certification agencies measure performance compliance with ISO regulations. Moreover, these organizations are audited every year and are awarded ISO certification for three years between renewals.
FDA or EMA conducts annual inspections and reviews to ascertain GMP conformity. Moreover, they can reject or withdraw manufacturing permissions if guidelines are not implemented properly. The supervising bodies, found in almost every country across the globe, examine GMP adherence by regularly visiting facilities.
There are some harsh punishments and monetary penalties if GMP standards are not followed in the book.
Inspection Procedures
Inspection Procedures
FDA inspectors are allowed to review compliance with the newest or current regulations that are approved as required industrial procedures even though they are not specially mentioned in written guidelines. Conversely, ISO inspectors can only assess ISO compliance to the very last version of the ISO standard.
Scope
Scope- Picture Courtesy: CordenPharma
There are different variants of ISO and its scope is a lot broader than GMP. ISO 9001 usually accentuates quality management and quality assurance. ISO 14001 defines criteria for environmental management systems, while ISO 45001 deals with occupational health and safety management. Conversely, GMP envelops every facet of manufacturing, such as starting material, training, hygiene, facilities, equipment, and documentation.
Requisites
Requisites
ISO needs a management assessment review, quality strategy, quality guidelines, or quality auditing. It also defines a supplier assessment protocol or a procurement process. Opposingly, GMP mandates that buildings, warehouses, facilities, and equipment must adhere to strict regulations for size, cleaning and maintenance ease, sterility maintenance, ventilation, calibration, heating, cooling, electricity, plumbing, water treatment, sewage, and routine hygiene.
Quality Control
Quality Control
ISO does not overtly mandate the formation of a quality control unit, consigned with the power to accept or reject products. Instead, ISO urges businesses and companies to specify the roles and duties in quality management systems. It demands the appointment of management personnel who have the power to implement the standard.
Conversely, GMP specifies the need for the creation of quality control units with complete and absolute clout to accept or reject the product. It also defines the particular structure and responsibility of the quality control unit.
Documentation
Documentation
ISO usually necessitates a documented record of quality management systems, operational practices, and risk management strategies. Since GMP is more concerned with the implementation of quality requirements, it needs more thorough and stringent documentation, centering on batch records, SOPs, and product testing protocols.
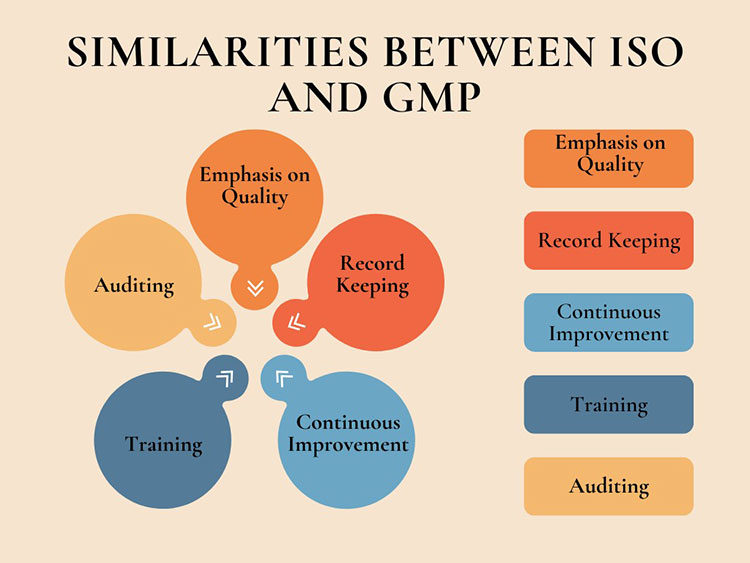
4.How are ISO and GMP similar?
ISO and GMP concur on important points related to quality management. They both are designed to ascertain that products and processes fulfill required quality regulations. Some significant similarities between ISO and GMP are discussed below:
Simmilarities between ISO and GMP
Emphasis on Quality
Emphasis on Quality- Picture Courtesy: World Pharma Today
ISO 9001 and GMP are focused on quality. Both entail constant assessment to boost quality outcomes. They ensure the manufacturing of superior-quality goods. Consistent quality and operative fineness are their top priority. Both approaches are developed to prevent the errors in first place.
Record Keeping
Record Keeping
ISO and GMP heavily prioritize detailed and thorough documentation. They dictate the importance of comprehensive record-keeping for auditing, inspection, and, quality management. Correct records in ISO standards are essential for maintaining process consistency and continuous improvement. Whereas, in GMP, documentation plays an integral role in product traceability and is indispensable in quality control and accountability.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous Improvement
Both standards prescribe the need for incessant improvement in manufacturing and servicing Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is vital to process improvement in ISO standards. It advises organizations to routinely evaluate and boost their processing quality.
On the other hand, continual improvement in the fulfillment of GMP quality requirements occurs through regular assessment, and CAPA (corrective and preventive actions).
Both ISO and GMP monitor unceasing quality enhancement by product testing, supplier auditing, process evaluation, product assessment, self-inspection, and addressing customer complaints.
Training
Training- Picture Courtesy: BiOZEEN
ISO and GMP dictate that employees and operators in facilities must be properly trained and equipped with the necessary skills to perform their duties capably. ISO regulations obligate that the workforce must be rightly qualified for the jobs they perform, which minimizes errors and boosts product quality. Similarly, GMP mandates operators must be trained so that they can learn about hygienic practices, contamination hazards, and their processing duties.
Auditing
Auditing- Picture Courtesy: TPA Group
It is mentioned in both ISO and GMP guidelines that organizations must carry out external and internal inspections to certify compliance with regulations. ISO inspections are performed by accredited organizations, whereas GMP inspections are conducted by regulatory agencies to evaluate safety and quality compliance.
5.What are the Benefits of Implementing ISO and GMP?
Implementing both ISO and GMP comes with numerous benefits, including enhanced quality assurance, regulatory conformity, customer satisfaction, and operational performance. Let’s detail the different advantages of adopting ISO and GMP in businesses:
Improved Quality and Safety
Improved Quality and Safety- Picture Courtesy: Sirocco Consulting
Implementing one or both of these industrial standards will lead to improved manufacturing quality. By complying with these standards, organizations are consistently boosting their operational, packing, and distribution excellence. Moreover, safe, pure, and potent pharmaceutical, medical, and, cosmetic products will be delivered to end-consumers by adhering to the strict specifications of ISO and GMP- related to manufacturing, handling, and, storage.
More Market Access
More Market Access
Adherence to these globally recognized standards means that companies follow best manufacturing practices and reduce manufacturing errors and deviations. This leads to a boost in customer trust and brand popularity. So, brands gain access to far and wide market areas and fulfill global trade requirements.
High Employee Competence
High Employee Competence
ISO and GMP stress the necessity of continuous employee training to promote quality awareness and hygienic practices in organizations. This creates a skilled batch of knowledgeable and committed workforce who always strive to uphold industrial standards, leading to increased workforce engagement and productivity.
Better Supply Chain Management
Better Supply Chain Management
Rigorous supplier assessment protocols by ISO ensure better quality and consistency of the supply chain. GMP mandates stringent quality controls on raw feed, procurement of equipment, and other parts. With both these standards, a strong and trustworthy supply chain is created, promoting optimized product quality, lowering disruptions of the supply chain, and decreasing the rate of ambiguous materials entering production facilities.
Waste Reduction
Waste Reduction
The basis of ISO 14001 lies in minimizing the environmental impact of processes by increasing resource use, decreasing waste, and augmenting energy consumption. Moreover, GMP controls also cut down resource and product wastage by reducing production anomalies, contamination, and, item recall. This implementation of both ISO and GMP results in green, eco-friendly, and cost-effective operations.
Safer Operational Environment
Safer Operational Environment
ISO standard is also related to minimal operational accidents and incidents, in turn improving the safety of the workplace. GMP stresses the importance of sterile, aseptic, and safe procedures to avert contamination and thus protect workers from health adversities. They both assist in establishing safe and compliant operational settings, safeguarding employees as well as the composition of products.
6.How can ISO Complement GMP?
Although ISO and GMP have somewhat diverse focus, employing them together is an intelligent approach. They both complement each other successfully in regulated industries, for instance, pharmaceutical, food, and healthcare.
Risk-Based Strategy
Risk-Based Strategy- Picture Courtesy: Stratex hub
GMP incorporates risk management strategies, for instance, detecting device failure and product flaws. In ISO, a structured approach is utilized to implement risk-based thinking across the whole organization. The latter urges firms and businesses to proactively detect hazards and opportunities in the operating processes, which complements the GMP approach of averting quality errors and deviations.
Customer Focus
Customer Focus- Picture Courtesy: Medium
ISO strongly emphasizes learning and fulfilling customer requirements. Incorporating customer-centric principles into GMP regulations urges companies to take into account regulatory compliance and the needs of end-consumers.
Thus, by associating manufacturing processes with consumers' needs, GMP can concentrate on product quality, strength, and safety that directly fulfill or surpass customer expectations. It can result in the creation of customer-compliant goods that reverberate well with consumers, boosting their trust and loyalty.
Organization Efficiency
Organization Efficiency
The focus on GMP lies on the practical aspect of product engineering, whereas, ISO considers a methodical approach to improve the efficiency of organizations and non-production procedures, for instance, buying, sales, and customer support.
Therefore, by incorporating ISO process improvement with GMP standards a stronger regulatory framework is created, which boosts product quality, manufacturing efficiency, and risk management approaches, and cuts redundancies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ISO and GMP are two distinct standards with diverse scope, purpose, focus, regulatory requirements, and, auditing processes. ISO is more process-centric while GMP is more product-centric. However, the end goal of both these regulations is to ensure better and enhanced product quality. The anticipated advantages of effectively integrating these regulations are huge in terms of return on investment. By implementing these standards in harmony, you can achieve superior-quality products, decrease product shortages, reduce validation and documentation, and rapidly deliver more products to market. For more details and queries regarding differences between ISO and GMP, you are encouraged to contact Allpack customer care.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide