What Is the Difference Between Capsule and Tablet?
You have always noticed the controversy concerning efficiency and potency between capsule and tablets. Although both of these are oral solid dosage forms, but why there’s needed to develop them separately.
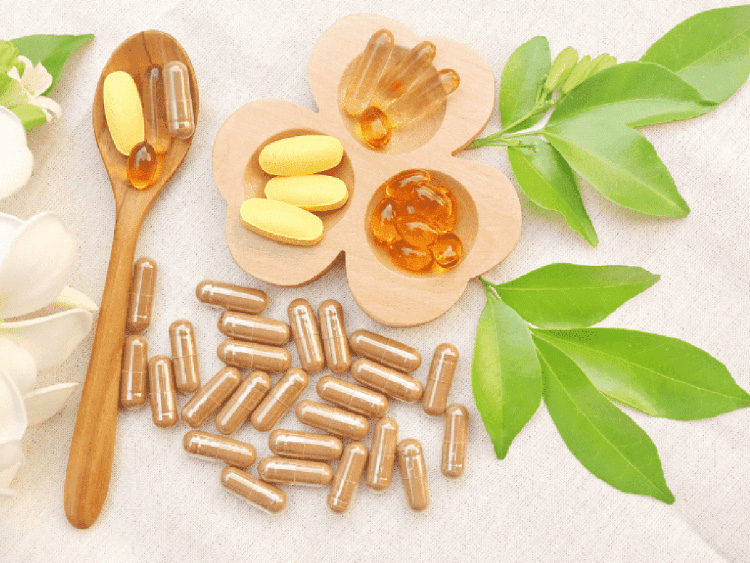
Battle Between Capsule and Tablet- Picture Courtesy: GoodRx
No doubt! There are a lot of distinction between capsule and tablet; sometime tablets compete over capsule and vice versa. But you can’t ignore both in various cases. What is the difference between capsule and tablet? You’ll find in this blog post. So let’s get ready to explore.
1.What Is the Difference Between Capsule and Tablet?
Capsule Vs Tablet- Picture Courtesy: NOW Foods
Description
Capsule
An Enclosed Shell Offering Substances in Various States- Picture Courtesy: The Guardian
You must have administered capsule various times, which is an enclosed gelatin shell holding active substance with therapeutic or non-therapeutic actions. The external gel like structure is mainly made up of animal derived gelatin which is slowly and gradually replacing with vegan or plant derived substance that offering an elastic and gel like structure to capsule strictly following dietary restriction and preferable in many diets conscious people. So, it is catering people of different preferences with safety and flexibility.
Inside capsule, there is a broad compliance to pour either powdery, liquid, granular, beads, or any other form of substance. According to renowned pharmacist, Dr. Elizabeth Holmes, capsule is a unique structure benefits you by encasing medication belonging from various states and formulation. However, you need to keep them more protective against its interaction with air and light, you are packaging condition must be sensitive from external physical environment to sustain the efficacy and stability of active.
Tablet
A flexible dosage with compression of multiple substances and active- Picture Courtesy: Soft Gel Tech
On contrary, tablets are prepared by compression of powdered or granulated materials to form a solid formulation which is mostly composed of medication or active ingredients with other excipients which you will be reading in further section of this blog.
This is mostly known as pharmaceutical solid dosage form, known for not only its traditional applications but ensuring of stable releasing of therapeutic effects inside your body. As compared to capsule, it is not very sensitive to the external atmosphere and exhibits stable properties. Also, the preparation of tablet is flexible in the marking of score lines that allows easy splitting of the drug and easy to adjust the dose without compromising the dose integrity and dosage titration.
Pros
Capsule
Benefits of capsule- Picture Courtesy: Dallas Morning News
Capsules tend to act faster in releasing the drug because of it’s faster disintegration and offer quick ailment of symptoms.
It is Patient compliant and has great taste masking effect. Capsules are unharmful to gastrointestinal tract as they are protective against degradation by stomach acids. Capsules are made in a shell form and the medicinal powder is enclosed inside it, so they do not require the use of binders or fillers. Capsules are manufactured usually by gelatinous shells (however there are now vegetarian based capsules also available), which makes them categorized as whether they will be suitable for vegetarians or not.
Tablet
Benefits of Tablets- Picture Courtesy: Pixabay
It can also be taken by those patients who have difficulty in swallowing as tablets are also available in easy forms. Tablets can accommodate different forms of dosage according to many routes of administration (such as oral, buccal, sublingual, vaginal, rectal).
Tablets have longer shelf life and have better stability at environmental conditions. You would find tablets with easy storage offers, it is not prone to hygroscopicity and rapid degradation in open environment.
Cons
Capsule
Cons of Capsule- Picture Courtesy: MantraCare
In terms of dose division, capsule cannot be broken down into two parts and hence it is taken in a single dose only. Geriatric and paediatric patients might feel that capsules are hard to swallow because of their oblong shape, however it might not be a problem for adults. Capsules are only taken orally or rectally. Typically tablets have a better storage life rather than of capsules. Capsules are not that stable in terms of their expiry and may degrade quicker in adverse environmental conditions.
Tablet
Cons of Tablets- Picture Courtesy: VerywellHealth
The rate of disintegration of the tablet affects the bioavailability of the drug inside and has slower response rate than capsules or powders. Tablets need taste masking as it’s usually not palatable, which sometimes makes the patient unwilling to take it.
Owing to patient compliance, the tablet can be broken down and taken in divided doses because of it’s score line (the symmetrical division line on tablet surface).
Tablets are usually irritative to the gastrointestinal tract however some of them are also now enteric coated which resolves this problem.
Types
Capsule
Types of capsule- Picture Courtesy: Healthline
Capsules can be identified on their types of formulation such as whether they’re soft gelled or hard shelled or they’re constituted of plant based or animal based ingredients.
Soft Gelled:Soft gelatinous capsules are made up of gelatin and glycerine which forms the outer cover of the capsule. A liquid medicine is added inside the cover
Hard Shelled: Hard shell capsules are also made of gelatin, but they are combined with cellulose as the body part of capsule is manufactured using the former ingredient and the cap part is made using the latter one. Powdered medicinal substance is placed inside the body of capsule and enclosed by a cap
Animal Based capsule: Usually the capsules are made up of gelatin which is a product obtained by animal bones and skin ligaments. Gelatin has many health benefits and so supplement manufacturers or pharmaceutical manufacturers use this type of capsule.
Plant based capsule: Plant based capsules are intended for those vegetarians or culturally restricted people who can’t take animal based products. These capsules are HPMC or pullulan which are made from cellulose or plant parts.
Tablet
Types of tablet- Picture Courtesy: NPR
Tablets can be categorized into four of the main types, which is based on their route of administration.
Chewable Tablets: These tablets are intended to release their medicine when being chewed before swallowing. They are quickly absorbed into the stomach and have rapid onset of action. Chewable tablets are now available in many flavors.
Orally Disintegrating Tablet: Once you engulf them, they are supposed to quickly dissolve in your mouth and release their medicated ingredient. ODT is the fastest acting medicine and so it can be used for many purposes without using water for gulping it.
Sublingual Tablet: These tablets are placed beneath the tongue which gives rapid onset of action , without water for swallowing. It is used in emergency applications such a as Nitro-glycerine for angina.
Effervescent tablets: Effervescent tablets are supposed to be dissolved in water releasing bubbles in the process and they form a solution or suspension for drinking. This dosage form is constituted as decongestants, antacids or multivitamins.
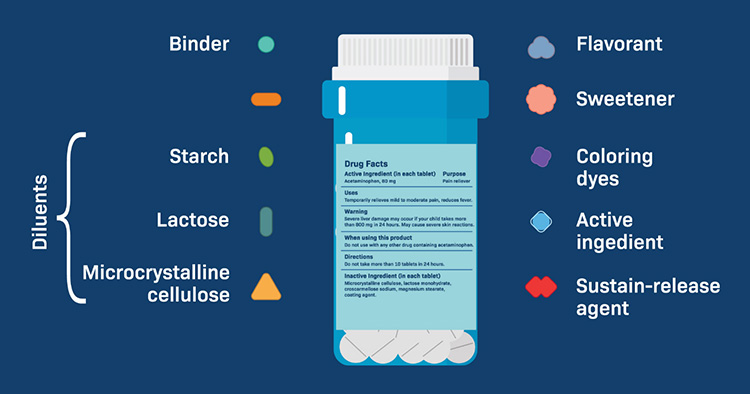
Ingredients
| Ingredient | Capsule | Tablet |
| Active Ingredients | Medicine/minerals/Vitamins | Medicine/minerals/vitamins |
| Binder | Lactose, Starch, Cellulose | Polymers, Gelatin, Plant Based Polymers |
| Shell | No External Shell | Hard and Soft Gel |
| Colorants | Iron Oxide and Dyes | Titanium Dioxide and Dyes |
Capsule
Simple formulation & Fewer Additives- Picture Courtesy: Lipa Pharmaceuticals
This is a simple formulation as compared to tablet dosage form. That’s why this is considered as a suitable and more preferable option for the patient with allergic or intolerance problems.
Because it is considered as the most beneficial route of administration for catering people suffering digestive intolerance like lactose or gluten, sensitivity, or allergic problems.
Also, the formulation alteration and specific dietary requirement has developed new amendments and advancements as now capsules ingredients are composed of plant based formulation which making it more wider range for people with dietary restrictions.
Tablet
Mixture of Binders, fillers, & additives- Picture Courtesy: LabXchnage
Tablets on other side, often composed of various list of ingredients such as binders, fillers, and associated additives in maintain and stabilize the shape, shelf life and disintegration rate.
If you are concerned about the safety of these binders, fillers or excipients used in the tablet, then don’t worry, all additives are potentially safe for patients and their presence is essential for structural integrity and releasing of active inside the body. Means, they’re not only require for stability and shape, but it is significantly important for releasing of medicine whether controlled or sustained releasing. Thanks to additives which perform this job practically safe for you.
Methods
Capsule
With Different Shell Types- Picture Courtesy: Softgel machine
Hard shell capsules preparation: Hard shell capsules are formulated firstly by the preparation of gelatin solution ( or plant based solution) which is moved via a pumping mechanism onto the pin shaped capsule molds. These molds are made to ensure that the pins are completely immersed in that solution. Later those pins are dried in a maintained temperature and trimmed and cut into two equal or fairly equal parts (which are later identified as body and cap). The machine conjoins the both parts and is ready for filling of medicinal substance. When required to be filled the body part of the capsule is removed and drug is placed inside it in powdered form and then closed by placement of cap.
Soft gelled capsules preparation: Gelatin is first melted and then filled in the paste form in an encapsulation machine. The hopper will pour the filling material and combine the shell to shape it as a capsule. It is later placed into die cavities and gelatinous ribbons form a seal around it and then it is moved for drying process.
Tablet
Forming by Compression & Granulation- Picture Courtesy: Pharmatech
Tablets can be formulated by three kinds of strategies.
Direct Compression: Ingredients of the tablet are combined together by mixing and force is applied directly to compress it into a tablet shape. There is no need of adding any liquid binders here.
Dry Granulation: This is somewhat similar to direct compression as tablet ingredients are mixed without the addition of any liquid . Dry Granulation method is used specially when the particles of medicated ingredients are fine enough to have a restricted flow.
Wet Granulation: In this method a liquid binders is used to mix and incorporate the other medicinal ingredients and later compressed into a tablet form. Wet Granulation is also used when the particle size of powder is fine enough that it doesn’t flow.
Ease of Swallowing
Capsule
Smooth Textured & Easy to Administer- Picture Courtesy: UTIVA
Nevertheless, the smooth texture and shape of the capsule offers an easy swallowing to user. According to research, the external gelatinous make up of the capsule allowing extra palatability and offering easy ingestion in patients with difficult swallowing problems. For instance, adult or elder patient or people with oesophageal problems. According to research study conducted by Swallowing Disorders Foundation, around 67% users preferred capsules over tablets as it is very easy and smooth to ingest, so it is beneficial for those who’re facing struggle to ingest large medication.
Tablet
Versatile but Potentially Challenging- Picture Courtesy: Science Photo Library
As compared to capsule, tablets are somewhat hard to ingest in some patients. Although there are various new alteration and modifications are aided into its manufacturing that supports the swallowing. In capsule, you cannot find the way to divide the dose, but tablets are designed with score lines which helps in dose management. So if you find difficulty ingesting a large tablet; you can take divided doses.
Taste
Capsule
Best Known for Masking Unfavorable Taste- Picture Courtesy: Outsourcing Pharma
Bad taste of medicines can easily be masked if it is enclosed in a shell. The capsule acts as a barrier for drugs taste and odor, your taste buds and sense of smell won’t transmit any unwanted signal to brain. The capsule is preventing medication as well as its after-taste. So people pick them as a preferred choice as it is more palatable upon ingestion.
Tablet
Potential for Inducing Taste- Picture Courtesy: Manufacturing Chemist
By comparing to capsule, tablets may pose some unwanted challenges particularly when it comes to taste of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients or any Active compound and excipients.
Moreover, the compression method also exposes the drug and its bitterness which contributes into the tablet. But manufacturers employed coatings and flavoring to mask undesirable taste but it sometime imparting its releasing and mechanism of action.
Absorption
Capsule
Rapid Absorption Properties- Picture Courtesy: mHealthintellegence
Capsule composed of ingredients which offering you high protection against its disintegration in the stomach or its interaction with stomach juices. This is because, medicine is degraded when enters in stomach’s acidic environment. Moreover, it is made up of external shell and internal ingredients; the purpose of this design is to keep capsule intact till it reaches intestine where alkaline pH allows its disintegration and high bioavailability. So, medications can rapidly enter the bloodstream and shows more effectiveness.
Tablet
Steady Release and Absorption- Picture Courtesy: Australian Journal of Pharma
As read above, the tablet is a compressed and a hard formulation made up of various ingredients. So, its disintegration and absorption pattern is changed than capsule. Like, some tablets are starts releasing and shows its role soon after ingesting for example, sub-lingual tablets releases and absorbs in mouth cavity.
In this way, various design alteration is implemented to control the releasing and absorption spike. Due to presence of various ingredients, the releasing of tablets takes time than capsule. Because the compressed form has to dissolution time, then upon reaching the active site, releasing excipients and active take standard time and shows it efficacy. That is why, several research studies have shown capsule absorption as fast than tablets.
Stability
Capsule
Prone to Interacting with Certain Conditions- Picture Courtesy: Fierce Pharma
Capsules are less stable and have lower integrity values than tablets. Due to hygroscopic formulation and texture stability of the capsules the can be affected by this factor. Stability may be compromised by the physical harm that capsules are prone to, such as breaking or cracking. Handling and storing substances properly are crucial.
Tablet
A Stable Solid Dosage Form- Picture Courtesy: the Pharmacist
The tablets are more stable than the capsules. Tablets are more compact and provide more resistance to moisture, so they provide more stability to the tablets. In general, tablets are more durable and less prone to physical harm. They still have the potential to chip or break, though, if the protective layer is compromised.
Shelf life
Capsule
No Extended Shelf Life- Picture Courtesy: SWK Tech
Capsules have a shorter shelf life than the tablets. So, it needs to be stored in the proper way to guarantee they do not depreciate. The shell of capsules is made up of polymers or gelatin, allowing the capsules for more exposure to oxygen contents. Since oxygen involves the degradation of particular capsules, so its decreases the shelf life of capsules. Moisture affects the stability of the medications thus leading to degradation of capsules over time, and due to the capsule shell's permeability you will need a carefully handling consideration to reduce exposure to outside influences.
Tablet
A Stable Shelf Life- Picture Courtesy: Hunter Lab
The tablet is more stable and has a long shelf life compared to capsules. Tablets are usually coated with sugar, film, or enteric. So, it protects the drugs and enhances the shelf life of tablets. Tablets are less permeable and more compact than capsules, so it does not easily affect by moisture. Due to this property, tablets sustain more shelf life compared to capsules.
2.Which is Better? Capsule or Tablet?
Which is Better- Capsule or Tablet
Justifying any one of them as better option would not be entirely appropriate, as capsules and tablets both of them have their own benefits and drawbacks. However, it can be chosen by the patient that which one seems to be a best choice for them.
Tablets have a longer shelf life but have a slow onset of action and therefore slower bioavailability while capsules act rapidly but have a very short expiry date and they are costly too. Sometimes it becomes hard to swallow a capsule or a tablet , deeming it unsuitable for patient compliance. However, it varies from patient to patients, as mostly paediatric and geriatric patients face this difficulty. Moreover, ingredients formulating a capsule such as gelatin can be problematic for those who are conservative in regards of their cultural or religious beliefs, so they would prefer a vegan option instead.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, the battle between preference of capsule over tablet or tablet over capsule goes on. It is up to the end-user and their prescribers who select the right choice of medication at appropriate situations. We hope you have enjoyed our post on ‘what is difference between capsule and tablet’. But if you have any questions, or you feel confused about any information mentioned in our blog; we would suggest you contact us right now. Allpack team member will contact soon to answer your queries.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide